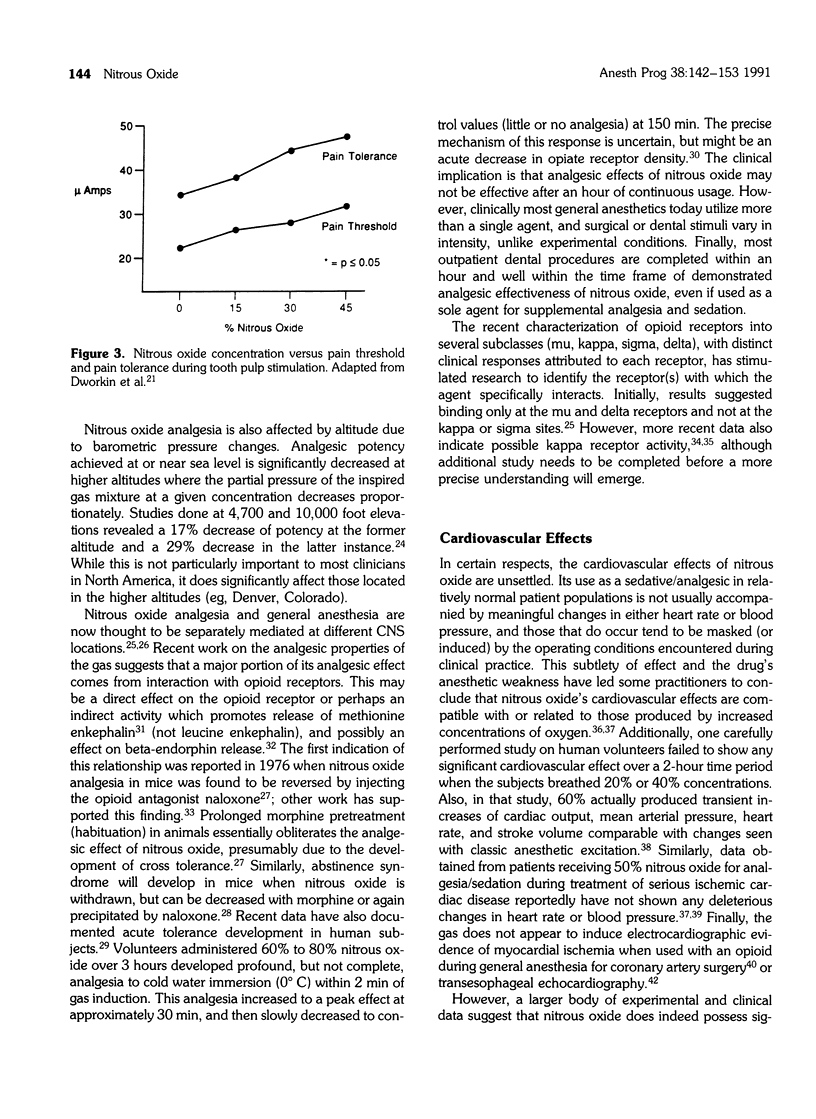
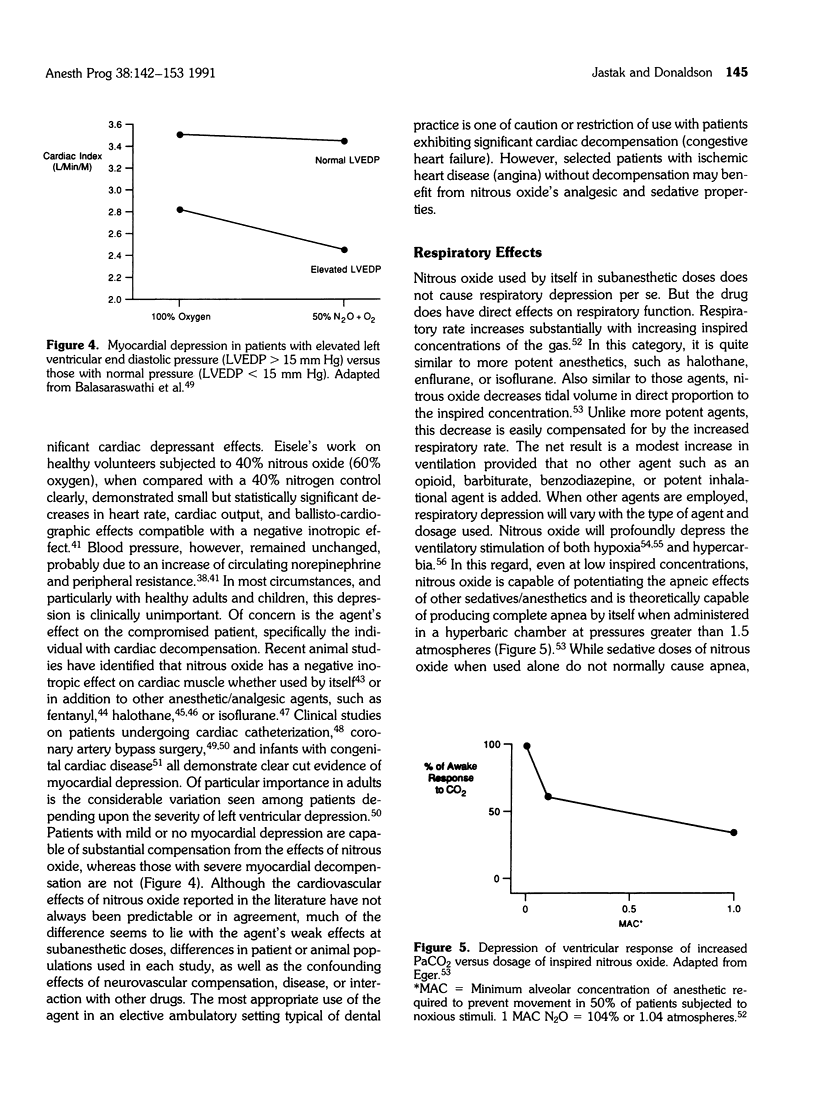
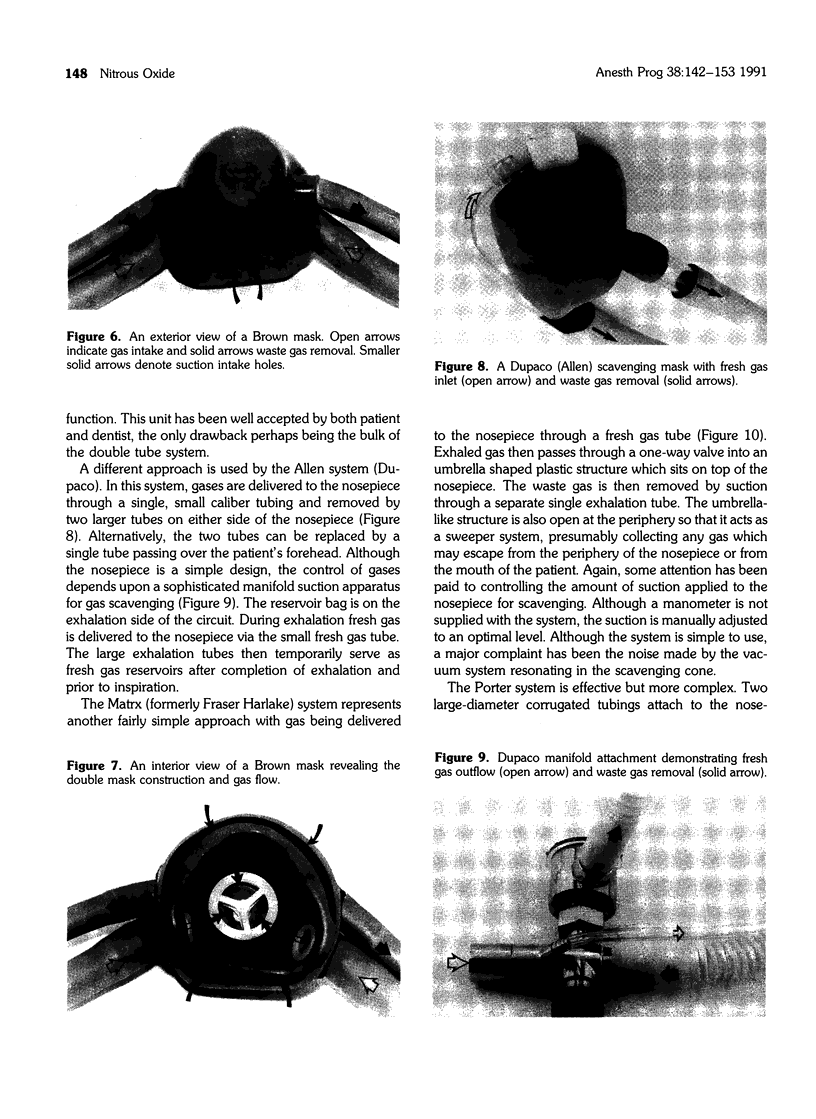
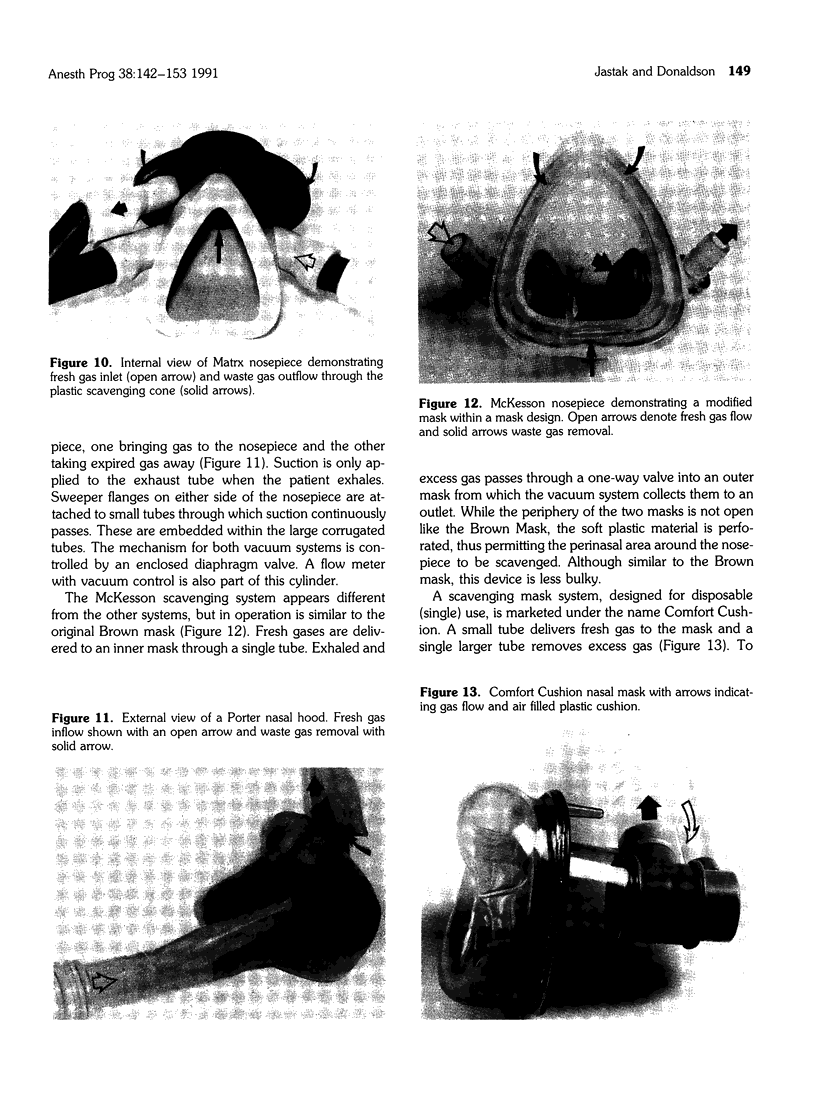
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen W. A. Nitrous oxide in the surgery: pollution and scavenging. Some clinical experiences. Br Dent J. 1985 Oct 5;159(7):222–230. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4805685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amess J. A., Burman J. F., Rees G. M., Nancekievill D. G., Mollin D. L. Megaloblastic haemopoiesis in patients receiving nitrous oxide. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):339–342. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92941-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askrog V., Harvald B. Teratogen effekt af inhalationsanaestetika. Nord Med. 1970 Apr 16;83(16):498–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasaraswathi K., Kumar P., Rao T. L., El-Etr A. A. Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) as an index for nitrous oxide use during coronary artery surgery. Anesthesiology. 1981 Dec;55(6):708–709. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198155060-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskett P. J. The use of entonox in the ambulance service. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Jan;65(1):7–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. F., Salmon P. R., Branch R. A., Baskett P. J., Read A. E. The use of inhalational analgesia during fibre-optic colonoscopy. Anaesthesia. 1971 Jul;26(3):294–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1971.tb04787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Ngai S. H., Finck A. D. Nitrous oxide "analgesia": resemblance to opiate action. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):967–968. doi: 10.1126/science.982058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelkhagen H., Sundström F., Angmar-Månsson B., Rydén H. Early detection of enamel caries by the luminescence excited by visible laser light. Swed Dent J. 1982;6(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky J. B., Baden J. M., Serra M., Kundomal Y. Nitrous oxide inactivates methionine synthetase activity in rat testis. Anesthesiology. 1984 Jul;61(1):66–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L., Eide K. A., Linde H. W., Eckenhoff J. E. Causes of death among anesthesiologists: a 20-year survey. Anesthesiology. 1968 May-Jun;29(3):565–569. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196805000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L., Eide K. A., Smith N. J., Seltzer F., Dykes M. H. A prospective survey of anesthesiologist mortality, 1967-1971. Anesthesiology. 1974 Jul;41(1):71–74. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197407000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussard D. A., Stoelting R. K., Peterson C., Ishaq M. Fetal changes in hamsters anesthetized with nitrous oxide and halothane. Anesthesiology. 1974 Sep;41(3):275–278. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197409000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. K., Prakash O., Rulf E. N., Cahalan M. T., Mayala A. P., Lurz F. C., Rosseel P., Lachitjaran E., Siphanto K., Gussenhoven E. J. Addition of nitrous oxide to fentanyl anesthesia does not induce myocardial ischemia in patients with ischemic heart disease. Anesthesiology. 1987 Dec;67(6):925–929. