Abstract
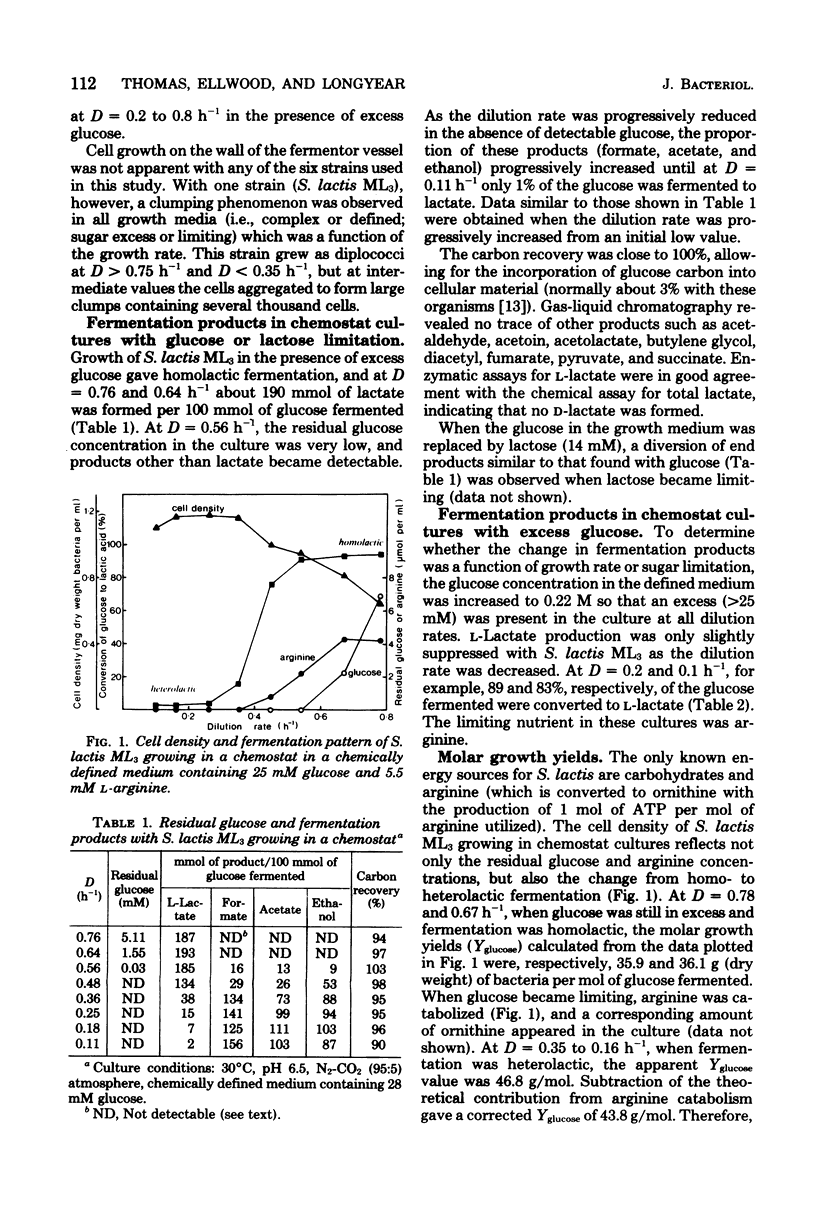
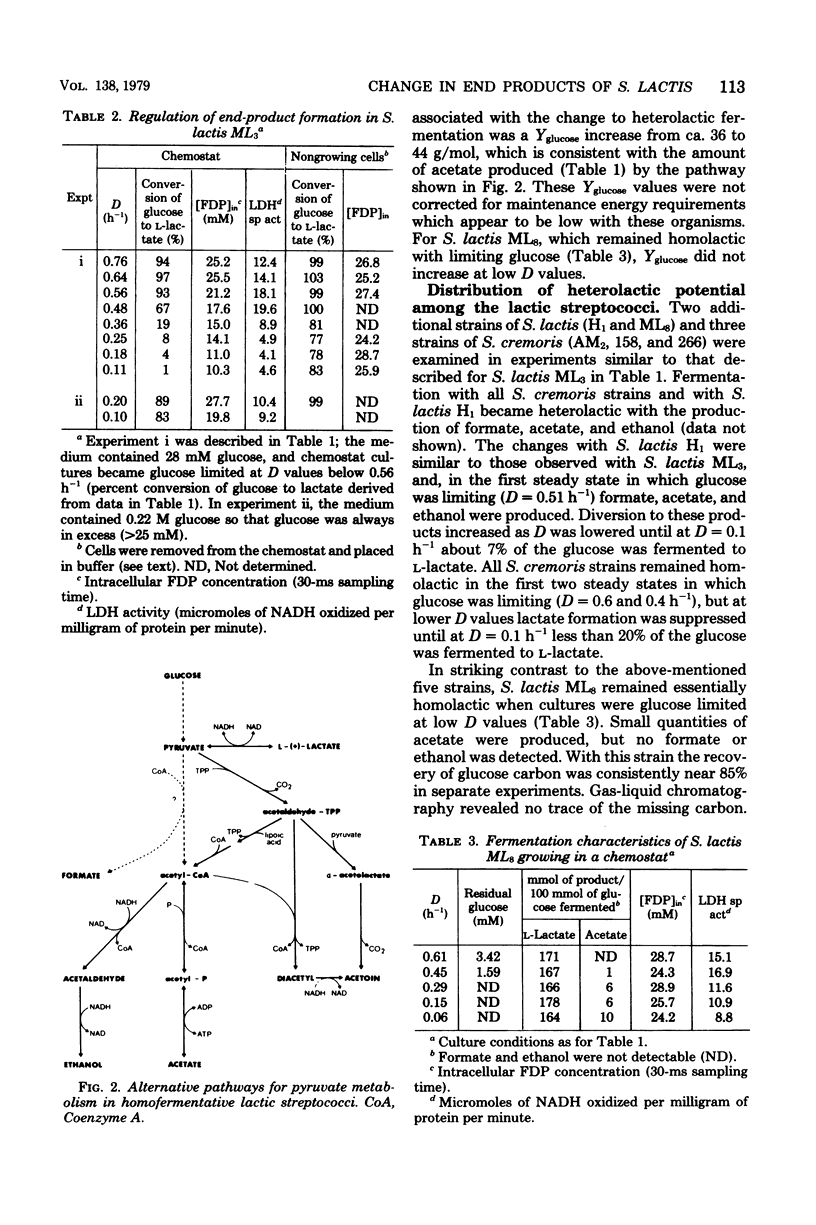
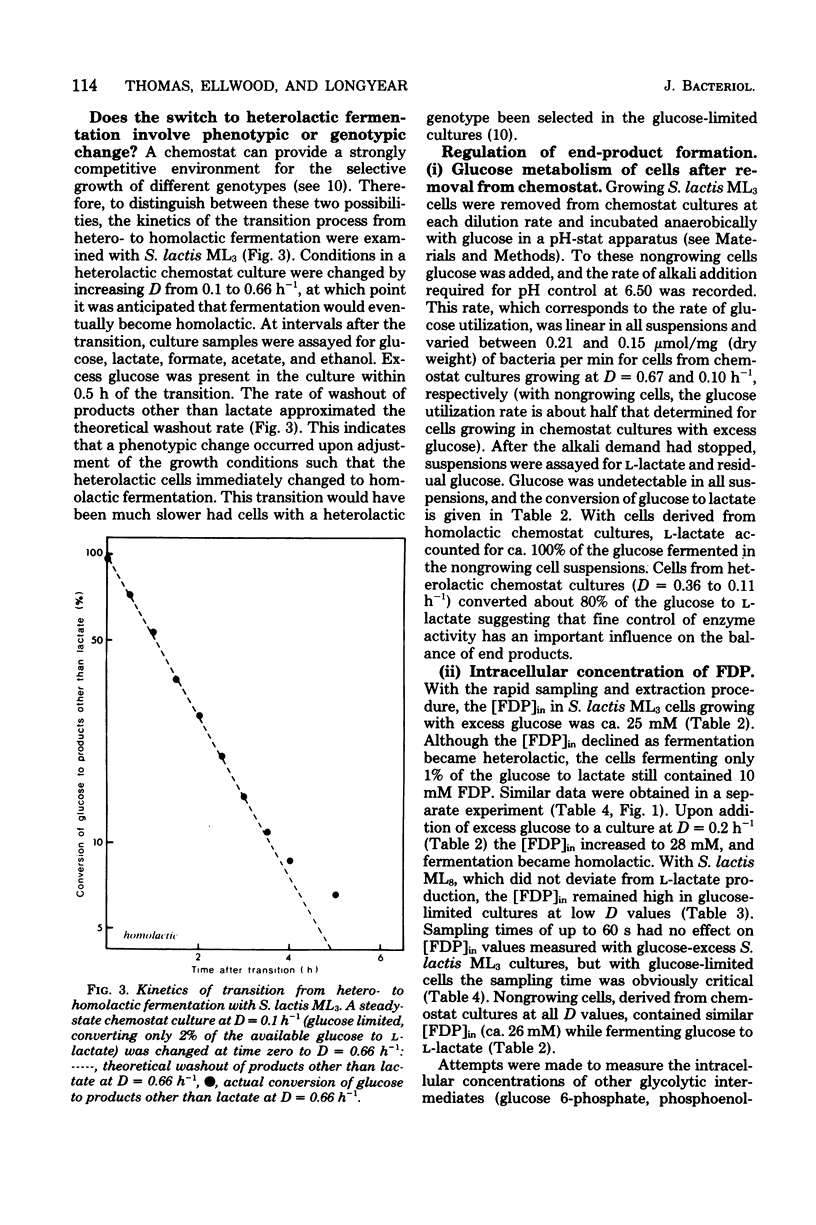
Lactic streptococci, classically regarded as homolactic fermenters of glucose and lactose, became heterolactic when grown with limiting carbohydrate concentrations in a chemostat. At high dilution rates (D) with excess glucose present, about 95% of the fermented sugar was converted to l-lactate. However, as D was lowered and glucose became limiting, five of the six strains tested changed to a heterolactic fermentation such that at D = 0.1 h−1 as little as 1% of the glucose was converted to l-lactate. The products formed after this phenotypic change in fermentation pattern were formate, acetate, and ethanol. The level of lactate dehydrogenase, which is dependent upon ketohexose diphosphate for activity, decreased as fermentation became heterolactic with Streptococcus lactis ML3. Transfer of heterolactic cells from the chemostat to buffer containing glucose resulted in the nongrowing cells converting nearly 80% of the glucose to l-lactate, indicating that fine control of enzyme activity is an important factor in the fermentation change. These nongrowing cells metabolizing glucose had elevated (ca. twofold) intracellular fructose 1,6-diphosphate concentrations ([FDP]in) compared with those in the glucose-limited heterolactic cells in the chemostat. [FDP]in was monitored during the change in fermentation pattern observed in the chemostat when glucose became limiting. Cells converting 95 and 1% of the glucose to l-lactate contained 25 and 10 mM [FDP]in, respectively. It is suggested that factors involved in the change to heterolactic fermentation include both [FDP]in and the level of lactate dehydrogenase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in group N streptococci: presence of enzymes for both the D-galactose 1-phosphate and D-tagatose 6-phosphate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):318–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.318-320.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Wittenberger C. L. Fructose-1,6-diphosphate-dependent lactate dehydrogenase from a cariogenic streptococcus: purification and regulatory properties. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.604-615.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Collins E. B. End products and fermentation balances for lactic streptococci grown aerobically on low concentrations of glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):38–42. