Abstract
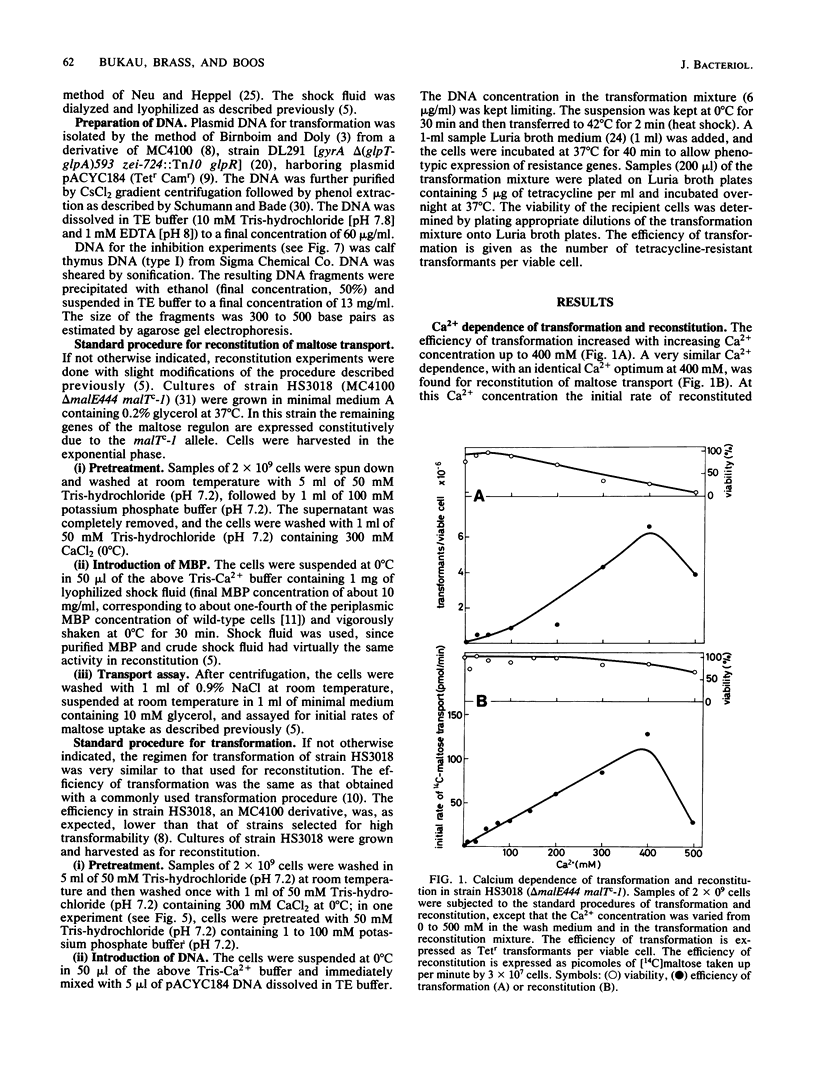
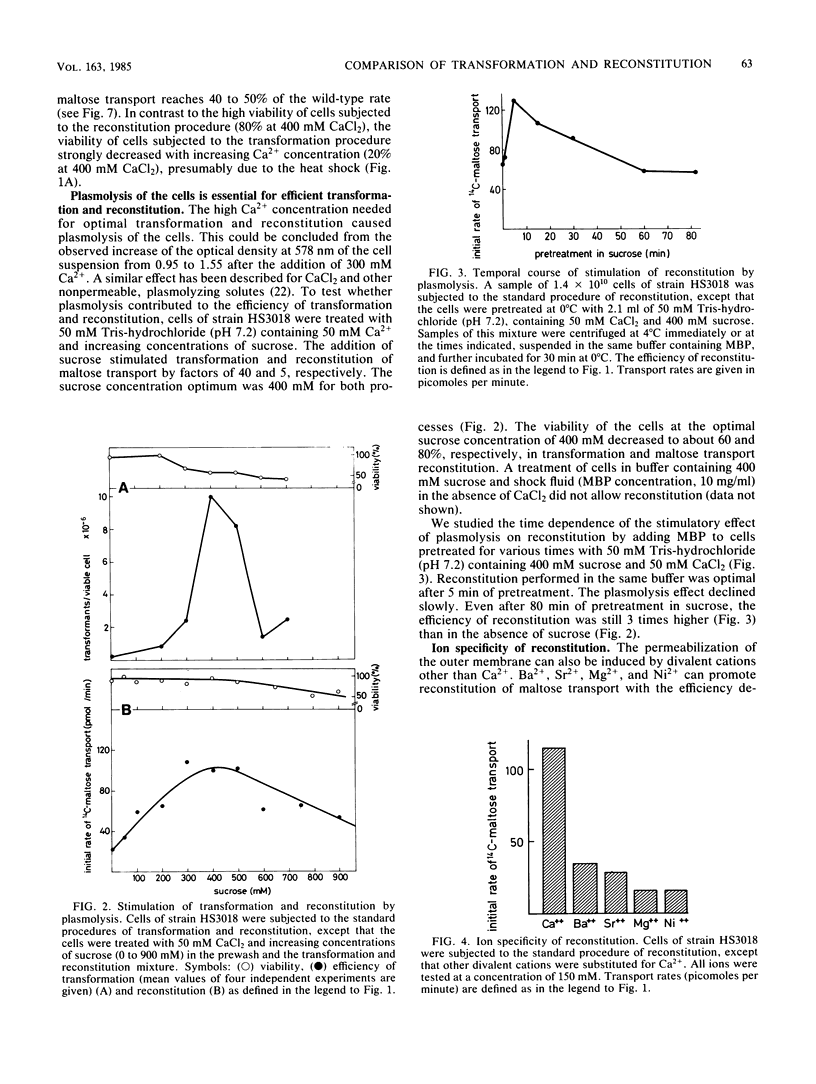
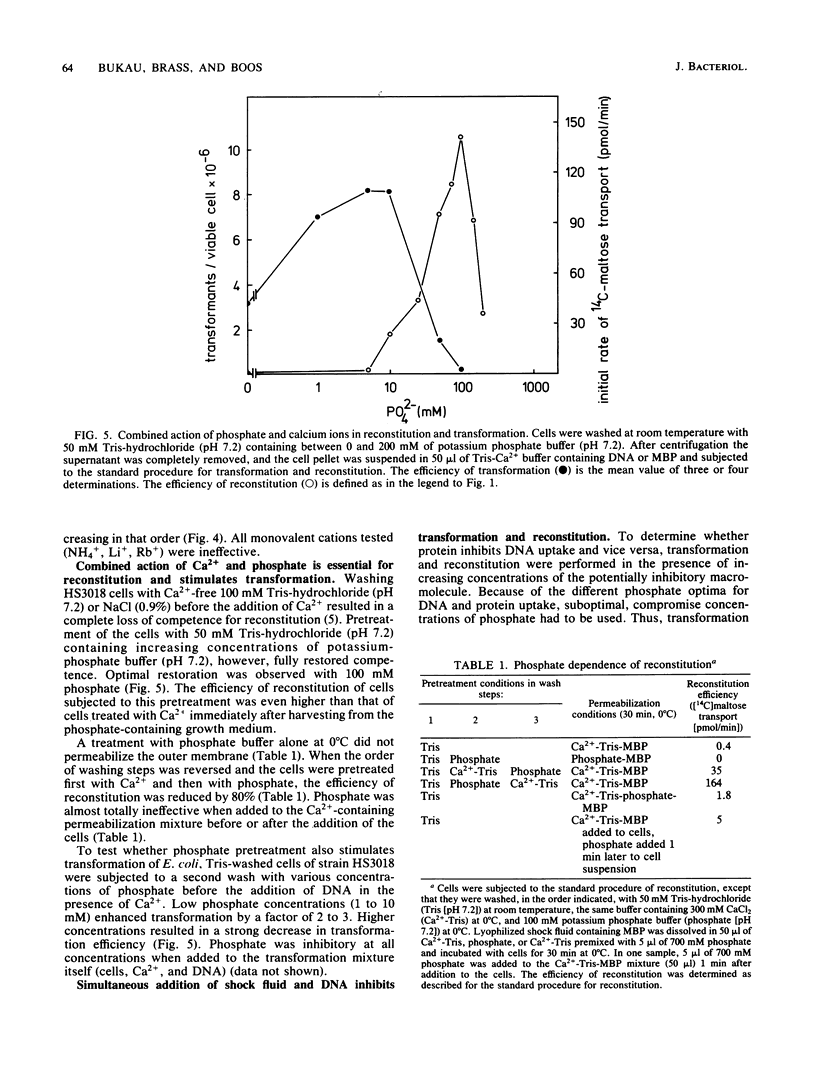
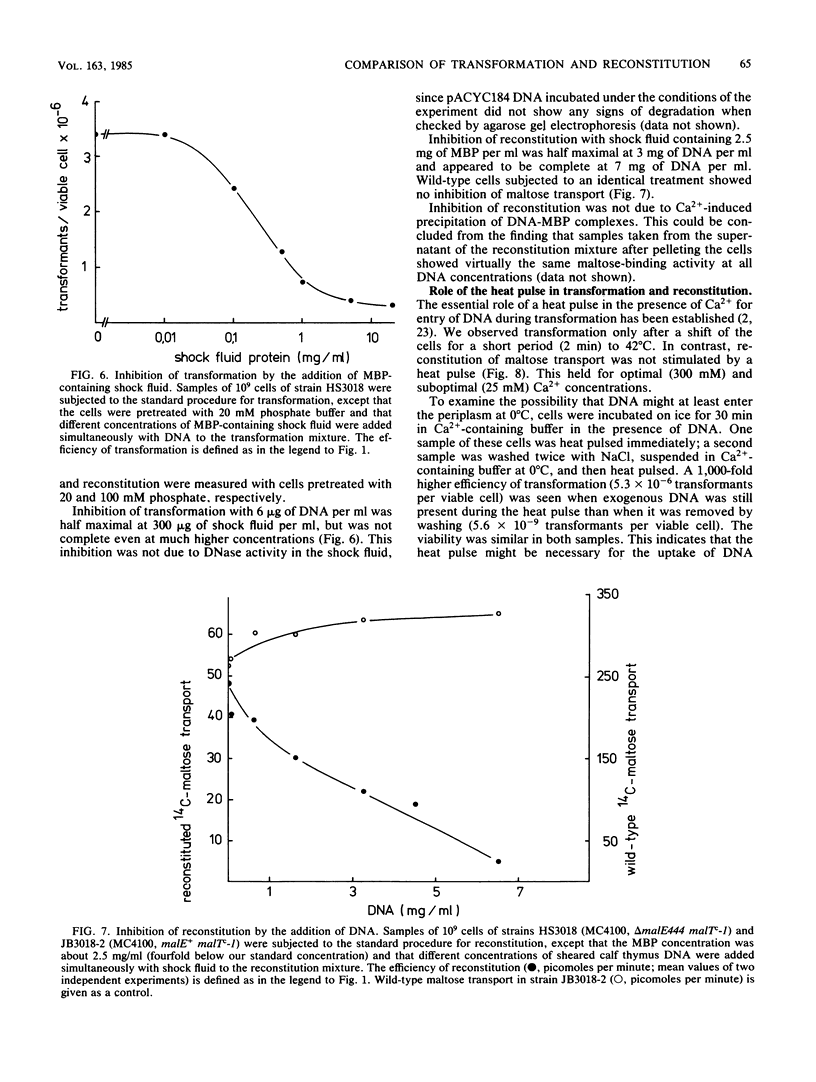
Ca2+ treatment renders the outer membrane of Escherichia coli reversibly permeable for macromolecules. We investigated whether Ca2+-induced uptake of exogenous protein into the periplasm occurs by mechanisms similar to Ca2+-induced uptake of DNA into the cytoplasm during transformation. Protein import through the outer membrane was monitored by measuring reconstitution of maltose transport after the addition of shock fluid containing maltose-binding protein. DNA import through the outer and inner membrane was measured by determining the efficiency of transformation with plasmid DNA. Both processes were stimulated by increasing Ca2+ concentrations up to 400 mM. Plasmolysis was essential for a high efficiency; reconstitution and transformation could be stimulated 5- and 40-fold, respectively, by a high concentration of sucrose (400 mM) in cells incubated with a suboptimal Ca2+ concentration (50 mM). The same divalent cations that promote import of DNA (Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Mg2+, and Ni2+) also induced import of protein. Ca2+ alone was found to be inefficient in promoting reconstitution; successive treatment with phosphate and Ca2+ ions was essential. Transformation also was observed in the absence of phosphate, but could be stimulated by pretreatment with phosphate. The optimal phosphate concentrations were 100 mM and 1 to 10 mM for reconstitution and transformation, respectively. Heat shock, in which the cells are rapidly transferred from 0 to 42 degrees C, affected the two processes differently. Incubation of cells at 0 degrees C in Ca2+ alone allows rapid entry of protein, but not of DNA. Transformation was observed only when exogenous DNA was still