Abstract
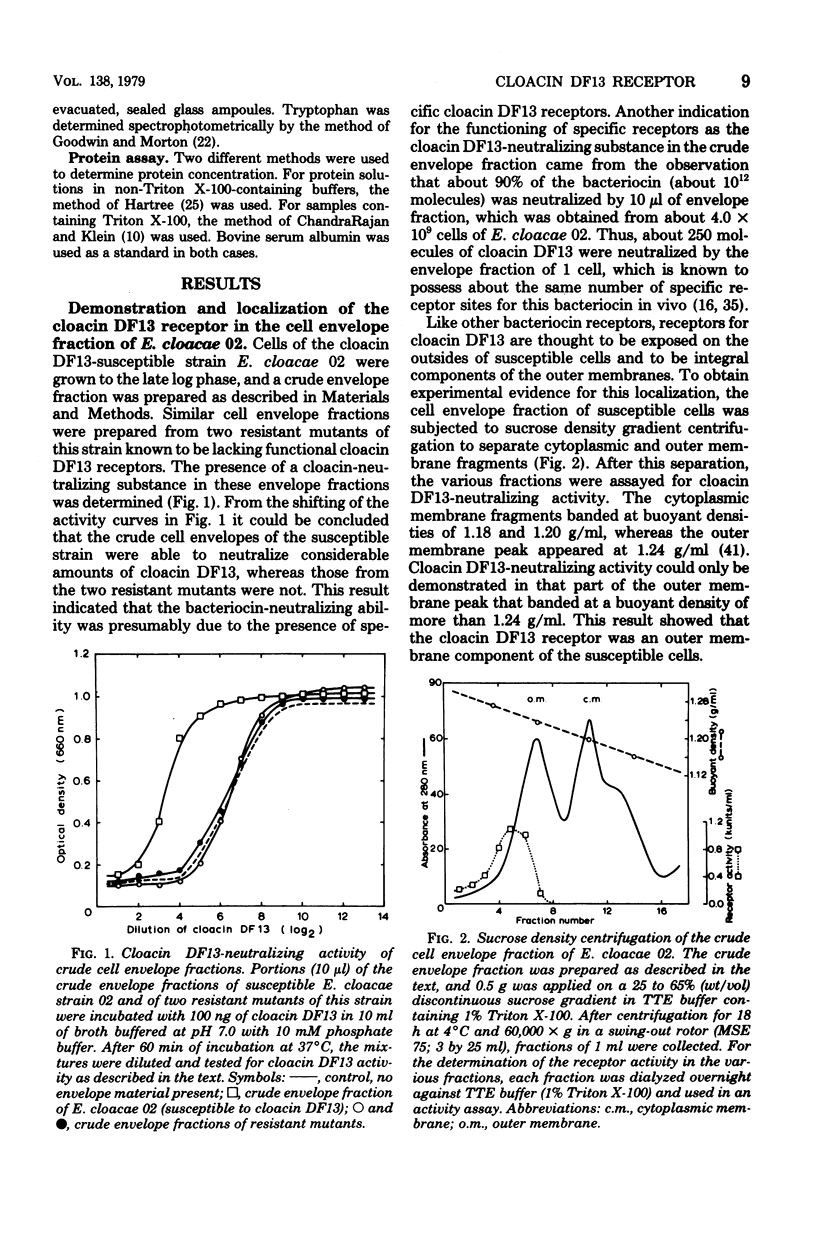
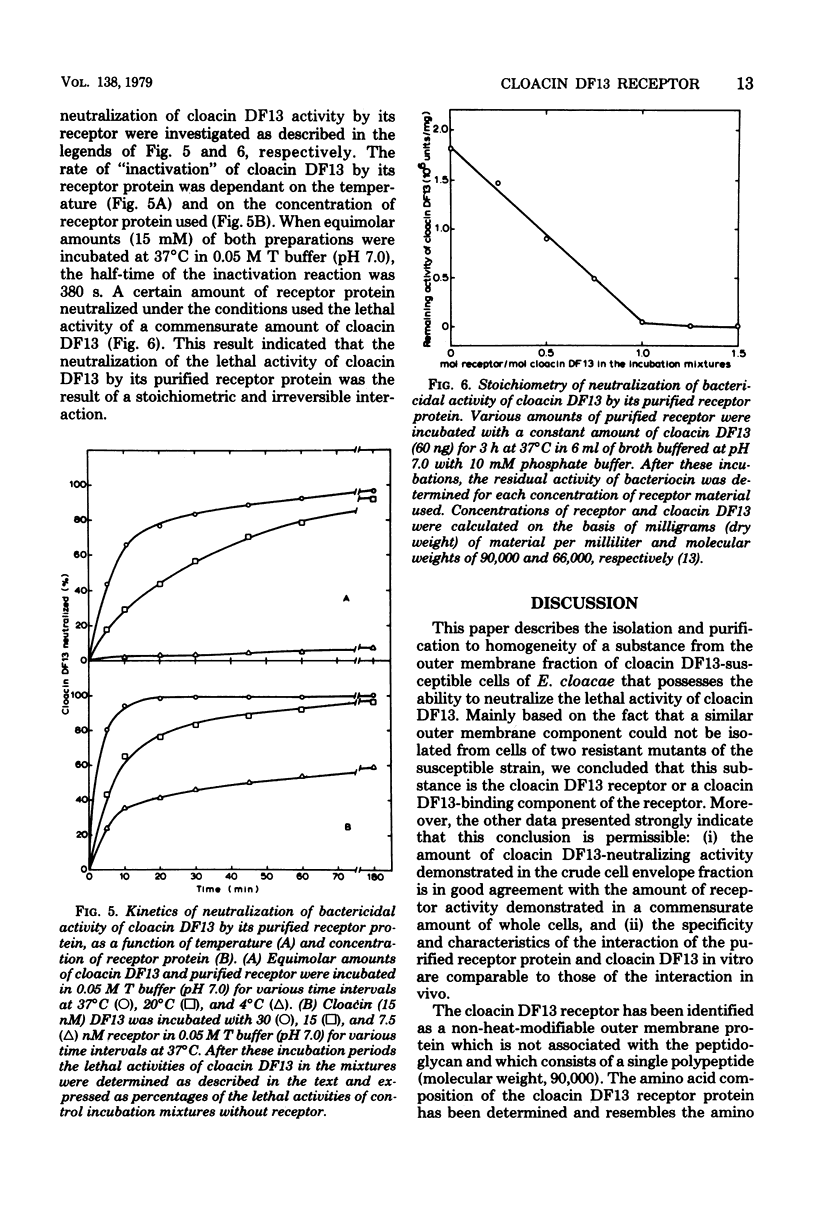
Extraction of the crude cell envelope fraction of cloacin DF13-susceptible Enterobacter cloacae strain 02 with Triton X-100 and ethylenediaminetetraacetate solubilized an outer membrane fraction which neutralized the lethal activity of cloacin DF13. A similar fraction could not be isolated from strains known to be lacking functional cloacin DF13 receptors. On this basis the isolated outer membrane fraction was assumed to contain the specific cloacin DF13 receptor. The receptor was purified to homogeneity by acetone precipitation and affinity chromatography, using cloacin DF13 as a ligand. The purified receptor was identified as a protein which consisted of a single polypeptide chain with an apparent molecular weight of 90,000 and a preponderance of acidic amino acids (pI = 5.0). The interaction of equimolar amounts of purified receptor and cloacin DF13 in vitro resulted in a complete, irreversible neutralization of the lethal activity of the bacteriocin. This interaction showed a temperature optimum at 43 degrees C but was only slightly affected by variation of the pH between 5.0 and 8.5 or by increasing the ionic strength of the incubation buffer. The receptor had no neutralizing activity towards other bacteriocins, such as colicin E1 or colicin E3.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 and its mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):549–552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Dahlberg J. E., Ikemura T., Konisky J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of 16S ribosomal RNA induced by colicin E3 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):964–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbeer C., Woodrow M. L., Khalifah L. I. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor system for vitamin B12 and bacteriophage BF23 on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1032–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1032-1039.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Hartmann A. Functional organization of the outer membrane of escherichia coli: phage and colicin receptors as components of iron uptake systems. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(1):37–58. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wolff H. A common receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Wolff H. Characterization of the receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of E. coli B. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D. Role of ionic strength in colicin K adsorption. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Mar;99(1):13–18. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrarajan J., Klein L. Lowry assay of dilute protein solutions containing high concentrations of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):632–636. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Klaasen-Boor P. Purification and characterization of a complex between cloacin and its immunity protein isolated from Enterobacter cloacae (Clo DF13). Dissociation and reconstitution of the complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Planta R. J., Stouthamer A. H. Effect of a bacteriocin produced by Enterobacter cloacae on protein biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 17;240(1):123–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Masi D. R., White J. C., Schnaitman C. A., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli: common receptor sites for vitamin B12 and the E colicins on the outer membrane of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):506–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.506-513.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garewal H. S. A procedure for the estimation of microgram quantities of triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Braun V. Iron transport of Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the colicin B receptor and of a citrate-inducible protein. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1370–1375. