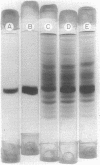
Abstract
Serial culture of Rhodospirillum rubrum with 2% CO2 in H2 as the exclusive carbon source resulted in a rather large fraction of the soluble protein (greater than 40%) being comprised of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase (about sixfold higher than the highest value previously reported). Isolation of the enzyme from these cells revealed that it has physical and kinetic properties similar to those previously described for the enzyme derived from cells grown on butyrate. Notably, the small subunit (which is a constituent of the carboxylase from eucaryotes and most procaryotes) was absent in the enzyme from autotrophically grown R. rubrum. Edman degradation of the purified enzyme revealed that the NH2 terminus is free (in contrast to the catalytic subunit of the carboxylase from eucaryotes) and that the NH2-terminal sequence is Met-Asp-Gln-Ser-Ser-Arg-Tyr-Val-Asn-Leu-Ala-Leu-Lys-Glu-Glu-Asp-Leu-Ile-Ala-Gly-Gly-Glx-His-Val-Leu-. Crystals of the enzyme were readily obtained by dialysis against distilled water.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akazawa T., Sato K., Sugiyama T. Structure and function of chloroplast proteins. 8. Some properties of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of athiorhodaceae in comparison with those of plant enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. IV. Isolation and characterization of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3105–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. 3. Metabolic control of reductive pentose phosphate and tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes. Plant Physiol. 1967 Apr;42(4):497–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. S., Eisenberg D., Eiserling F. A., Weissman L. The structure of form I crystals of D-ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90267-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. S., Eisenberg D., Eiserling F. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase: a two-layered, square-shaped molecule of symmetry 422. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):293–295. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4287.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. S., Suh S. W., Eisenberg D. Structure of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase: Form III crystals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1037–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Steitz T. A. X-ray diffraction studies of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:63–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L. Oxygen inhibition and other properties of soybean ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Sakano K., Singh S., Wildman S. G. Crystalline fraction I protein: preparation in large yield. Science. 1972 Jun 9;176(4039):1145–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4039.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activities by temperature pretreatment and chloroplast metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Isolation and preliminary characterization of two forms of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.818-823.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C. Synthesis and characterization of 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-bisphosphate, a potential affinity label for enzymes that bind sugar bisphosphates. J Org Chem. 1975 Sep 5;40(18):2638–2642. doi: 10.1021/jo00906a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai S., Tanabe Y., Kawashima N. Origin of sequence heterogeneity of the small subunit of fraction 1 protein from Nicotiana tabacum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):993–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Singh S., Wildman S. G. Reversible cold inactivation and heat reactivation of RuDP carboxylase activity of crystallized tobacco fraction I protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):664–668. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction-I protein. I. Effect of crystallization of fraction-I protein from tobacco leaves on ribulose diphosphate carboxylase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):240–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Improved methods for the activation and assay of catalytic activities. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Regeneration of amino acids from thiazolinones formed in the Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Akazawa T. Further proof for the catalytic role of the larger subunit in the spinach leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):842–848. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90770-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Akazawa T. Studies on spinach leaf ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Carboxylase and oxygenase reaction examined by immunochemical methods. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2277–2281. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton I. L., Welch M. H., Hartman F. C. Evidence for essential lysyl residues in ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by use of the affinity label 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8062–8068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paech C., Ryan F. J., Tolbert N. E. Essential primary amino groups of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase indicated by reaction with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Feb;179(1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penke B., Ferenczi R., Kovács K. A new acid hydrolysis method for determining tryptophan in peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Cohen A. L. Purification, quaternary structure, composition, and properties of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.505-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. K., Gibbs M. Partial purification and characterization of two fructose diphosphate aldolases from Chlamydomonas mundana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutner A. C. Estimation of the molecular weight of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase sub-units. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jun 5;39(5):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan F. J., Jolly S. O., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. V. Presence in ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1233–1241. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan F. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. III. Isolation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4229–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Hartman F. C. Reaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase from rhodospirlilum rubrum with the potential affinity label 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-biphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 21;75(2):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Stringer C. D., Hartman F. C. Identification of essential lysyl and cysteinyl residues in spinach ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase modified by the affinity label N-bromoacetylethanolamine phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5707–5711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):395–403. doi: 10.1126/science.202030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Saluja A., McFadden B. A. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from methanol-grown Paracoccus denitrificans. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1123–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1123-1132.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. I., Lane M. D. Interaction of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase with 2-carboxyribitol diphosphate, an analogue of the proposed carboxylated intermediate in the CO 2 fixation reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):508–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90377-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. H., Morris I. Photosynthetic carbon dioxide assimilation by Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(3):213–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00421847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. L., Wold F. A new convenient method for estimation of total cystine-cysteine in proteins. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 15;32(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spomer G. G. Molecular diversity of the ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from photosynthetic microorganisms. Science. 1968 Aug 2;161(3840):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer C. D., Hartman F. C. Sequences of two active-site peptides from spinach ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):1043–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. R., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Thin-layer chromatography of sub-nanomole amounts of phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) amino acids on polyamide sheets. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):624–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A., Pfennig N. D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum Tassajara. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Stevens S. E., Jr, Gibson J. L. Carbon dioxide assimilation in blue-green algae: initial studies on the structure of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.531-539.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita R. F., Stevens S. E., Jr, Quijano R. D-ribulose 1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Akazawa T. Catalytic role of subunit A in ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Chromatium strain D. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jul;157(1):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Akazawa T. Oxidative formation of phosphoglycolate from ribulose-1,5-diphosphate catalysed by Chromatium ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1173–1179. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Tabita F. R. Modification of Rhodospirillum rubrum ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase with pyridoxal phosphate. 1. Identification of a lysyl residue at the active site. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1282–1287. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Tabita F. R. Modification of Rhodospirillum rubrum ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase with pyridoxal phosphate. 2. Stoichiometry and kinetics of inactivation. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1288–1293. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelitch I. Pathways of carbon fixation in green plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:123–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]