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198712000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman W. P., Arrowood J. G., Beecher H. K. THE ANALGETIC EFFECTS OF LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF NITROUS OXIDE COMPARED IN MAN WITH MORPHINE SULPHATE. J Clin Invest. 1943 Nov;22(6):871–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI101461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen R. P., Robison R. A., Robinson D. F., Ploeger B. J., Leavitt R. W., Bodily H. L. Antimicrobial activity of environmental surface disinfectants in the absence and presence of bioburden. J Am Dent Assoc. 1989 Oct;119(4):493–505. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8177(89)94006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. N., Brown B. W., Jr, Bruce D. L., Cascorbi H. F., Corbett T. H., Jones T. W., Whitcher C. E. A survey of anesthetic health hazards among dentists. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975 Jun;90(6):1291–1296. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1975.0270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. N., Gift H. C., Brown B. W., Greenfield W., Wu M. L., Jones T. W., Whitcher C. E., Driscoll E. J., Brodsky J. B. Occupational disease in dentistry and chronic exposure to trace anesthetic gases. J Am Dent Assoc. 1980 Jul;101(1):21–31. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1980.0345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H. Anesthetics as a cause of abortion. Fertil Steril. 1972 Nov;23(11):866–869. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)39319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H., Cornell R. G., Lieding K., Endres J. L. Incidence of cancer among Michigan nurse-anesthetists. Anesthesiology. 1973 Mar;38(3):260–263. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197303000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon R., Lumb M., Perry J., Chanarin I., Minty B., Halsey M., Nunn J. Inactivation of methionine synthase by nitrous oxide. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D., Allen G. D. The mechanisms of nitrous oxide scavenging devices. J Can Dent Assoc. 1989 Jul;55(7):531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D., Grabi J. The efficiency of nitrous oxide scavenging devices in dental offices. J Can Dent Assoc. 1989 Jul;55(7):541–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D., Orr J. A comparison of the effectiveness of nitrous oxide scavenging devices. J Can Dent Assoc. 1989 Jul;55(7):535–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll E. J. Dental anesthesiology: its history and continuing evolution. Niels Bjorn Jorgensen 2nd memorial lecture. Anesth Prog. 1978 Sep-Oct;25(5):143–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin S. F., Chen A. C., LeResche L., Clark D. W. Cognitive reversal of expected nitrous oxide analgesia for acute pain. Anesth Analg. 1983 Dec;62(12):1073–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin S. F., Chen A. C., Schubert M. M., Clark D. W. Analgesic effects of nitrous oxide with controlled painful stimuli. J Am Dent Assoc. 1983 Oct;107(4):581–585. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1983.0303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin S. F., Chen A. C., Schubert M. M., Clark D. W. Cognitive modification of pain: information in combination with N2O. Pain. 1984 Aug;19(4):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKENHOFF J. E., HELRICH M. The effect of narcotics, thiopental and nitrous oxide upon respiration and respiratory response to hypercapnia. Anesthesiology. 