present during the heat shock. Shock fluid containing maltose-binding protein inhibited transformation (with 6 microgram of DNA per ml, half-maximal inhibition occurred at around 300 microgram of shock fluid per ml). DNA inhibited reconstitution (with 5 microgram of shock fluid per ml, half-maximal inhibition occurred at around 3 mg of DNA per ml).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmans H. E., van Die I. M., Hoekstra W. P. Transformation in Escherichia coli: stages in the process. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Boos W., Hengge R. Reconstitution of maltose transport in malB mutants of Escherichia coli through calcium-induced disruptions of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.10-17.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Ehmann U., Bukau B. Reconstitution of maltose transport in Escherichia coli: conditions affecting import of maltose-binding protein into the periplasm of calcium-treated cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):97–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.97-106.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Manson M. D. Reconstitution of maltose chemotaxis in Escherichia coli by addition of maltose-binding protein to calcium-treated cells of maltose regulon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):881–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.881-890.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M., Feigenson G. W. Influence of metal ions on the phase properties of phosphatidic acid in combination with natural and synthetic phosphatidylcholines: an X-ray diffraction study using synchrotron radiation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):323–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel I., Kolb V., Boos W. Pole cap formation in Escherichia coli following induction of the maltose-binding protein. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00415731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraley R., Wilschut J., Düzgüneş N., Smith C., Papahadjopoulos D. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: role of phosphate in promoting calcium ion induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6021–6029. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Alterations in outer membrane permeability. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Boos W. Maltose and lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Examples of two different types of concentrative transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):443–478. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Wilschut J., Scherphof G. Kinetics of calcium phosphate-induced fusion of human erythrocyte ghosts monitored by mixing of aqueous contents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 13;732(1):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Jezierska A., Braun-Breton C. lamB mutations in E. coli K12: growth of lambda host range mutants and effect of nonsense suppressors. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00269595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludtke D., Larson T. J., Beck C., Boos W. Only one gene is required for the glpT-dependent transport of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):540–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00337962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J., KUCZYNSKI M., SCHATZBERG G., AVI-DOR Y. Turbidity changes in bacterial suspensions in relation to osmotic pressure. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Ito T. Calcium-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine--phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):881–887. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Domaradsky I. V. Effect of metabolic inhibitors on entry of exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid into Ca2+-treated Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.435-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann W., Bade E. G. In vitro constructed plasmids containing both ends of bacteriophage Mu DNA express phage functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00267550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A. Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Role of the periplasmic maltose-binding protein and evidence for a substrate recognition site in the cytoplasmic membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5455–5461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Danner D. B., Deich R. A. Genetic transformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:41–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to viral nucleic acid. 8. Idiosyncrasy of Ca2+-dependent competence for DNA. J Biochem. 1974 Apr;75(4):895–904. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to viral nucleic acid. V. Competence of calcium-treated cells. J Biochem. 1972 Oct;72(4):973–979. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A., Brown M. G., Perkins H. R., Saunders J. R., Humphreys G. O. Transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid: calcium-induced binding of deoxyribonucleic acid to whole cells and to isolated membrane fractions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):780–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.780-787.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Die I. M., Bergmans H. E., Hoekstra W. P. Transformation in Escherichia coli: studies on the role of the heat shock in induction of competence. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):663–670. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


