Abstract
Analyses of ribosomes extracted from spores of Bacillus cereus T by a dryspore disruption technique indicated that previously reported defects in ribosomes from spores may arise during the ribosome extraction process. The population of ribosomes from spores is shown to cotain a variable quantity of free 50S subunits which are unstable, giving rise to slowly sedimenting particles in low-Mg2+ sucrose gradients and showing extremely low activity in in vitro protein synthesis. The majority of the ribosomal subunits in spores, obtained by dissociation of 70S ribosomes and polysomes, are shown to be as stable as subunits from vegetative cells, though the activity of spore polysomes was lower than that of vegetative ribosomes. In spite of the instability and inactivity of a fraction of the spore's ribosomal subunits, the activity of the total population obtained from spores by the dry disruption technique was 32% of vegetative ribosome activity, fivefold higher than previously obtained with this species. The improvement in activity and the observed variability of subunit destabilization are taken as evidence for partial degradation of spore ribosomes during extraction.
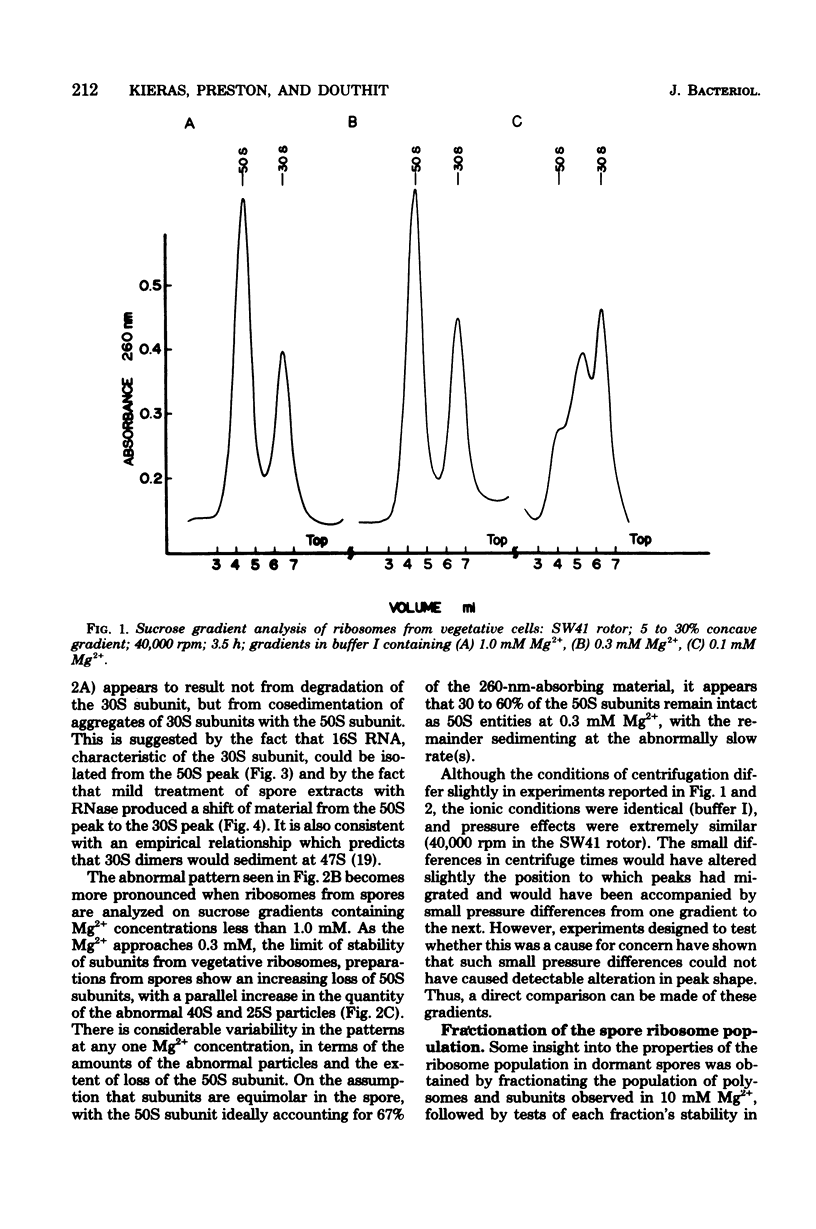
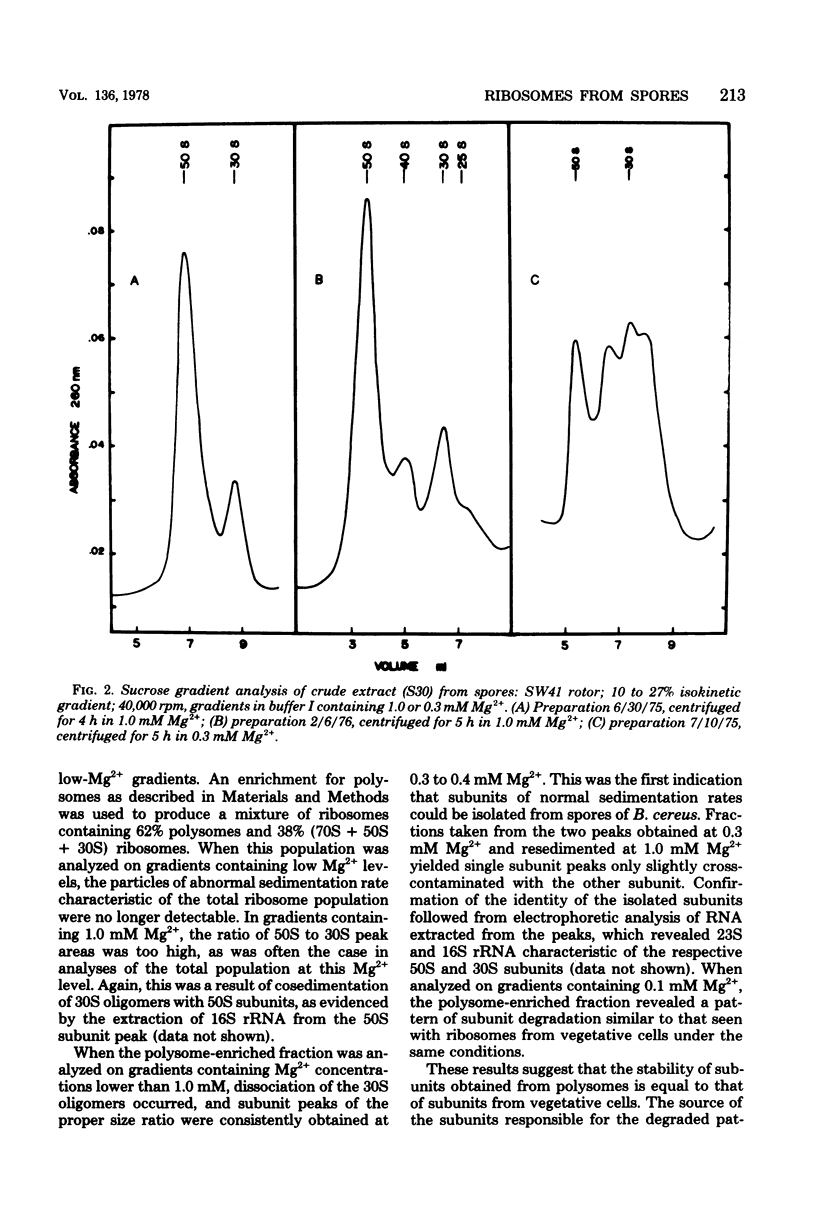
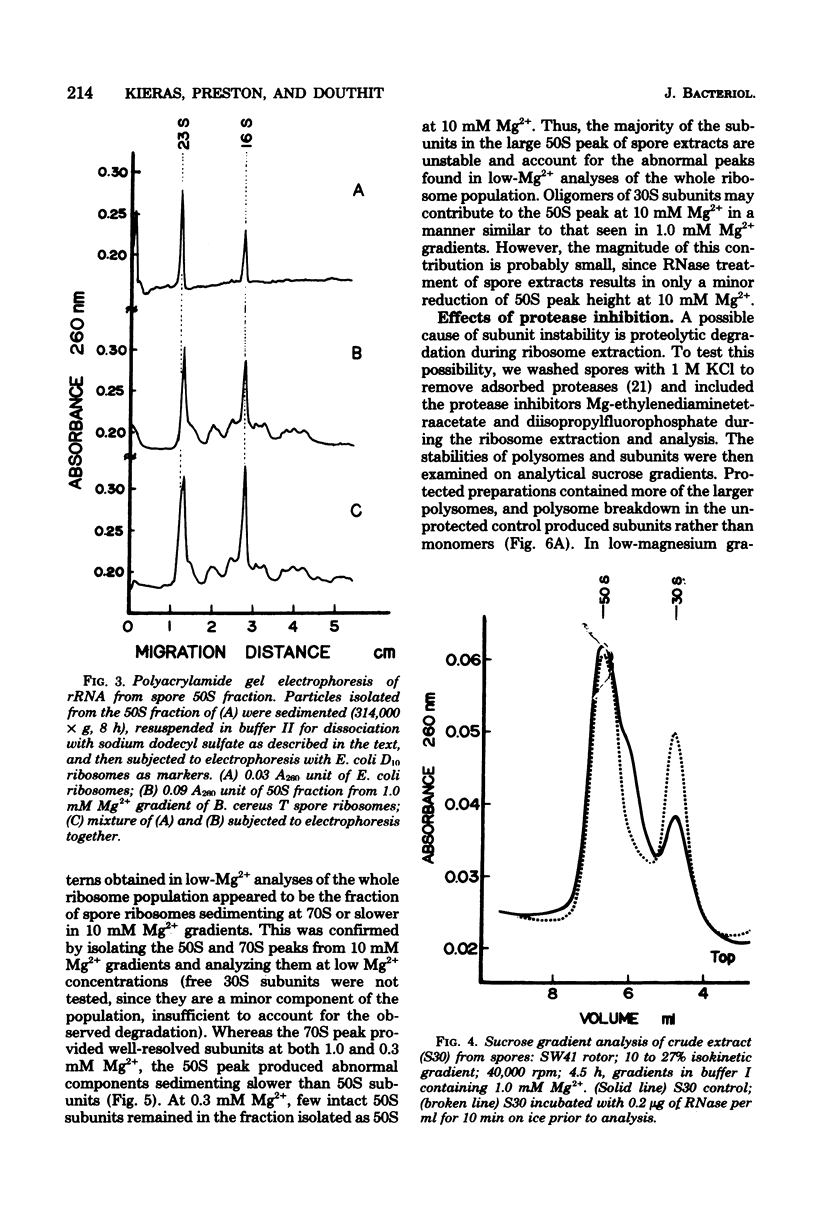
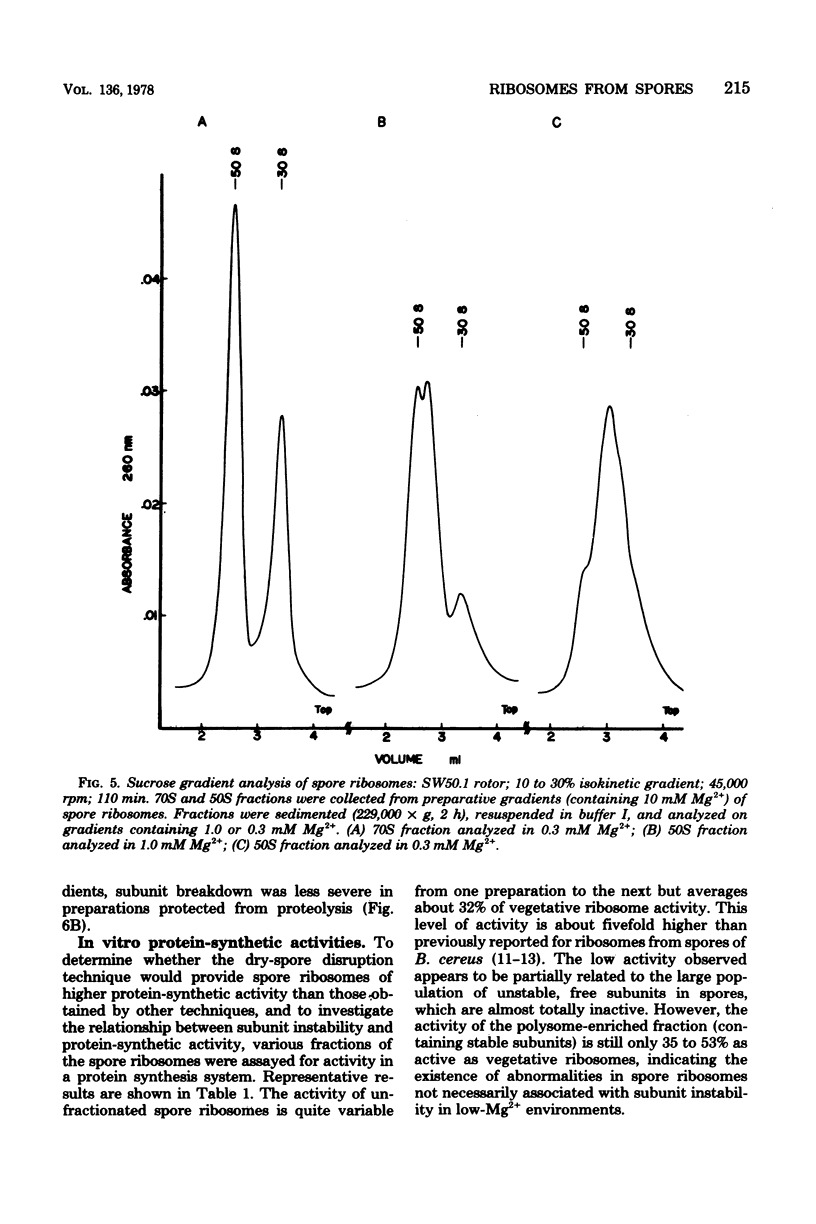
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop H. L., Doi R. H. Isolation and characterization of ribosomes from Bacillus subtilis spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):695–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.695-701.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop H. L., Migita L. K., Doi R. H. Peptide synthesis by extracts from Bacillus subtilis spores. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.771-778.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P., Deutscher M. P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. X. Ribosomes and nucleic acids of vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5110–5116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. S., Carr C. W. Ion-binding studies of ribonucleic acid and Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Chambon P., Konberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XI. Protein-synthesizing systems from vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5117–5125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinsod F. M., Douthit H. A. Ribosomes from spores of Bacillus cereus T. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):991–991. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Levine R. P. Chloroplast structure and function in ac-20, a mutant strain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. 3. Chloroplast ribosomes and membrane organization. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):547–562. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idriss J. M., Halvorson H. O. The nature of ribosomes of spores of Bacillus cereus T. and Bacillus megaterium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Sep;133(2):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90474-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Halvorson H. O. Evidence for a defective protein synthesizing system in dormant spores of Bacillus cereus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 11;123(3):622–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Switzer R. L. Apparent inactivation of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis Is an artifact of in vitro proteolysis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1269–1272. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1269-1272.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty K. S., Jr, Vollmer R. T., McCarty K. S. Improved computer program data for the resolution and fractionation of macromolecules by isokinetic sucrose density gradient sedimentation. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):165–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz E., Noll H. Characterization of cytoplasmic and chloroplast polysomes in plants: evidence for three classes of ribosomal RNA in nature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):774–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesone C., Torriani A. Protease associated with spores of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):593–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.593-594.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Kimes B. W., Morris D. R. Cations and ribosome structure. 3. Effects on the 30S and 50S subunits of replacing bound Mg 2+ by inorganic cations. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):450–456. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