1958 Mar-Apr;19(2):240–253. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195803000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson E. B., Reinarz J. A., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Nebulization equipment. A potential source of infection in gram-negative pneumonias. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Apr;111(4):357–360. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090070055004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele J. H., Reitan J. A., Massumi R. A., Zelis R. F., Miller R. R. Myocardial performance and N2O analgesia in coronary-artery disease. Anesthesiology. 1976 Jan;44(1):16–20. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197601000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele J. H., Smith N. T. Cardiovascular effects of 40 percent nitrous oxide in man. Anesth Analg. 1972 Nov-Dec;51(6):956–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett G. B., Allen G. D. Simultaneous evaluation of cardiorespiratory and analgesic effects of nitrous oxide-oxygen inhalation analgesia. J Am Dent Assoc. 1971 Jul;83(1):129–133. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1971.0281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer J., Taylor P. M., Gezon H. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic traced to delivery-room resuscitators. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 4;276(18):991–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705042761801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink B. R., Shepard T. H., Blandau R. J. Teratogenic activity of nitrous oxide. Nature. 1967 Apr 8;214(5084):146–148. doi: 10.1038/214146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillman M. A. Analgesic (sub anesthetic) nitrous oxide interacts with the endogenous opioid system: a review of the evidence. Life Sci. 1986 Oct 6;39(14):1209–1221. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene N. M. A consideration of factors in the discovery of anesthesia and their effects on its development. Anesthesiology. 1971 Nov;35(5):515–522. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197111000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey P. R., Hansen D. D., Strafford M., Thompson J. E., Jonas R. E., Mayer J. E. Pulmonary and systemic hemodynamic effects of nitrous oxide in infants with normal and elevated pulmonary vascular resistance. Anesthesiology. 1986 Oct;65(4):374–378. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman K. M., Saloojee Y., Brett I. I., Cole P. V. Nitrous oxide concentrations in the dental surgery, Atmospheric and blood concentrations of personnel. Anaesthesia. 1981 Mar;36(3):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1981.tb10197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbein T. F., Eger E. I., 2nd, Winter P. M., Smith G., Wetstone D., Smith K. H. The minimum alveolar concentration of nitrous oxide in man. Anesth Analg. 1982 Jul;61(7):553–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. M., Yagiela J. A. Bacterial contamination and transmission by nitrous oxide sedation apparatus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977 Sep;44(3):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(77)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS J. R., EDGAR W. M. STERILISATION OF ANAESTHETIC EQUIPMENT. Anaesthesia. 