Abstract
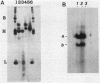
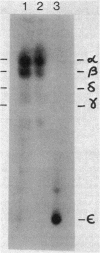
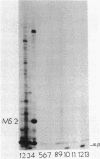
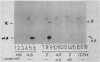
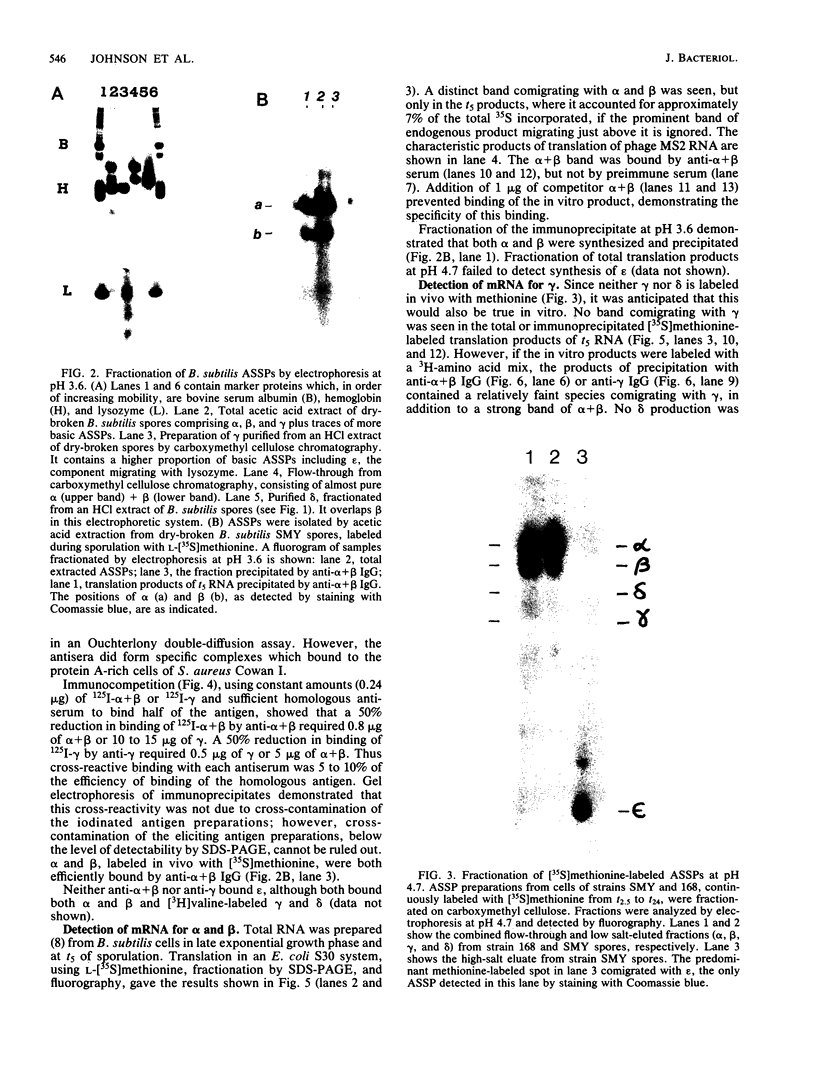
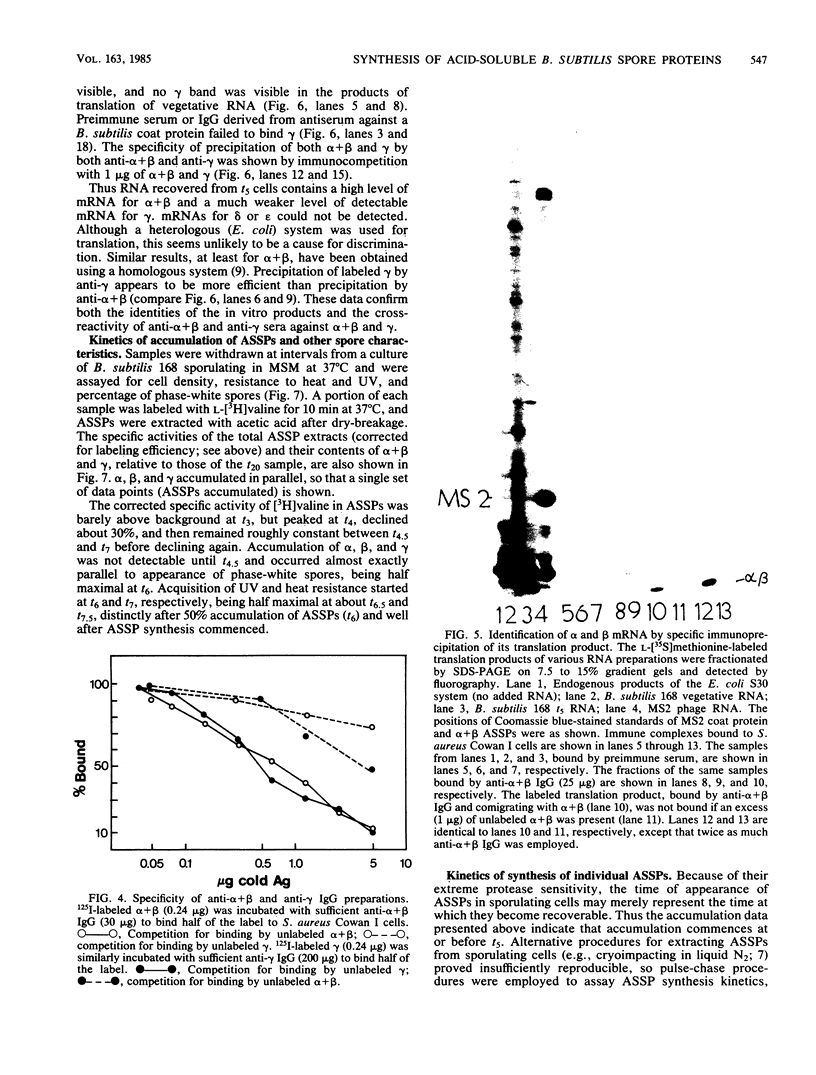
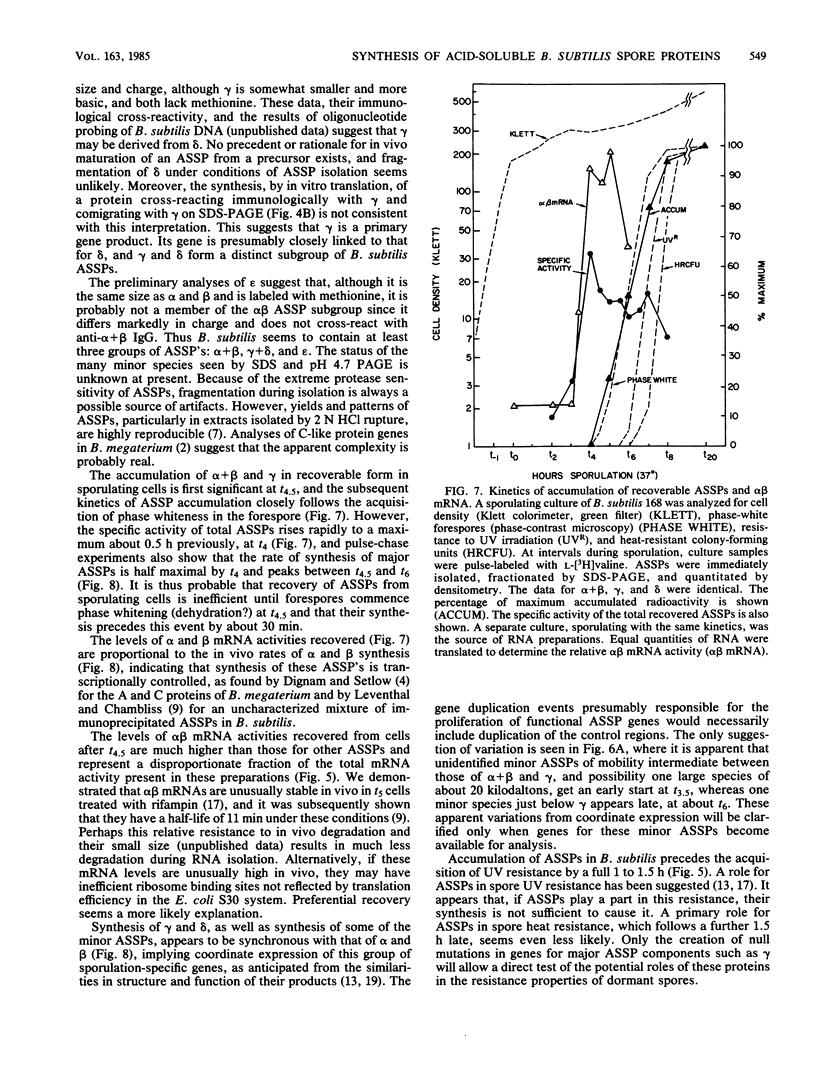
The major acid-soluble spore proteins (ASSPs) isolated from mature spores of Bacillus subtilis are designated alpha, beta, and gamma (about 60, 60, and 100 amino acids in length, respectively). Alpha and beta are very similar, and gamma is very similar to a less predominant ASSP called delta (about 115 amino acids). A minor and very basic ASSP called epsilon is the same size as alpha and beta but is unrelated antigenically. These and several minor ASSPs comprise at least three related families of sporulation-specific gene products. Expression of the alpha and beta genes, detectable as functional mRNA in vitro, coincides with the time of synthesis of all of the major ASSPs in vivo. This apparently coordinate expression is dependent on at least the spo0A, spoIIA, and spoIIIA loci, but not on the spoIVA or spoVA loci, consistent with the late stage of this expression (initiating at 3.5 h after the start of sporulation and peaking at 5 h after start of sporulation). A few minor ASSPs may be asynchronously expressed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud M., Mahler I., Halvorson H. O., Boschwitz H., Keynan A. In vitro translation of messenger ribonucleic acid from sporulating and nonsporulating strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):1045–1048. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.1045-1048.