Abstract
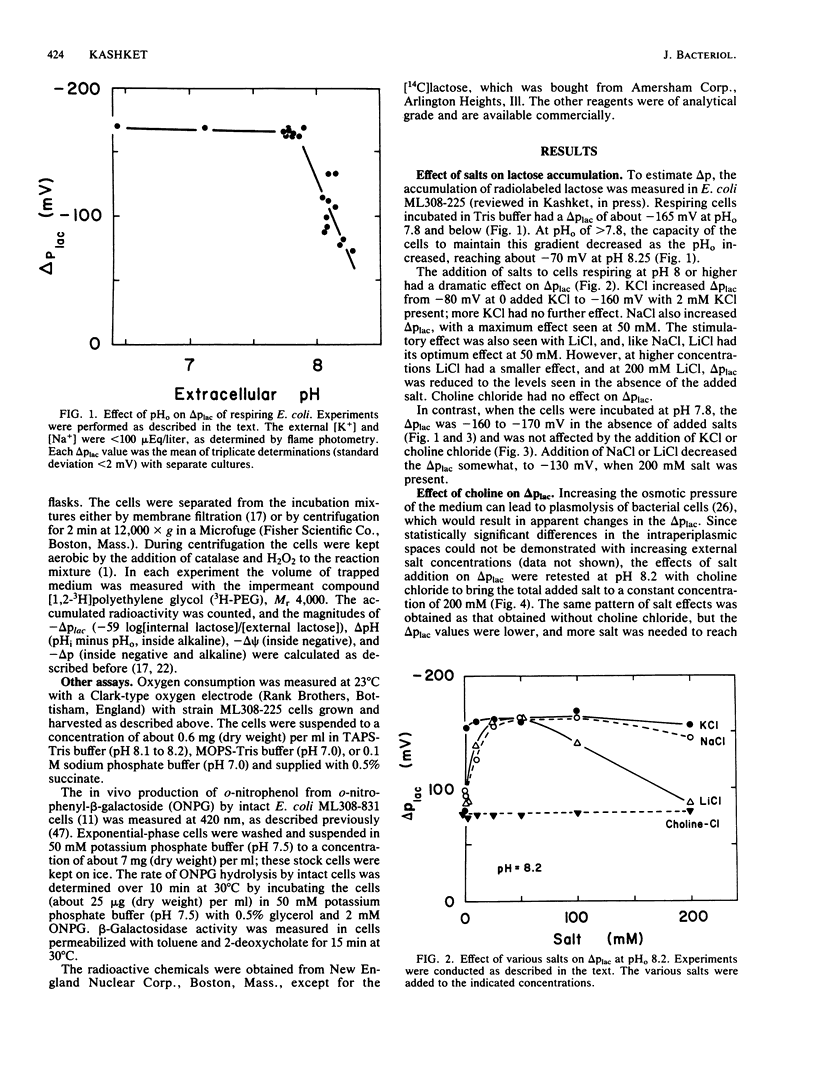
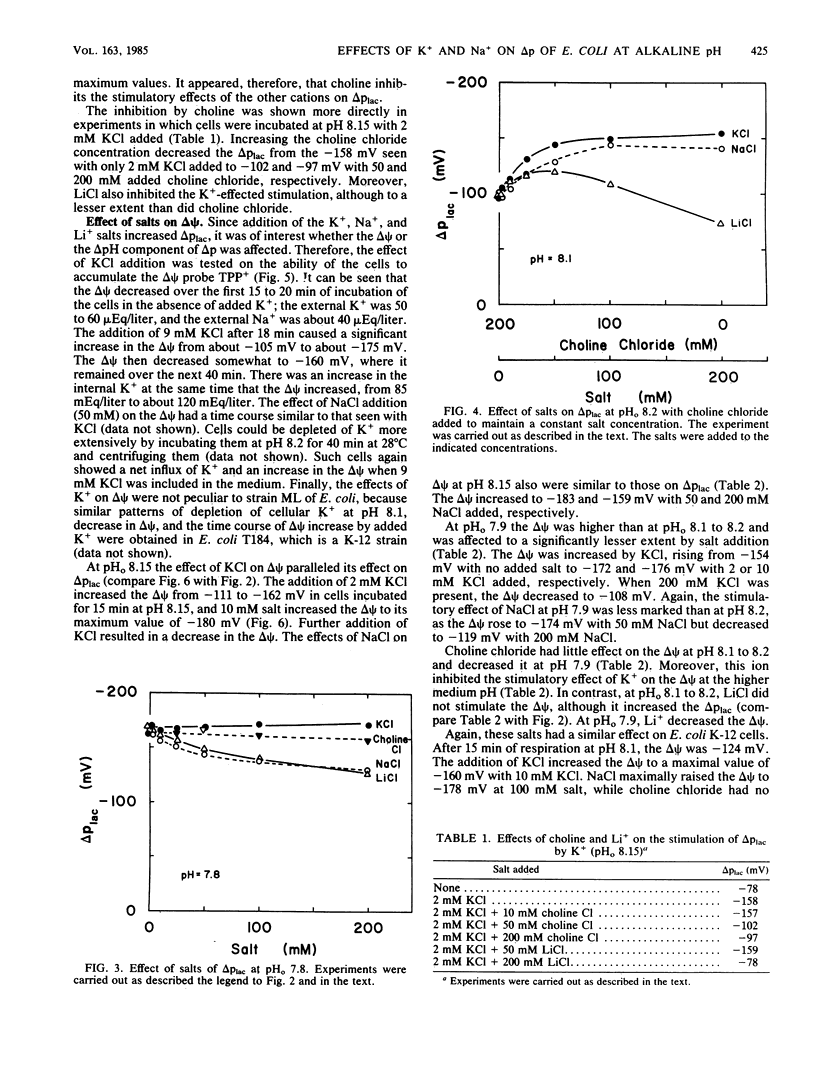
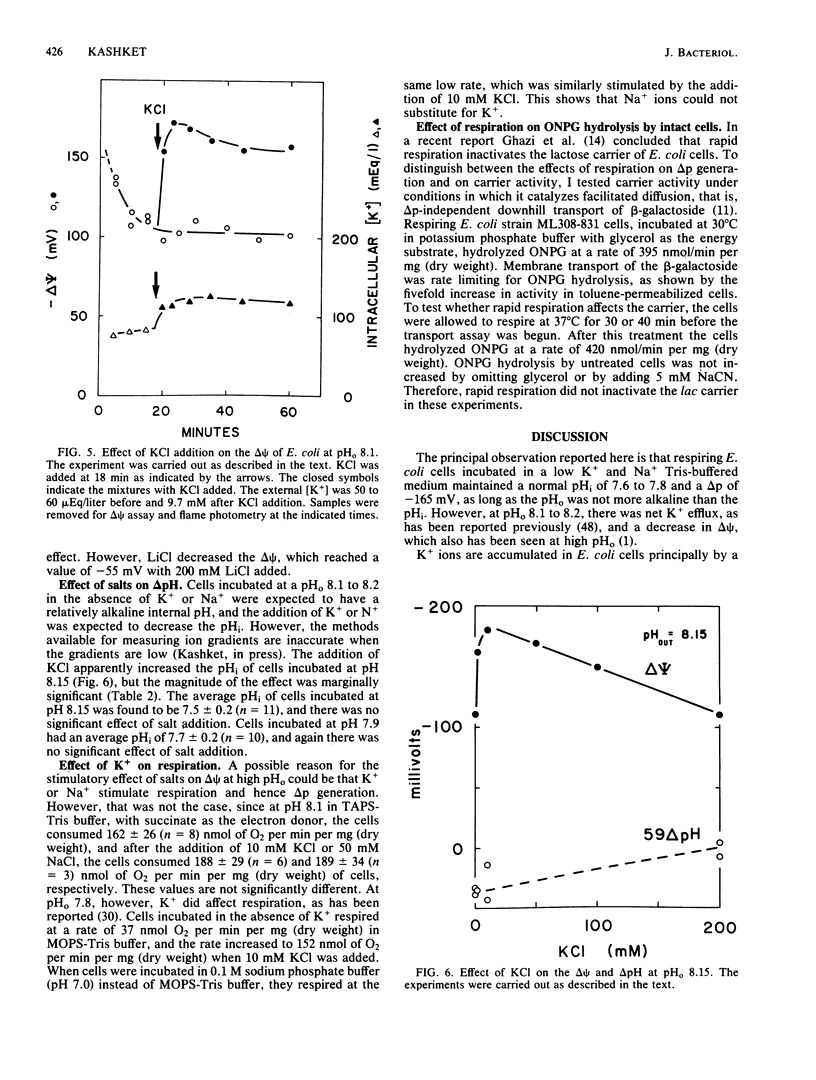
The role of K+ and Na+ in the maintenance of the proton motive force (delta p) was studied in Escherichia coli incubated in alkaline media. Cells respiring in Tris buffer (pH 7.8) that contained less than 100 microEq of K+ and Na+ per liter had a normal delta p of about -165 mV. At pH 8.2, however, the delta p was reduced significantly. The decrease in delta p at pH 8.2 was due to a marked decrease in the transmembrane potential (delta psi), while the internal pH remained at 7.5 to 7.7. When KCl or NaCl, but not LiCl or choline chloride, was added to the cells, the delta psi rose to the values seen at an external pH of 7.8. In addition, choline chloride inhibited the enhancement of delta psi by K+. None of the salts had a significant effect on the internal pH. The effects can be attributed to alterations of K+ or Na+ cycling in and out of the cells via the known K+ and Na+ transport systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. Quantitative measurements of the proton-motive force and its relation to steady state lactose accumulation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):573–581. doi: 10.1042/bj2000573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. The effect of beta-galactosides on the protonmotive force and growth of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2521–2529. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P. Membrane potential in a potassium transport-negative mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. The distribution of rubidium in the presence of valinomycin indicates a higher potential than that of the tetraphenylphosphonium cation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 15;681(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in escherichia coli: properties of the sodium/proton antiporter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Kroll R. G. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH (pH1) in bacteria and its relationship to metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):70–72. doi: 10.1042/bst0110070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borbolla M. G., Rosen B. P. Energetics of sodium efflux from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 15;229(1):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MONOD J. Bacterial permeases. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):169–194. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.169-194.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Therisod H., Shechter E. Comparison of lactose uptake in resting and energized Escherichia coli cells: high rates of respiration inactivate the lac carrier. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):92–103. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.92-103.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Stoichiometry of the H+-ATPase of growing and resting, aerobic Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5534–5538. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The relationship between intracellular pH, the pH gradient and potassium transport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):709–716. doi: 10.1042/bj2160709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tokuda H., Unemoto T. K+/H+ antiporter functions as a regulator of cytoplasmic pH in a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 3;776(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plack R. H., Jr, Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Absence of potassium/proton antiporter activity in a pH-sensitive mutant. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3824–3825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. IX. Regulation of K transport. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):283–295. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland G. C., Giffard P. M., Booth I. R. Genetic studies of the phs locus of Escherichia coli, a mutation causing pleiotropic lesions in metabolism and pH homeostasis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80794-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy buffering as the biological function of Na+/K+ gradient. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen E. N., Rosen B. P. Effects of sodium and lithium ions on the potassium ion transport systems of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1458–1462. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L. M., Bakker E. P., Booth I. R. Energy coupling to K+ uptake via the Trk system in Escherichia coli: the role of ATP. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):77–85. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Nakamura T., Unemoto T. Potassium ion is required for the generation of pH-dependent membrane potential and delta pH by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4198–4203. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Takeda K. Extrusion of sodium ions energized by respiration and glycolysis in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. H., Kashket E. R. Isolation and properties of thiogalactoside transacetylase-negative mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Moriyama Y., Futai M., Tsuchiya T. Uptake and extrusion of k+ regulated by extracellular pH in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):125–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Escherichia coli intracellular pH, membrane potential, and cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):246–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.246-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. The sodium/proton antiporter is part of the pH homeostasis mechanism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3687–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