1964 Apr;19:177–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1964.tb00365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPH J. M. Disease transmission by inefficiently sanitized anesthetizing apparatus. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Jul 26;149(13):1196–1198. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.02930300022006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. F., Manson E. D., Dennett J. E. Nitrous oxide analgesia and altitude. Anaesthesia. 1982 Mar;37(3):285–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1982.tb01100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jastak J. T. Issues of pain and anxiety control training and continuing education. J Dent Educ. 1989 May-Jun;53(5-6):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jastak J. T. Nitrous oxide in dental practice. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 1989 Summer;27(2):92–97. doi: 10.1097/00004311-198902720-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jastak J. T., Paravecchio R. An analysis of 1,331 sedations using inhalation, intravenous, or other techniques. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975 Dec;91(6):1242–1249. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1975.0579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura R., Stanley T. H., English J. B., Hill G. E., Liu W. S., Webster L. R. Cardiovascular responses to nitrous oxide exposure for two hours in man. Anesth Analg. 1980 Feb;59(2):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr F., Irving J. B., Ewing D. J., Kirby B. J. Nitrous-oxide analgesia in myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):63–66. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr F., Irving J. B., Ewing D. J., Kirby B. J. Nitrous-oxide analgesia in myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):63–66. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knill R. L., Clement J. L. Variable effects of anaesthetics on the ventilatory response to hypoxaemia in man. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1982 Mar;29(2):93–99. doi: 10.1007/BF03007983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Osborne M. L., Kolhouse J. F., Binder M. J., Podell E. R., Utley C. S., Abrams R. S., Allen R. H. Nitrous oxide has multiple deleterious effects on cobalamin metabolism and causes decreases in activities of both mammalian cobalamin-dependent enzymes in rats. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1270–1283. doi: 10.1172/JCI110155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke B. J., Kelman A. D., Shah N. K., Balogh K., Handler A. H. Testicular reaction to prolonged exposure to nitrous oxide. Anesthesiology. 1976 Feb;44(2):104–113. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN H. C., HENRIKSEN E., NEUKIRCH F., KRISTENSEN H. S. Treatment of tetanus; severe bone-marrow depression after prolonged nitrous-oxide anaesthesia. Lancet. 1956 Apr 28;270(6922):527–530. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90593-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B. Myeloneuropathy after prolonged exposure to nitrous oxide. Lancet. 1978 Dec 9;2(8102):1227–1230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone B. J., Philbin D. M., Lehot J. J., Foëx P., Ryder W. A. Gradual or abrupt nitrous oxide administration in a canine model of critical coronary stenosis induces regional myocardial dysfunction that is worsened by halothane. Anesth Analg. 