Abstract
A variety of N-acetylneuraminic acid (AcNeu) derivatives and analogs were examined as inducers of the extracellular neuraminidase of Arthrobacter sialophilus. Neuraminidase inductions were primarily studied with tryptone-yeast extract-grown cells after washing and resuspension in a defined replacement medium. The addition of readily metabolizable carbon sources to the latter, such as 0.1% casein hydrolysate, glutamate, or glucose, enhanced enzyme synthesis. Enzyme appearance occurred after a lag in the uptake of inducers, suggesting the participation of a co-inducible transport system. Neuraminidase formation during exponential growth in the presence of AcNeu ceased after depletion of this end product from the medium. It was found, besides AcNeu, that its methyl ester, 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid and 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid methyl ester are each active inducers, whereas beta-anomers of AcNeu-ketosides are not. These results, in comparison to known enzyme specificity, have revealed significant differences and parallels between the inductive and catalytic processes for neuraminidase. In particular, it would appear that the free carboxylate and oxygenation at C-2 of AcNeu, essential for enzyme catalysis with traditional AcNeu substrates, are not necessary for induction and, furthermore, that transition state analogs can specifically induce this enzyme. The failure to observe catabolite repression in this system is discussed in relation to the intermediary metabolism of the genus Arthrobacter.
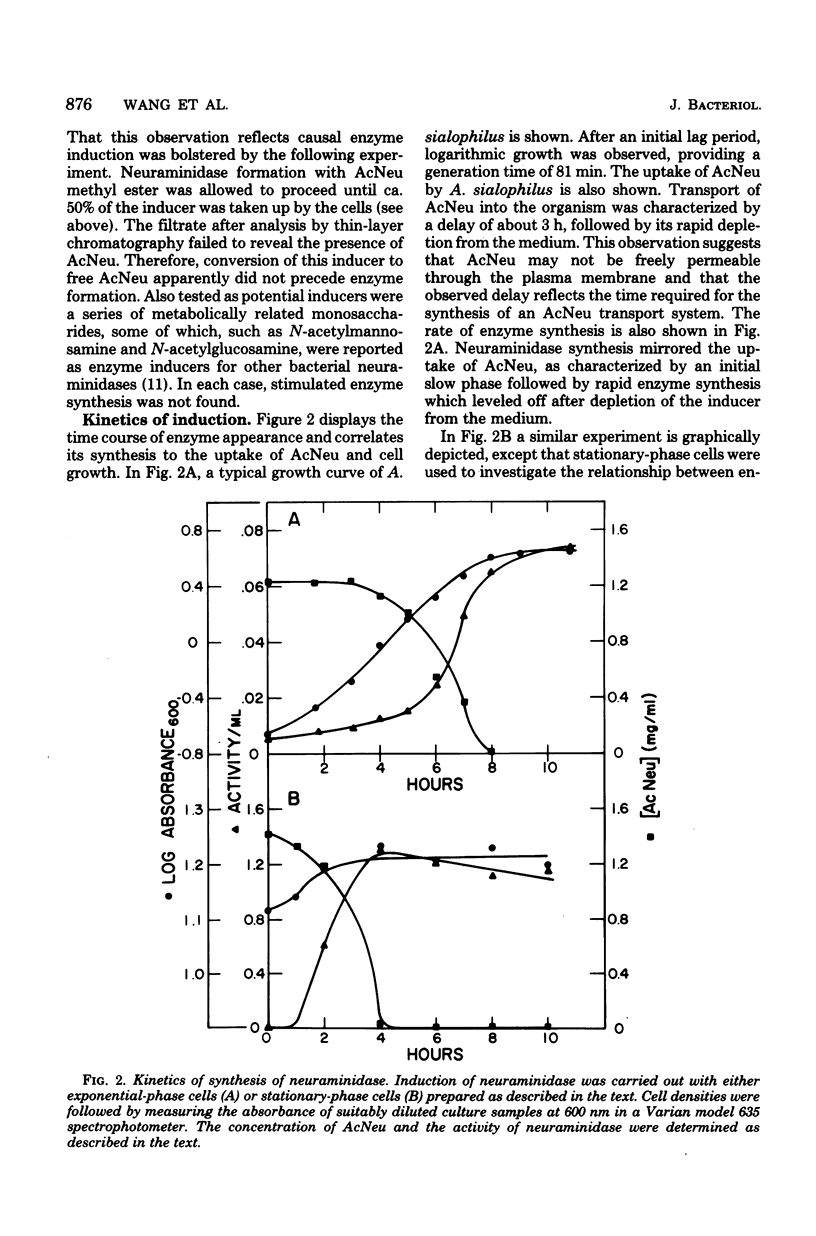
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boethling R. S. Regulation of extracellular protease secretion in Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):954–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.954-961.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R. Substrate specificity of neuraminidases. Histochem J. 1973 May;5(3):271–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01004994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R. Viral and bacterial neuraminidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;59:35–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65444-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisu S., Kato K., Kotani S., Misaki A. Isolation and purification of Flavobacterium alpha-1,3-glucanase-hydrolyzing, insoluble, sticky glucan of Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1489–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1489-1501.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner M., Wang P., Hurley J. B., Tanenbaum S. W. Properties of an inducible extracellular neuraminidase from an Arthrobacter isolate. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1457-1465.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWE C., LEE L. T., ROSE H. M. Collocalia mucoid: a substrate for myxovirus neuraminidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:512–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. W., Kolenbrander P. E. Regulation of cyclic AMP levels in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes and a morphogenetic mutant. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1064–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1064-1073.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. T., Greiff D., Farmer S. Neuraminidase activity in Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):601–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.601-603.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R., Lutz P., MacDonald D. L. Synthese anomerer Sialinsäure-methylketoside. Chem Ber. 1966 Feb;99(2):611–617. doi: 10.1002/cber.19660990235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. H., Blackburn T. H. Cellulase production by a thermophilic clostridium species. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):346–353. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.346-353.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. L., Krulwich T. A. Alternate pathways of L-rhamnose transport in Arthrobacter pyridinolis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Tanenbaum S. W., Flashner M. A facile procedure for the isolation of N-acetylneuramic acid from edible bird's-nest. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Jul;56(2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Wang P., Flashner M. Mechanism of Arthrobacter sialophilus neuraminidase: the binding of substrates and transition-state analogs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1479–1487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Parke D. The evolution of induction mechanisms in bacteria: insights derived from the study of the beta-ketoadipate pathway. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1977;12:209–262. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152812-6.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanenbaum S. W., Flashner M. Arthrobacter sialophilus sp. nov.; a neuraminidase-producing coryneform. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Nov;23(11):1568–1572. doi: 10.1139/m77-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Tanenbaum S. W., Flashner M. Purification and properties of Arthrobacter neuraminidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 14;523(1):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson E. B., Sobel M. E., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. Pathways of D-fructose transport in Arthrobacter pyridinolis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu R. K., Ledeen R. Configuration of the ketosidic bond of sialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1306–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


