Abstract
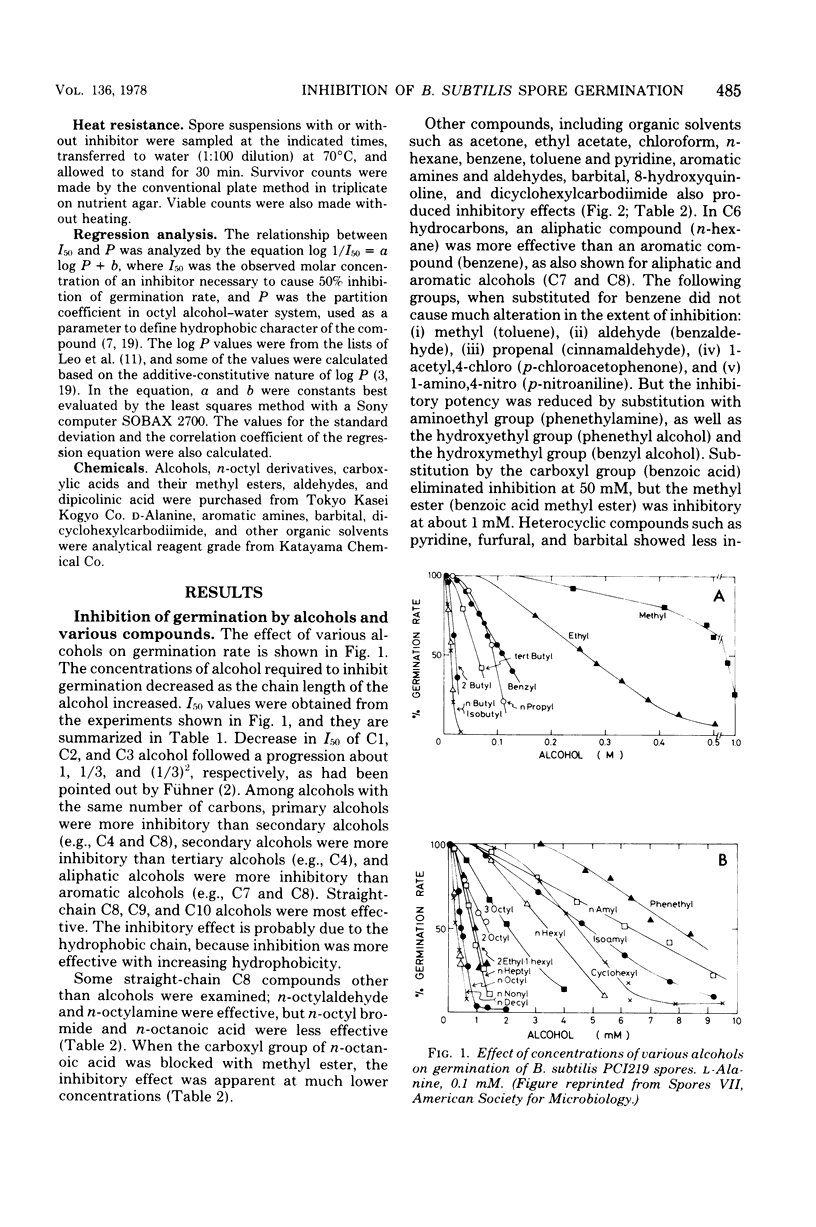
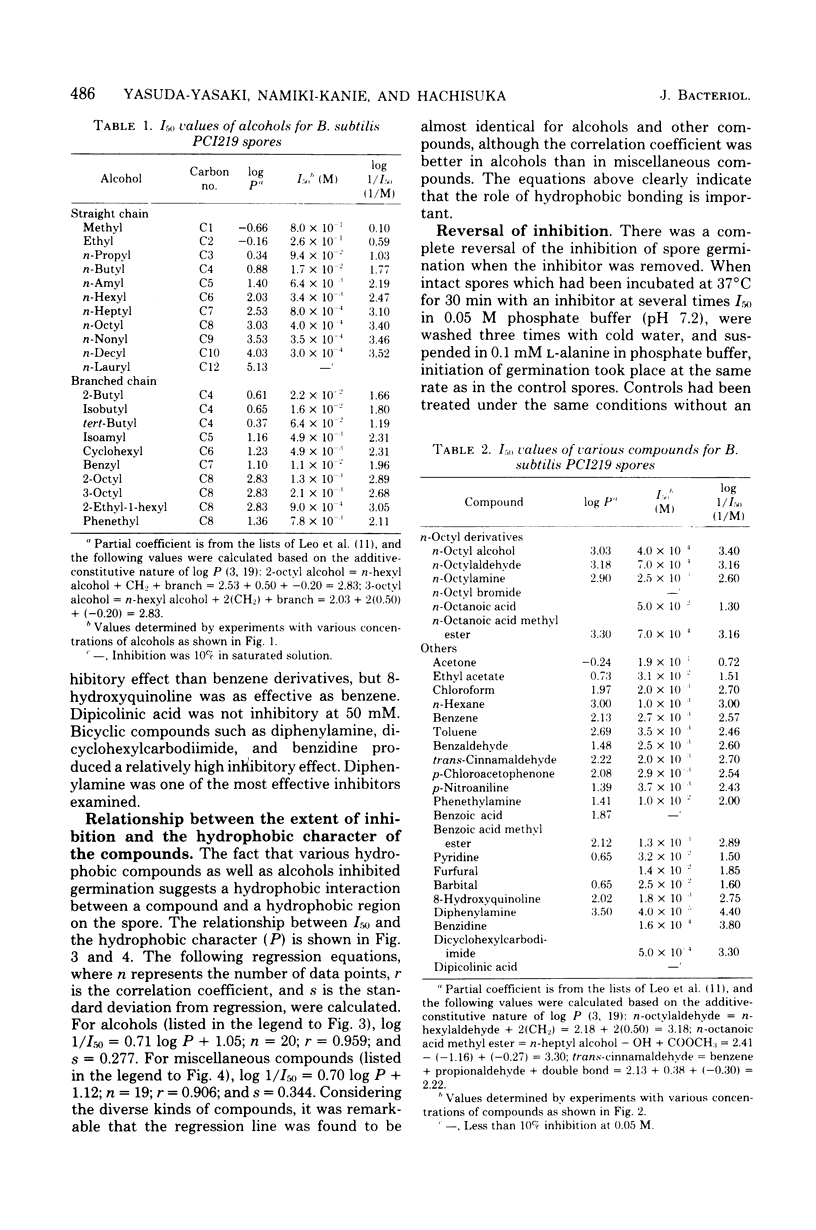
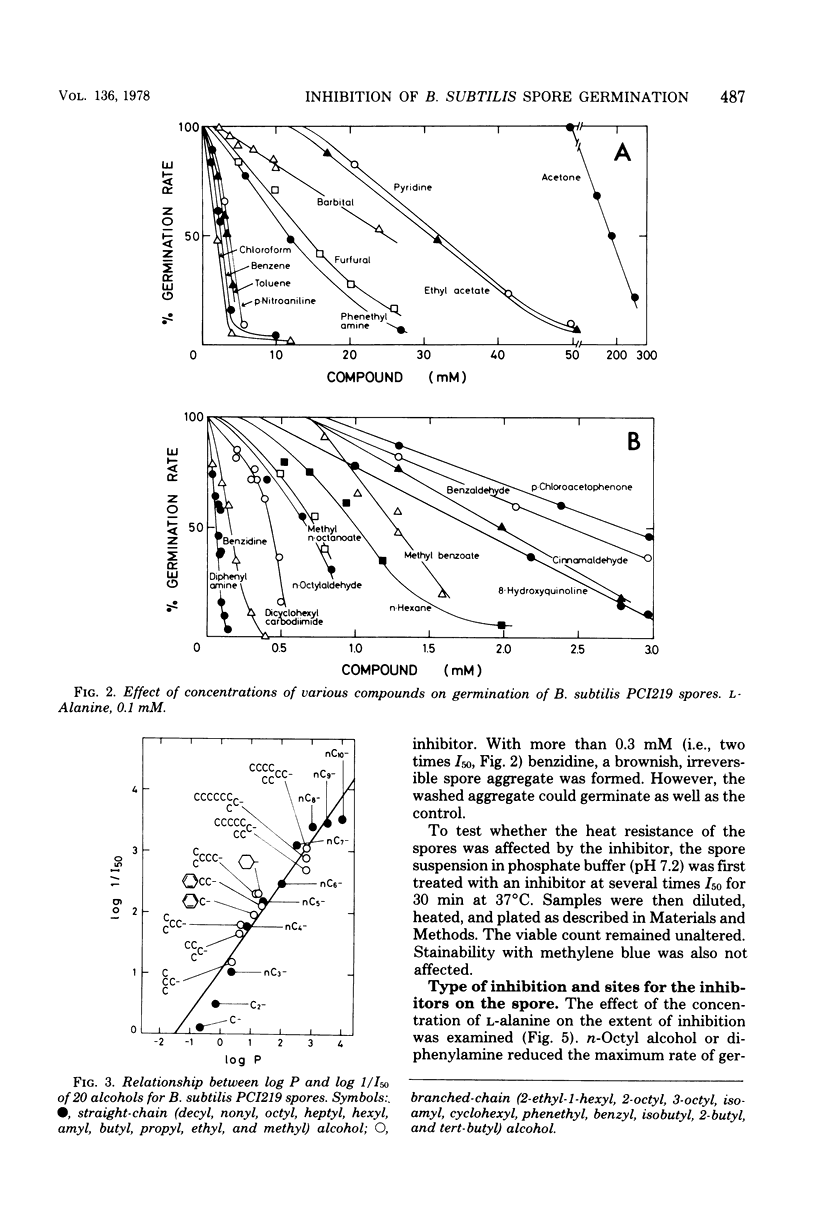
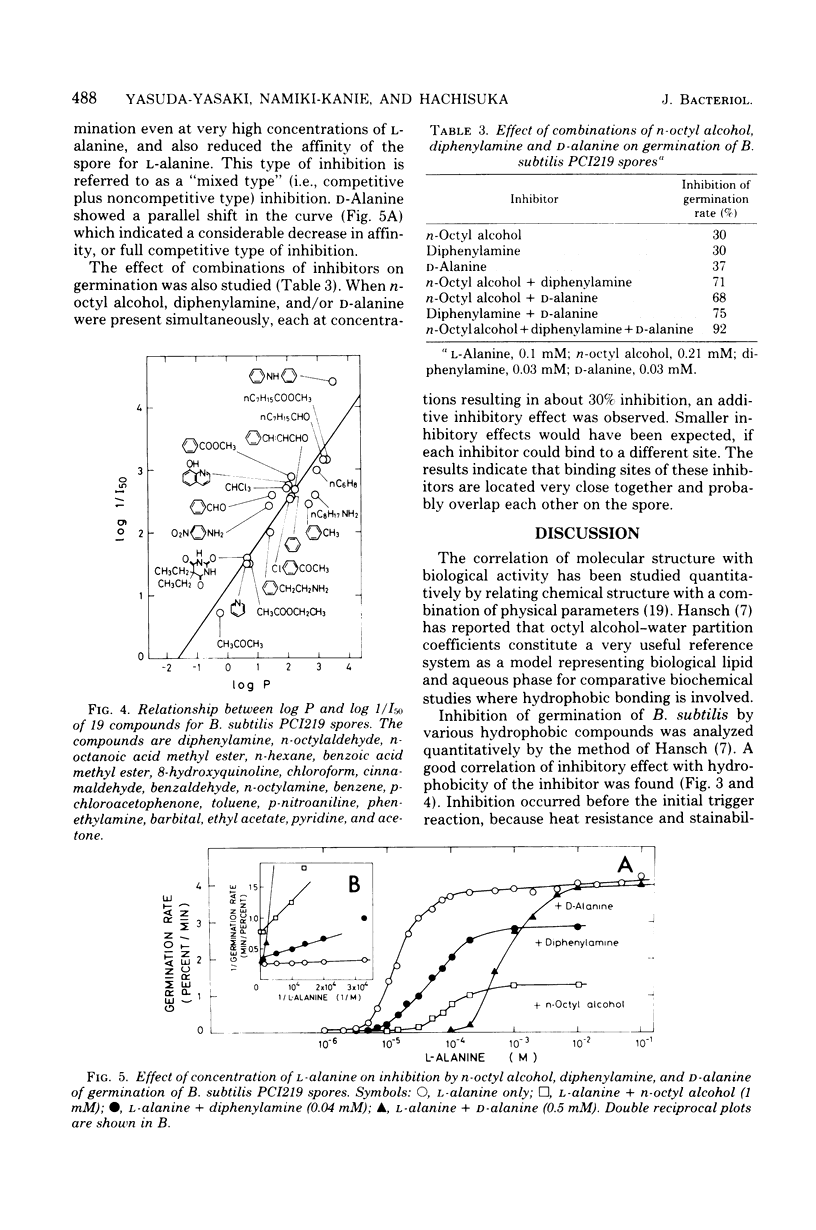
L-Alanine-initiated germination of Bacillus subtilis spores was inhibited by various kinds of hydrophobic compounds. Good correlation of inhibitory effect with hydrophobicity of the compound was demonstrated by using regression analysis in which the hydrophobic character was expressed by the partition coefficient in an octyl alcohol-water system. The correlation coefficient for 20 alcohols was 0.959, and that for 19 miscellaneous compounds was 0.906. Regression lines of the alcohols and other hydrophobic compounds were almost identical, showing that hydrophobic interaction played an important role in inhibition. Diphenylamine was one of the most effective inhibitors examined. n-Octyl, n-nonyl, and n-decyl alcohols were the most effective alcohols. The mode of inhibition by diphenylamine and n-octyl alcohol was a "mixed type" (competitive plus noncompetitive type) with respect to L-alanine; that by D-alanine was competitive inhibition. Sites for diphenylamine, n-octyl alcohol, and D-alanine may have