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.38-42.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. B., Thomas T. D. Pyruvate kinase of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.52-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow V. L., Pritchard G. G. Fructose 1,6-diphosphate-activated L-lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus lactis: kinetic properties and factors affecting activation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):82–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.82-91.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demko G. M., Blanton S. J., Benoit R. E. Heterofermentative carbohydrate metabolism of lactose-impaired mutants of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1335–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1335-1345.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Hunter J. R., Longyear V. M. Growth of Streptococcus mutans in a chemostat. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Aug;19(8):659–664. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Control of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid biosyntheses in chemostat cultures of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1042/bj1110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., COLLINS E. B. ROLES OF CITRATE AND ACETOIN IN THE METABOLISM OF STREPTOCOCCUS DIACETILACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1301–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1301-1307.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E., Maitra P. K. Control of respiration and metabolism in growing Klebsiella aerogenes. The role of adenine nucleotides. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):647–656. doi: 10.1042/bj1120647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert D., Kornberg H. L. Glucose transport as rate-limiting step in the growth of Escherichia coli on glucose. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):477–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1560477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert D., Phipps P. J., Tempest D. W. The chemostat: design and instrumentation. Lab Pract. 1965 Oct;14(10):1150–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Anders R. F., Jago G. R. Factors affecting the activity of the lactate dehydrognease of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):397–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.397-403.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark D. G., Paolella P., Wood N. P. The pyruvate formate-lyase system of Streptococcus faecalis. I. Purification and properties of the formate-pyruvate exchange enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3605–3612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. J. Occurence of lactose-negative mutants in chemostat cultures of lactic streptococci. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):245–251. doi: 10.1139/m75-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Altered metabolism in a Streptococcus lactis C2 mutant deficient in lactic dehydrogenase. J Dairy Sci. 1974 Feb;57(2):181–186. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(74)84857-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven D. F., Collins P. A., Knowles C. J. Adenylate energy charge during batch culture of Beneckea natriegens. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):95–108. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATT T. B., FOSTER E. M. Products of glucose metabolism by homofermentative streptococci under anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):453–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.453-459.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D. Allosteric controls of amphilbolic pathways in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Mar;34(1):20–39. doi: 10.1128/br.34.1.20-39.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Regulation of lactose fermentation in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):474–478. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.474-478.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Tagatose-1, 6-diphosphate activation of lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus cremoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and change of fermentation products in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.55-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W., Kapteijn W. M., van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Molar growth yields and fermentation balances of Lactobacillus casei L3 in batch cultures and in continuous cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):333–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