1988 Sep;67(9):814–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson H. J., Dyke G., Melling J., Gough M. The effect of naloxone and morphine on convulsions in mice following withdrawal from nitrous oxide. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1983 Jan;30(1):28–31. doi: 10.1007/BF03007713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milocco I., Schlossman D., William-Olsson G., Appelgren L. K. Fentanyl-droperidol-nitrous oxide anaesthesia in patients with ischaemic heart disease and various degrees of left ventricular functional impairment. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985 Oct;29(7):683–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1985.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobbs I. G., Parbrook G. D., McKenzie J. The effect of various concentrations of nitrous oxide on the 24-hour explanted chick embryo. Br J Anaesth. 1966 Nov;38(11):866–870. doi: 10.1093/bja/38.11.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Mattson M., Newman A. H., Rice K. C., Skolnick P. Stereospecific reversal of nitrous oxide analgesia by naloxone. Life Sci. 1989;44(11):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motomura S., Kissin I., Aultman D. F., Reves J. G. Effects of fentanyl and nitrous oxide on contractility of blood-perfused papillary muscle of the dog. Anesth Analg. 1984 Jan;63(1):47–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan H. J. Nitrous oxide worsens myocardial ischemia in isoflurane-anesthetized dogs. Anesthesiology. 1988 Mar;68(3):407–415. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198803000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai S. H., Finck A. D. Prolonged exposure to nitrous oxide decreased opiate receptor density in rat brainstem. Anesthesiology. 1982 Jul;57(1):26–30. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198207000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn J. F., Sharer N., Royston D., Watts R. W., Purkiss P., Worth H. G. Serum methionine and hepatic enzyme activity in anaesthetists exposed to nitrous oxide. Br J Anaesth. 1982 Jun;54(6):593–597. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.6.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary U., Puglia C., Friehling T. D., Kowey P. R. Nitrous oxide anesthesia in patients with ischemic chest discomfort: effect on beta-endorphins. J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;27(12):957–961. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1987.tb05596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Occupational disease among operating room personnel: a national study. Report of an Ad Hoc Committee on the Effect of Trace Anesthetics on the Health of Operating Room Personnel, American Society of Anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology. 1974 Oct;41(4):321–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds J. W., Kisch A. L., Eberle B. J., Wilson J. N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory tract infection acquired from a contaminated anesthesia machine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Apr;105(4):628–632. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.4.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds J. W., Kisch A. L., Eberle B. J., Wilson J. N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory tract infection acquired from a contaminated anesthesia machine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Apr;105(4):628–632. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.4.