overlapped. Inhibition was reversible by washing; heat resistance, stainability, and germination rate of the washed spores remained unaltered. Thus, we confirmed that the inhibition may occur before the initial trigger reaction of germination and that it may be due to the interaction between a hydrophobic compound and a hydrophobic region closely associated with the L-alanine receptor site on the spore.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HACHISUKA Y., ASANO N., KATO N., OKAJIMA M., KITAORI M., KUNO T. Studies on spore germination. I. Effect of nitrogen sources on spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.399-406.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALMANN M., KEYNAN A. Stages in germination of spores of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1187–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1187-1193.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYATT M. T., LEVINSON H. S. Conditions affecting Bacillus megaterium spore germination in glucose or various nitrogenous compounds. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1231–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1231-1237.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O. IV. : Dormancy, Germination, and Outgrowth. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Dec;23(4):267–272. doi: 10.1128/br.23.4.267-272.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansch C., Clayton J. M. Lipophilic character and biological activity of drugs. II. The parabolic case. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Jan;62(1):1–21. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISHNA MURTY G. G., HALVORSON H. O. Effect of enzyme inhibitors on the germination and respiration of and growth from Bacillus cereus var. terminalis spores. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.230-234.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien E. J., Hansch C., Anderson S. M. Structure-activity correlations for antibacterial agents on gram-positive and gram-negative cells. J Med Chem. 1968 May;11(3):430–441. doi: 10.1021/jm00309a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. Factors affecting the germination of thick suspensions of bacillus subtilis spores in L-alanine solution. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):330–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. The sporulation and germination of a strain of Bacillus megatherium. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Nov;5(5 Suppl):993–1000. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-5-993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEPECKY R. A. INHIBITION OF SPORULATION AND GERMINATION OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM BY PHENETHYL ALCOHOL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:369–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra G., Bowman A. Mechanism and factors influencing the veronal inhibition of bacterial spore germination. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):372–378. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.372-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tute M. S. Principles and practice of Hansch analysis: a guide to structure-activity correlation for the medicinal chemist. Adv Drug Res. 1971;6:1–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinter V. Symposium on bacterial spores: V. Germination and outgrowth: effect of inhibitors. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):50–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