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel-Quesada E., Setlow B., Setlow P. Cloning of the gene for C protein, a low molecular weight spore-specific protein from Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3250–3254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel-Quesada E., Setlow P. Cloning of a new low-molecular-weight spore-specific protein gene from Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.751-757.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam S. S., Setlow P. In vivo and in vitro synthesis of the spore-specific proteins A and C of bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8417–8423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Tipper D. J. Morphology and patterns of protein synthesis during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis Eryr spo(Ts) mutants. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):625–637. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.625-637.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Tipper D. J. Acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):972–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.972-982.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legault-Demare L., Chambliss G. H. Natural messenger ribonucleic acid-directed cell-free protein-synthesizing system of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1300–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1300-1307.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal J. M., Chambliss G. H. Synthesis of acid-soluble spore proteins by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1117–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1117-1125.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. M., Setlow P. Expression of Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus subtilis small acid-soluble spore protein genes during stationary-phase growth of asporogenous B. subtilis mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):931–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.931-933.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Setlow P. Localization of low-molecular-weight basic proteins in Bacillus megaterium spores by cross-linking with ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):486–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.486-494.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Identification and localization of the major proteins degraded during germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8159–8167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Ozols J. Covalent structure of protein A. A low molecular weight protein degraded during germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11938–11942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Ozols J. Covalent structure of protein C. A second major low molecular weight protein degraded during germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8413–8416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Ozols J. The complete covalent structure of protein B. The third major protein degraded during germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10445–10450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood F. T., Wu M. M., Gerhart J. C. The radioactive labeling of proteins with an iodinated amidination reagent. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan K., Johnson W. C., Tipper D. J., Setlow P. Comparison of various properties of low-molecular-weight proteins from dormant spores of several Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):965–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.965-971.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]