Abstract
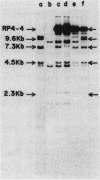
A 200-megadalton plasmid was mobilized from Rhizobium japonicum USDA 191 to other Rhizobium strains either that cannot nodulate soybeans or that form Fix- nodules on certain cultivars. The symbiotic properties of the transconjugants indicate that both soybean specificity for nodulation and cultivar specificity for nitrogen fixation are plasmid encoded.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cutting J. A., Schulman H. M. The site of heme synthesis in soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):486–493. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90398-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Sym plasmid transfer to various symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium trifolii, R. leguminosarum, and R. meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1035–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1035-1045.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori J., Johnson D. A. Fast-Growing Rhizobium japonicum That Effectively Nodulates Several Commercial Glycine max L. Merrill Cultivars. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):234–235. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.234-235.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Bohlool B. B., Hu T. S., Weber D. F. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1631–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4540.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Russell P. R., Atherly A. G. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes and large plasmids of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):928–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.928-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. A., Cen Y. H., Chen H. C., Plazinski J., Ridge R., Rolfe B. G. Mobilization of a Sym plasmid from a fast-growing cowpea Rhizobium strain. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):483–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.483-487.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. A., Hau C. Y., Trinick M. J., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Heat curing of a sym plasmid in a fast-growing Rhizobium sp. that is able to nodulate legumes and the nonlegume Parasponia sp. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.527-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Casse-Delbart F., Dusha I., David M., Boucher C. Megaplasmids in the plant-associated bacteria Rhizobium meliloti and Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.402-406.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]