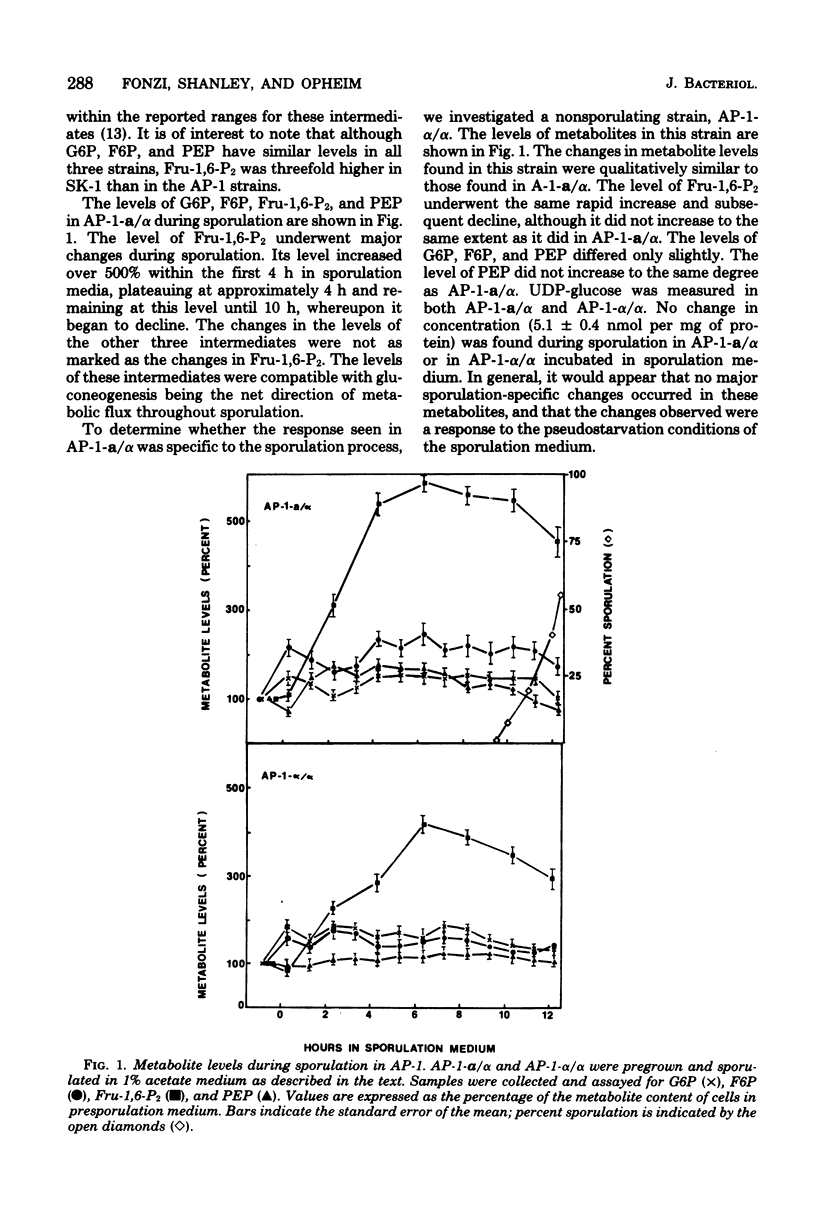
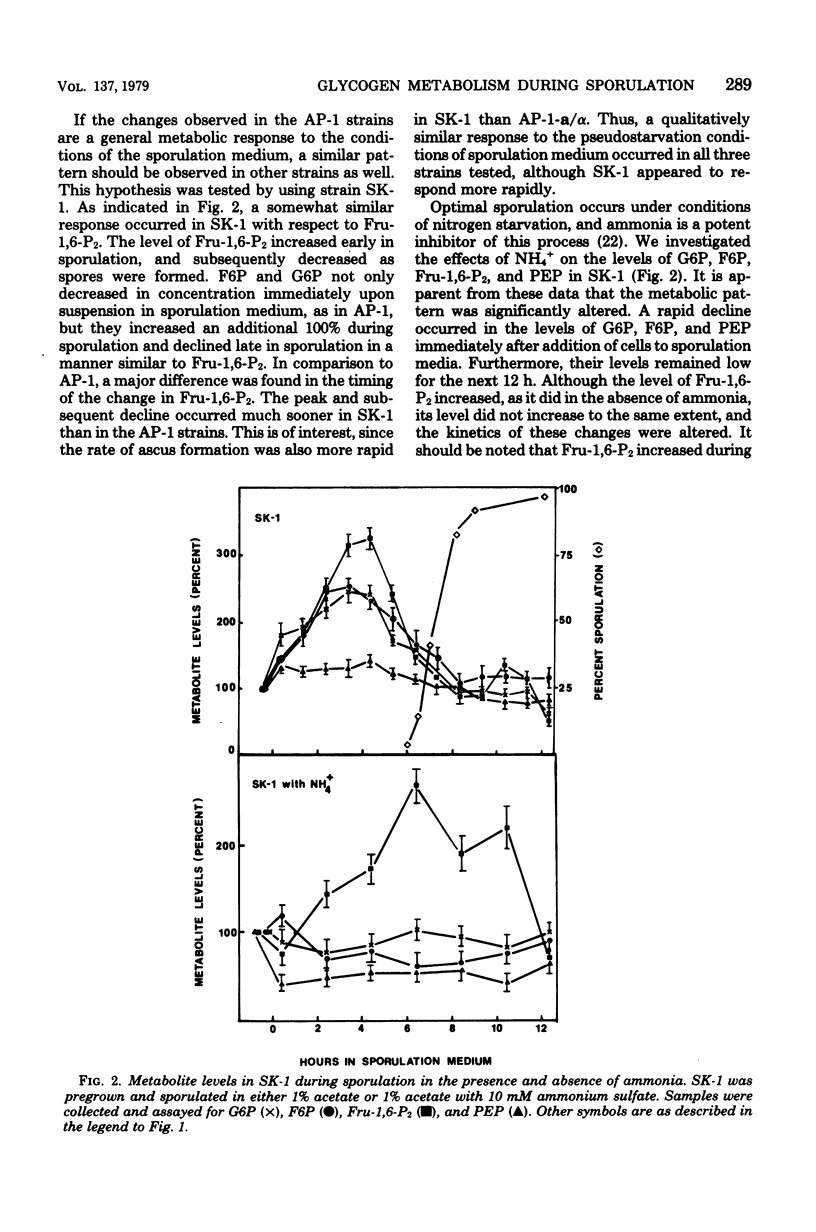
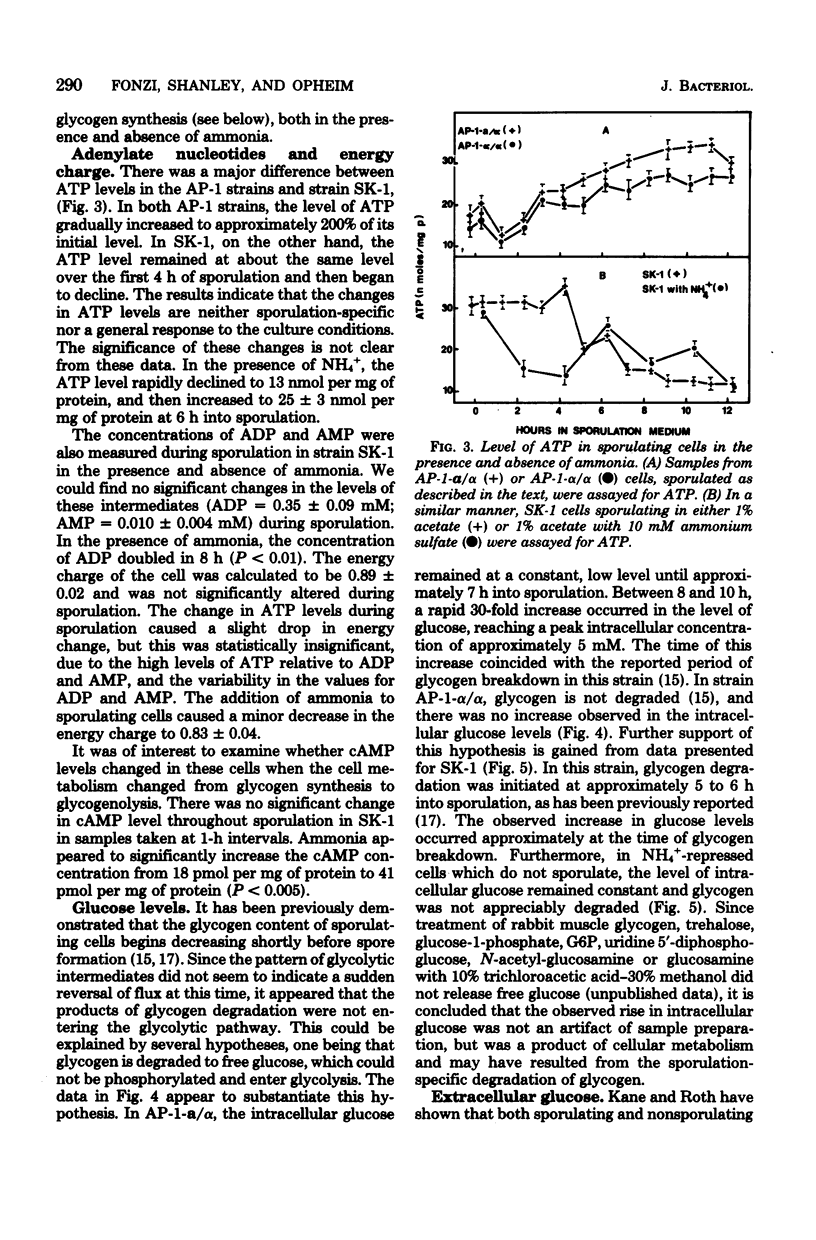
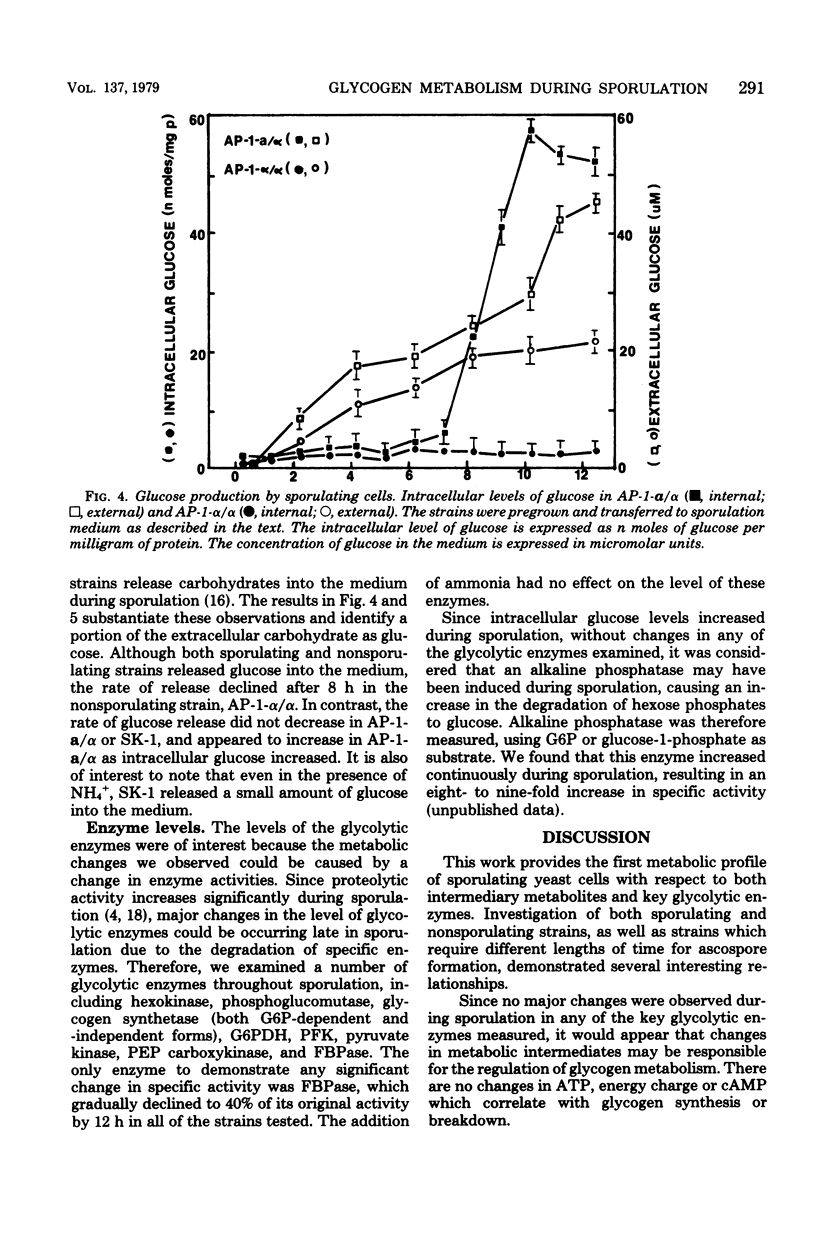
Abstract
To identify the factors which control glycogen synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we have studied the regulation of glycogen metabolism during sporulation, since in vivo glycogen has been reported to undergo significant changes in concentration during this process. We examined the concentration of a number of key glycolytic intermediates and enzymes in strains that sporulate at different rates and those that are deficient in sporulation. There were no significant changes found in the adenylate energy charge or cyclic AMP levels throughout sporulation. Although significant alterations occurred in the levels of glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate, and ATP during sporulation, only the fourfold increase in fructose-1,6-bisphosphate appeared to correlate with glycogen synthesis in all of the strains examined. Only limited changes occurred in the level of a number of glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes which were examined during this process. Intracellular glucose content underwent a dramatic 30- to 40-fold increase in sporulating cells. Comparison of strains with different rates of sporulation demonstrated that this increase in glucose content coincides with the time of glycogen degradation in each strain. Both the increase in glucose content and the degradation of accumulated glycogen were not observed in nonsporulating α/α strains, or in cells incubated in NH4+ supplemented sporulation medium. Although