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ori C., Ford-Rice F., London E. D. Effects of nitrous oxide and halothane on mu and kappa opioid receptors in guinea-pig brain. Anesthesiology. 1989 Mar;70(3):541–544. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198903000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARBROOK G. D., REES G. A., ROBERTSON G. S. RELIEF OF POST-OPERATIVE PAIN: COMPARISON OF A 25 PER CENT NITROUS-OXIDE AND OXYGEN MIXTURE WITH MORPHINE. Br Med J. 1964 Aug 22;2(5407):480–482. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5407.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parbrook G. D. The levels of nitrous oxide analgesia. Br J Anaesth. 1967 Dec;39(12):974–982. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.12.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope W. D., Halsey M. J., Lansdown A. B., Simmonds A., Bateman P. E. Fetotoxicity in rats following chronic exposure to halothane, nitrous oxide, or methoxyflurane. Anesthesiology. 1978 Jan;48(1):11–16. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197801000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price H. L. Myocardial depression by nitrous oxide and its reversal by Ca++. Anesthesiology. 1976 Mar;44(3):211–215. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197603000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the Anaesthetic Research Society. Cardiff meeting, July 2, 1982. Abstracts. Br J Anaesth. 1982 Oct;54(10):1129–1141. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.10.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Graczak L. M. Influence of narcotic antagonist drugs upon nitrous oxide analgesia in mice. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 2;440(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Kouchich F. J., Tseng L. F. Does nitrous oxide induce release of brain opioid peptides? Pharmacology. 1985;30(2):95–99. doi: 10.1159/000138056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay J. G., Arvieux C. C., Foëx P., Philbin D. M., Jeavons P., Ryder W. A., Jones L. A. Regional and global myocardial function in the dog when nitrous oxide is added to halothane in the presence of critical coronary artery constriction. Anesth Analg. 1986 May;65(5):431–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran R. S., Bates M. L., Strausburg B. J. Epinephrine and duration of spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1982 Apr;61(4):395–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer M. D., Bulard R. A. Microwave sterilization. J Am Dent Assoc. 1985 Feb;110(2):194–198. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1985.0250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupreht J., Dworacek B., Bonke B., Dzoljic M. R., van Eijndhoven J. H., de Vlieger M. Tolerance to nitrous oxide in volunteers. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985 Aug;29(6):635–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1985.tb02271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A. M., Braude B. M., Cleaton-Jones P. E., Moyes D. G., Mallett J. Nitrous oxide sedation in dentistry. A comparison between Rotameter settings, pharyngeal concentrations and blood levels of nitrous oxide. Anaesthesia. 1984 Mar;39(3):236–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb07233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavik J. R., LaMantia K. R., Kopriva C. J., Prokop E., Ezekowitz M. D., Barash P. G. Does nitrous oxide cause regional wall motion abnormalities in patients with coronary artery disease? An evaluation by two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. Anesth Analg. 