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1370-1375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Phage T6--colicin K receptor and nucleoside transport in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80737-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide N., Muramatsu T. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase acting on carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4897–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Cowell B. S., Gilchrist M. J. Colicin Ia and Ib binding to Escherichia coli envelopes and partially purified cell walls. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):208–219. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Soucek S., Frick K., Davies J. K., Hammond C. Relationship between the transport of iron and the amount of specific colicin Ia membrane receptors in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.249-257.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., De Graaf F. K. Mode of action of the cloacin DF13-immunity protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 5;392(1):184–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., Sneeuwloper G., De Graaf F. K. Interaction of the complex between cloacin and its immunity protein and of cloacin with the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of sensitive cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Comparison of colicins B-K260 and D-CA23: purification and characterization of the colicins and examination of colicin immunity in the producing strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):345–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Reeves P. R. Kinetics of adsorption of colicin CA42-E2 and reversal of its bactericidal activity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):301–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.301-309.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Localization and solubilization of colicin receptors. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):422–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.422-430.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Purification and properties of the colicin E3 receptor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. Reversible interaction between coliphage lambda and its receptor protein. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):185–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon R., Hedges A. J. Reversibility of the specific adsorption of colicin E2-P9 to cells of colicin-sensitive strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1136–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1136-1144.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R. Recent developments in chemical modification and sequential degradation of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:261–308. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieze G. A., Stouthamer A. H., Jansz H. S., Zandberg J., van Bruggen E. F. A bacteriocinogenic factor of Enterobacter cloacae. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;106(1):48–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O. Isoelectric focusing of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U., Jesaitis M. A. The nature of the cilicin K receptor of Escherichia coli Cullen. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):534–553. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K. Effects of cloacin DF13 on the functioning of the cytoplasmic membrane. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(1):109–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02578846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Niekus H. G., Klootwijk J. Inactivation of bacterial ribosomes in vivo and in vitro by cloacin DF13. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Spanjaerdt Speckman E. A., Stouthamer A. H. Mode of action of a bacteriocin produced by Enterobacter cloacae DF13. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):287–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02219150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Stukart M. J., Boogerd F. C., Metselaar K. Limited proteolysis of cloacin DF13 and characterization of the cleavage products. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1137–1142. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



