Abstract
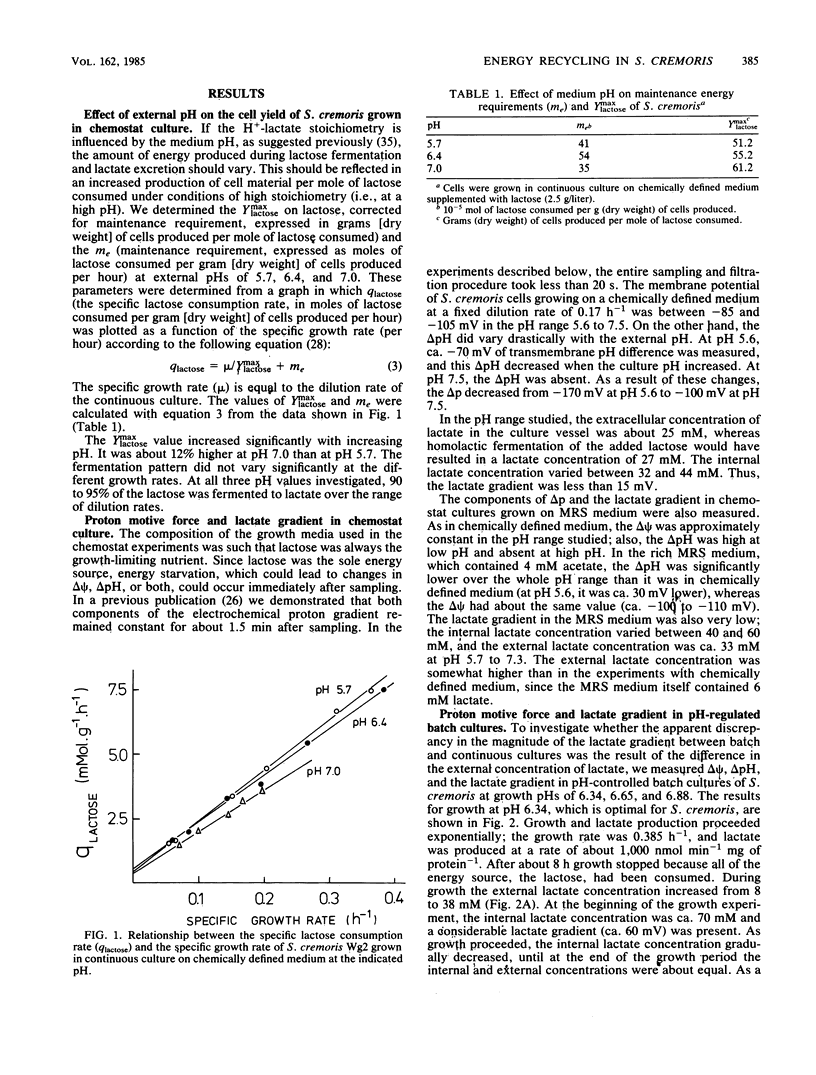
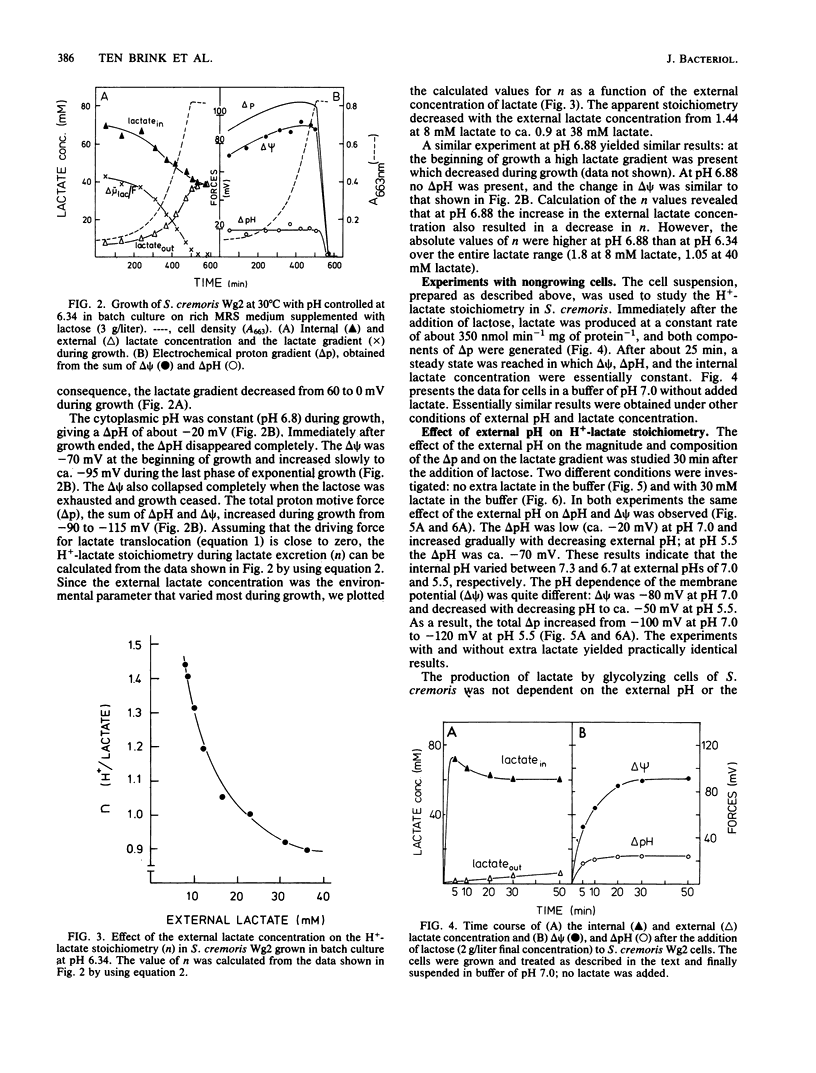
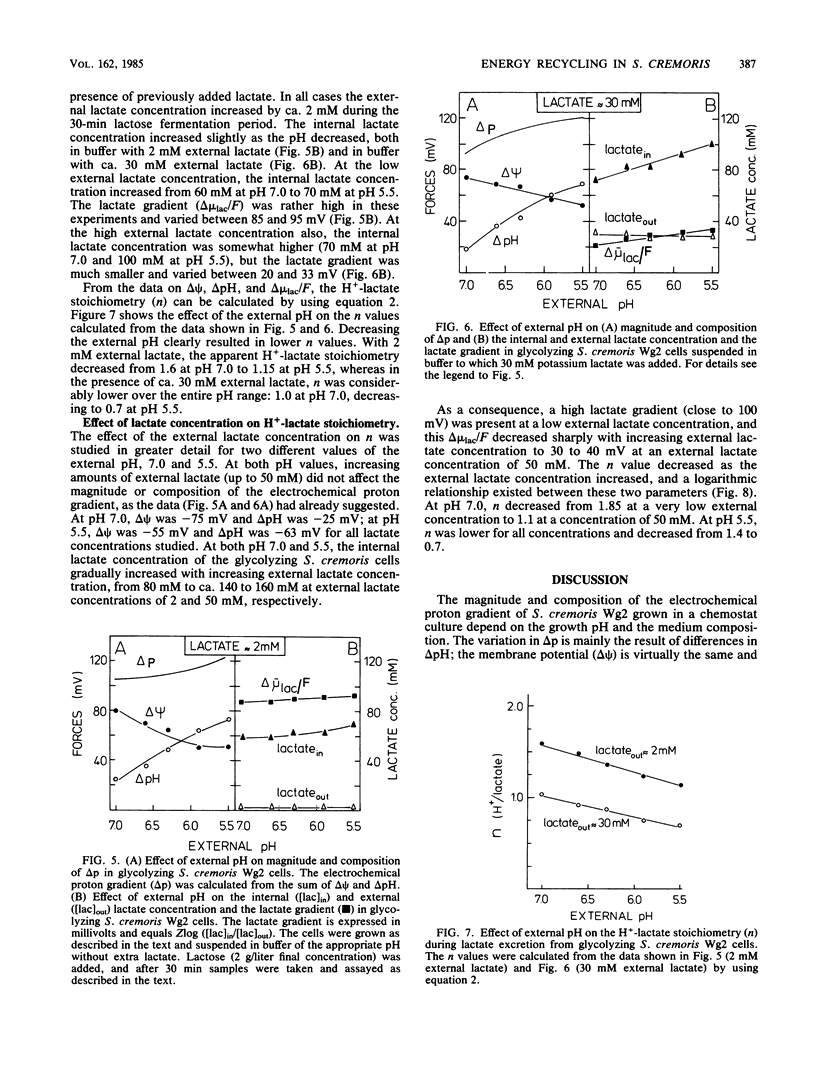
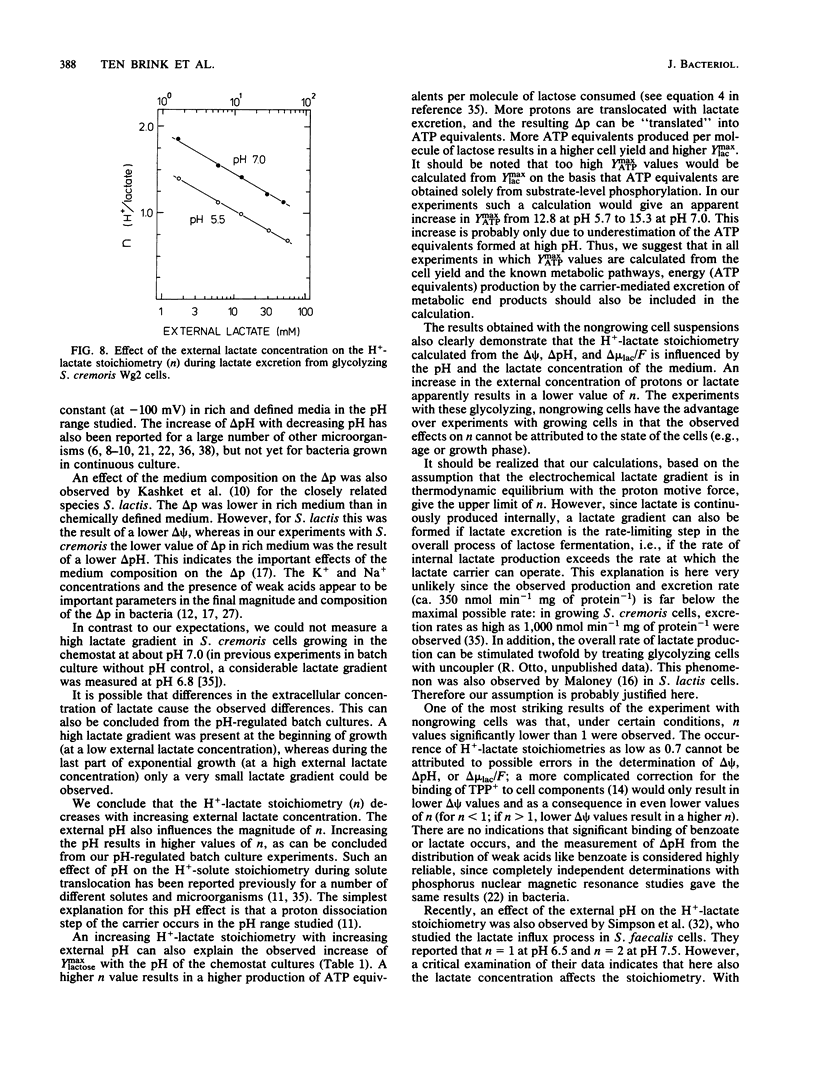
Streptococcus cremoris was grown in pH-regulated batch and continuous cultures with lactose as the energy source. During growth the magnitude and composition of the electrochemical proton gradient and the lactate concentration gradient were determined. The upper limit of the number of protons translocated with a lactate molecule during lactate excretion (the proton-lactate stoichiometry) was calculated from the magnitudes of the membrane potential, the transmembrane pH difference, and the lactate concentration gradient. In cells growing in continuous culture, a low lactate concentration gradient (an internal lactate concentration of 35 to 45 mM at an external lactate concentration of 25 mM) existed. The cell yield (Ymax lactose) increased with increasing growth pH. In batch culture at pH 6.34, a considerable lactate gradient (more than 60 mV) was present during the early stages of growth. As growth continued, the electrochemical proton gradient did not change significantly (from -100 to -110 mV), but the lactate gradient decreased gradually. The H+-lactate stoichiometry of the excretion process decreased from 1.5 to about 0.9. In nongrowing cells, the magnitude and composition of the electrochemical proton gradient was dependent on the external pH but not on the external