1988 Jul;67(7):695–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Gaub M. L., Moya F. Teratogenic effects of anesthetic agents: nitrous oxide. Anesth Analg. 1965 Nov-Dec;44(6):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. D., Paris P. M., Stoy W. A., Cannon G. Patient-controlled inhalational analgesia in prehospital care: a study of side-effects and feasibility. Crit Care Med. 1983 Nov;11(11):851–855. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198311000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney B., Bingham R. M., Amos R. J., Petty A. C., Cole P. V. Toxicity of bone marrow in dentists exposed to nitrous oxide. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Aug 31;291(6495):567–569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6495.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thal E. R., Montgomery S. J., Atkins J. M., Roberts B. G. Self-administered analgesia with nitrous oxide. Adjunctive aid for emergency medical care systems. JAMA. 1979 Nov 30;242(22):2418–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. L., Lown B. Nitrous oxide as an analgesic in acute myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1976 Mar 1;235(9):924–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. A., Fleming J. S., Goldberg A. D., Baird D. Cardiovascular effects of 50 per cent nitrous oxide and 50 per cent oxygen mixture. Anaesthesia. 1973 Sep;28(5):484–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1973.tb00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinne J. E., Gordon A. M., Bain W. H., Mackey W. A. Cross-infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a hazard of intensive surgery. Br Med J. 1967 Nov 11;4(5575):313–315. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5575.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman A. I. Usloviia truda v operatisionnykh i ikh vliianie na zdorov'e anesteziologov. Eksp Khir Anesteziol. 1967 May-Jun;12(3):44–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira E., Cleaton-Jones P. E., Austin J., Fatti P. L. Intermittent exposure of gravid rats to 1% nitrous oxide and the effect on the postnatal growth of their offspring. S Afr Med J. 1978 Jan 21;53(3):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter C. W. Cross-infection and the anesthesiologist. Twelfth annual Baxter-Travenol Lecture. Anesth Analg. 1974 Sep-Oct;53(5):631–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcher C. E., Zimmerman D. C., Tonn E. M., Piziali R. L. Control of occupational exposure to nitrous oxide in the dental operatory. J Am Dent Assoc. 1977 Oct;95(4):763–776. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1977.0493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yacoub O., Doell D., Kryger M. H., Anthonisen N. R. Depression of hypoxic ventilatory response by nitrous oxide. Anesthesiology. 1976 Oct;45(4):385–389. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197610000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. K., Graves D. C., Rohrer M. D., Bulard R. A. Microwave sterilization of nitrous oxide nasal hoods contaminated with virus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985 Dec;60(6):581–585. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(85)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]