Abstract
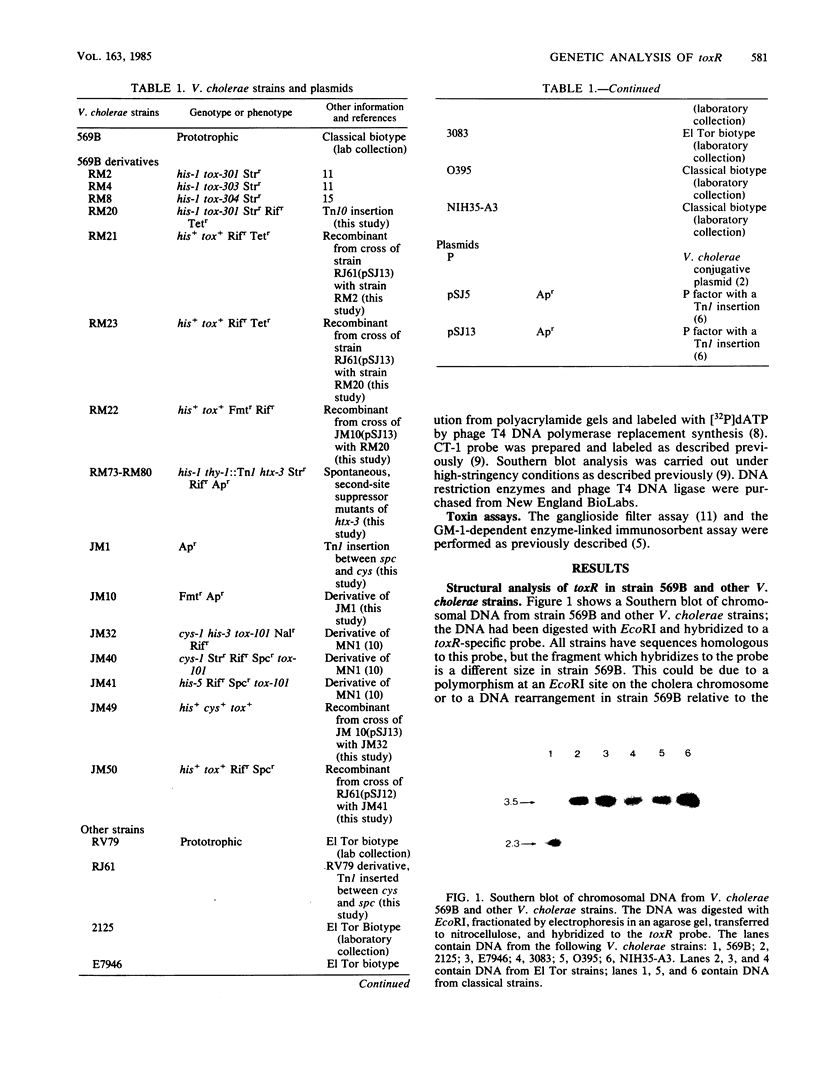
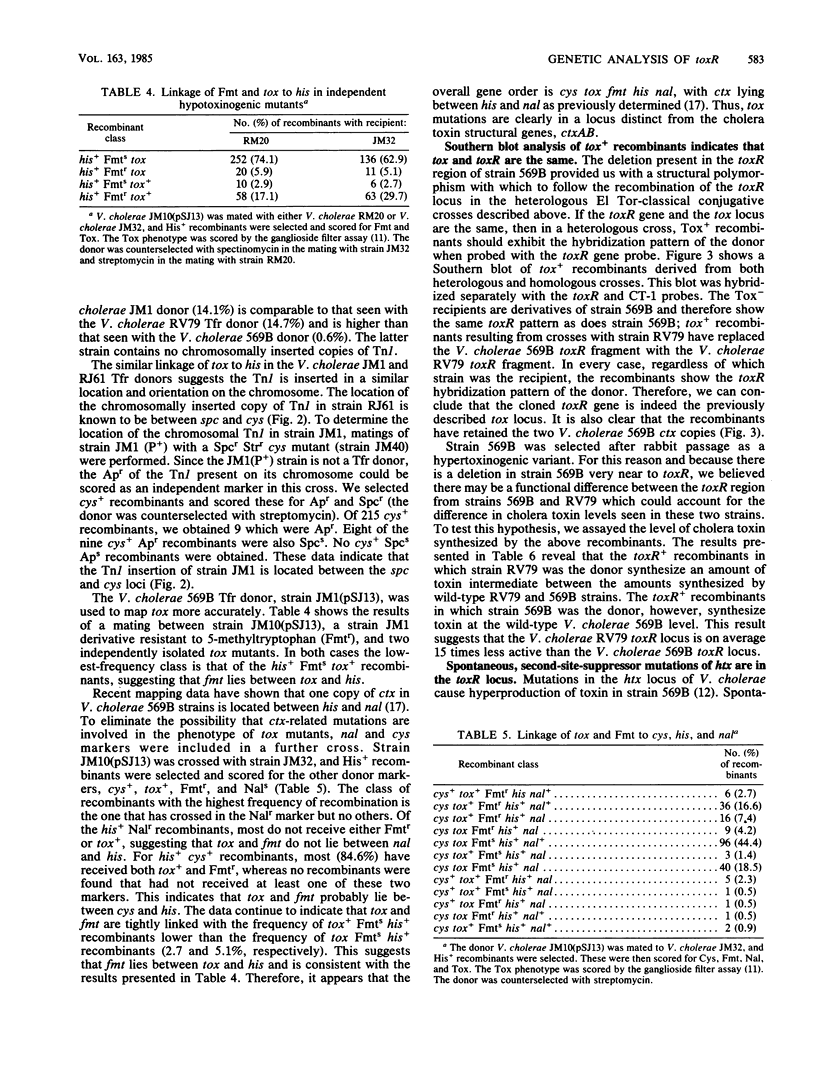
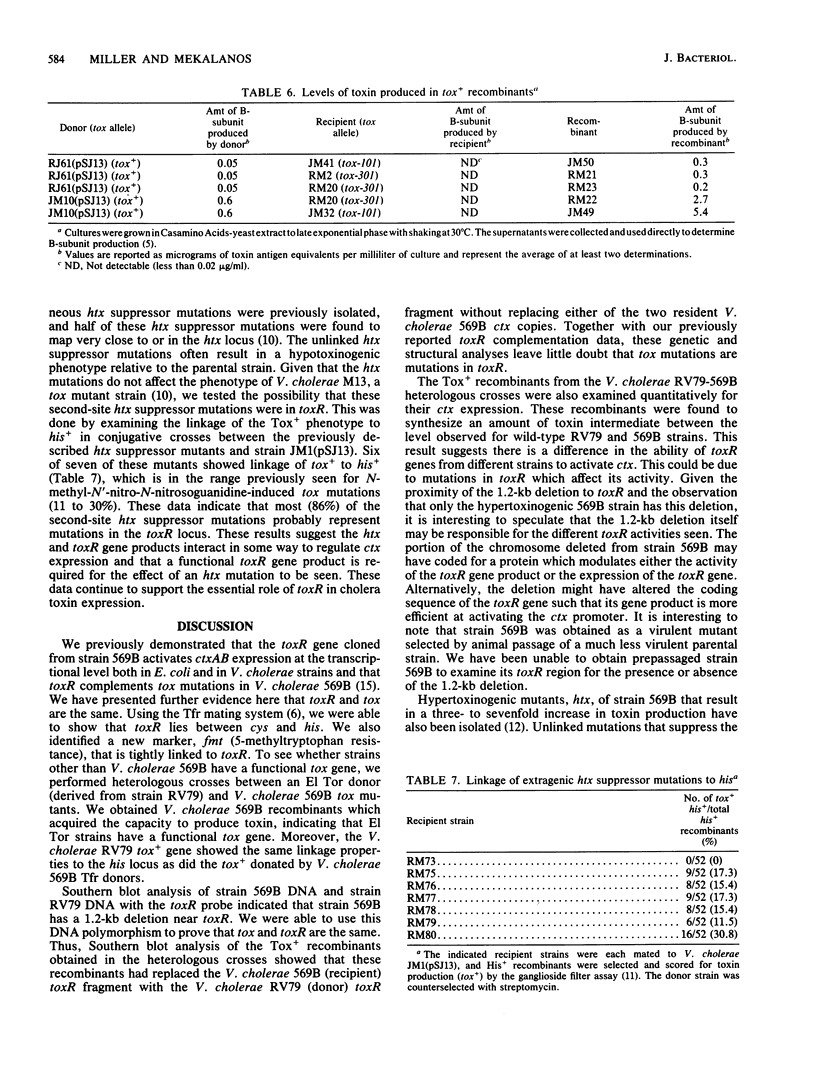
Southern blot analysis with a toxR-specific gene probe indicates that Vibrio cholerae 569B has a 1.2-kilobase deletion near the toxR gene. Heterologous conjugative crosses were carried out between the EI Tor strain RV79 and 569B tox mutants. Tox+ recombinants showed the same linkage properties to the his locus as to the previously mapped tox locus of 569B. Southern blot analysis with the toxR probe of the Tox+ recombinants obtained in these heterologous crosses showed that these recombinants had replaced the V. cholerae 569B (recipient) toxR DNA with the V. cholerae RV79 (donor) toxR DNA, indicating that tox and toxR are the same locus. However, the Tox+ recombinants synthesized an amount of toxin intermediate between the level observed for wild-type RV79 and 569B strains, suggesting there is a difference in the ability of toxR genes from different strains to activate ctx. About half of the mutations which suppress the phenotype of hypertoxinogenic locus htx are unlinked to htx and in addition have a hypotoxinogenic phenotype relative to that of the wild type. Most of these hypotoxinogenic, second-site suppressors show a linkage to his similar to the linkage of toxR to his and are therefore probably mutations in toxR. These results indicate that the toxR gene product is required for ctx expression and that a functional toxR gene is required for the effect of an htx mutation to be seen.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Genetic mapping of mutations in independently isolated nontoxinogenic mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.194-200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Baine W. B., Vasil M. L. Quantitative measurements of cholera enterotoxin in cultures of toxinogenic wild-type and nontoxinogenic mutant strains of Vibrio cholerae by using a sensitive and specific reversed passive hemagglutination assay for cholera enerotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.101-106.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Romig W. R. Transposon-facilitated recombination in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 16;170(1):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00268584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Affinity filters, a new approach to the isolation of tox mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Murphy J. R. Regulation of cholera toxin production in Vibrio cholerae: genetic analysis of phenotypic instability in hypertoxinogenic mutants. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):570–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.570-576.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Sublett R. D., Romig W. R. Genetic mapping of toxin regulatory mutations in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):859–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.859-865.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Mekalanos J. J. Molecular cloning of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporecke I., Castro D., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic mapping of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.253-261.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K., Finkelstein R. A. Conjugal transfer of a chromosomal gene determining production of enterotoxin in vibrio cholerae. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.1114331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