lactate concentration (up to 50 mM). The magnitude of the lactate gradient was independent of the external pH but decreased greatly with increasing external lactate concentrations. At very low lactate concentrations, a lactate gradient of 100 mV existed, which decreased to about 40 mV at 50 mM external lactate. As a consequence, the proton-lactate stoichiometry decreased with increasing external concentrations of protons and lactate at pH 7.0 from 1 mM lactate to 1.1 at 50 mM lactate and at pH 5.5 from 1.4 at l mM lactate to 0.7 at 50 mM lactate. The data presented in this paper suggest that a decrease in external pH and an increase in external lactate concentration both result in lower proton-lactate stoichiometry values and therefore in a decrease of the generation of metabolic energy by the end product efflux process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. The effects of partial and selective reduction in the components of the proton-motive force on lactose uptake in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):583–589. doi: 10.1042/bj2000583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Shechter E. Lactose transport in Escherichia coli cells. Dependence of kinetic parameters on the transmembrane electrical potential difference. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Pavlasová E., Baarda J. R. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The lac carrier protein in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02000610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Blanchard A. G., Metzger W. C. Proton motive force during growth of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.128-134.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Effects of aerobiosis and nitrogen source on the proton motive force in growing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):377–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.377-384.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Stoichiometry of the H+-ATPase of growing and resting, aerobic Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5534–5538. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Obligatory coupling between proton entry and the synthesis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.564-575.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in energy transduction: a logical development of biochemical knowledge. J Bioenerg. 1972 May;3(1):5–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01515993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. J., Booth I. R., Hamilton W. A. Quantitative analysis of proton-linked transport systems. Glutamate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):441–449. doi: 10.1042/bj1840441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay K., Lolkema J., Hellingwerf K. J., Kaptein R., Konings W. N. Quantitative agreement between the values for the light-induced delta pH in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides measured with automated follow-dialysis and 31P NMR. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Sonnenberg A. S., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient in Streptococcus cremoris by lactate efflux. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D., Hansen U. P., Gradmann D., Slayman C. L. Generalized kinetic analysis of ion-driven cotransport systems: a unified interpretation of selective ionic effects on Michaelis parameters. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(2):123–152. doi: 10.1007/BF01925862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson S. J., Bendall M. R., Egan A. F., Vink R., Rogers P. J. High-field phosphorus NMR studies of the stoichiometry of the lactate/proton carrier in Streptococcus faecalis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by lactate efflux in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therisod H., Ghazi A., Houssin C., Shechter E. Lactose transport in Escherichia coli cells. Evidence in favor of a permease-catalyzed efflux of lactose without protons. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80889-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Electrochemical proton gradient and lactate concentration gradient in Streptococcus cremoris cells grown in batch culture. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.682-686.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