glucose appears to be the direct product of glycogen degradation, a 10-fold increase in a nonspecific alkaline phosphatase occurs at this time, which may be degrading phosphorylated sugars to glucose. All of the strains examined released extracellular glucose while suspended in acetate sporulation medium. It is concluded that most of the changes in the glycolytic pathway that occur during sporulation, with the exception of glycogen degradation and the concomitant increase in intracellular glucose pools, are a response to the transfer to sporulation medium and are independent of sporulation-specific processes. Inhibition of sporulation with ammonium ions resulted in a different pattern of change in all of the glycolytic intermediates examined, including a twofold increase in cyclic AMP levels. Ammonia did not interfere with glycogen synthesis, but prevented sporulation-specific glycogen degradation. The levels of the glycolytic enzymes examined were not affected by ammonia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball W. J., Jr, Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during starvation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):975–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.975-982.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barwell C. J., Hess B. Application of kinetics of yeast pyruvate kinase in vitro to calculation of glycolytic flux in the anaerobic yeast cell. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1178–1184. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H., Weisner U. Protein degradation and proteinases during yeast sporulation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J., DOWNEY M. An outer metabolic region of the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):347–355. doi: 10.1042/bj0470347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty J. P., Kraemer W. F., Joshi J. G. Purification and properties of phosphoglucomutase from Fleischmann's yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. Sporulation synchrony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in various carbon sources. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):925–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.925-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo C., Schwerzmann K. Inactivation by glucose of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Sep 1;109(3):221–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00446632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo J. M., Clifton D., Fraenkel D. G. Yeast hexokinase mutants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4443–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Concentrations of intermediary metabolites in yeast. Biochimie. 1973;55(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting and non fermenting yeasts. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(2):132–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00411787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Cabib E. Yeast glycogen synthetase in the glucose 6-phosphate independent form: a case of cold lability without major changes in molecular size. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):240–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. M., Roth R. Carbohydrate metabolism during ascospore development in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.8-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Halvorson H. O. Proteinase activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.863-869.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopperschläger G., Augustin H. W. Fehlermöglichkeiten bei der Bestimmung von Metabolitgehalten in Hefezellen. Experientia. 1967 Aug 15;23(8):623–624. doi: 10.1007/BF02144159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opheim D., Bernlohr R. W. Purification and regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1150–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1150-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of yeast harvested during logarithmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):831–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.831-832.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman L. B., Cabib E. Regulation of glycogen synthesis in the intact yeast cell. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3332–3341. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. 7. Yeast carbohydrate fractions. Separation from nucleic acid, analysis, and behaviour during anaerobic fermentation. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):23–33. doi: 10.1042/bj0630023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. R., Stahly D. P. Modification of the valve of the French pressure cell. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1605–1605. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1605-.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


