Abstract
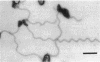
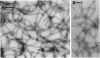
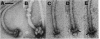
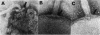
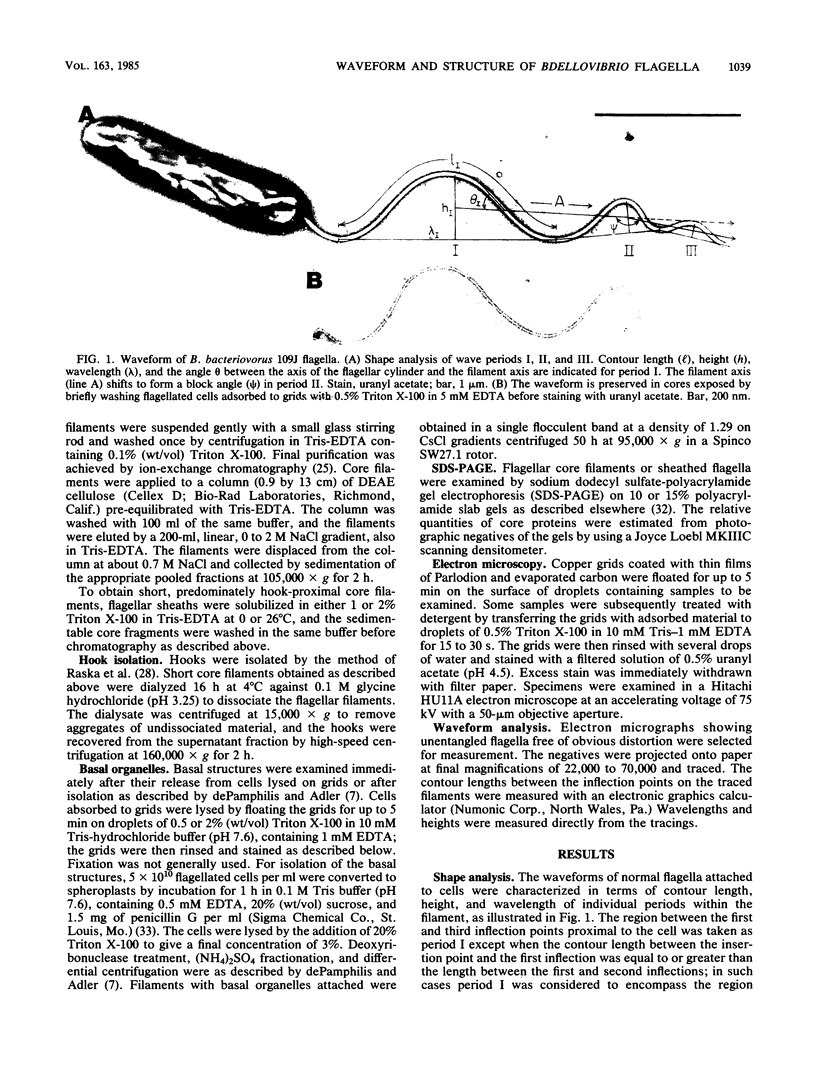
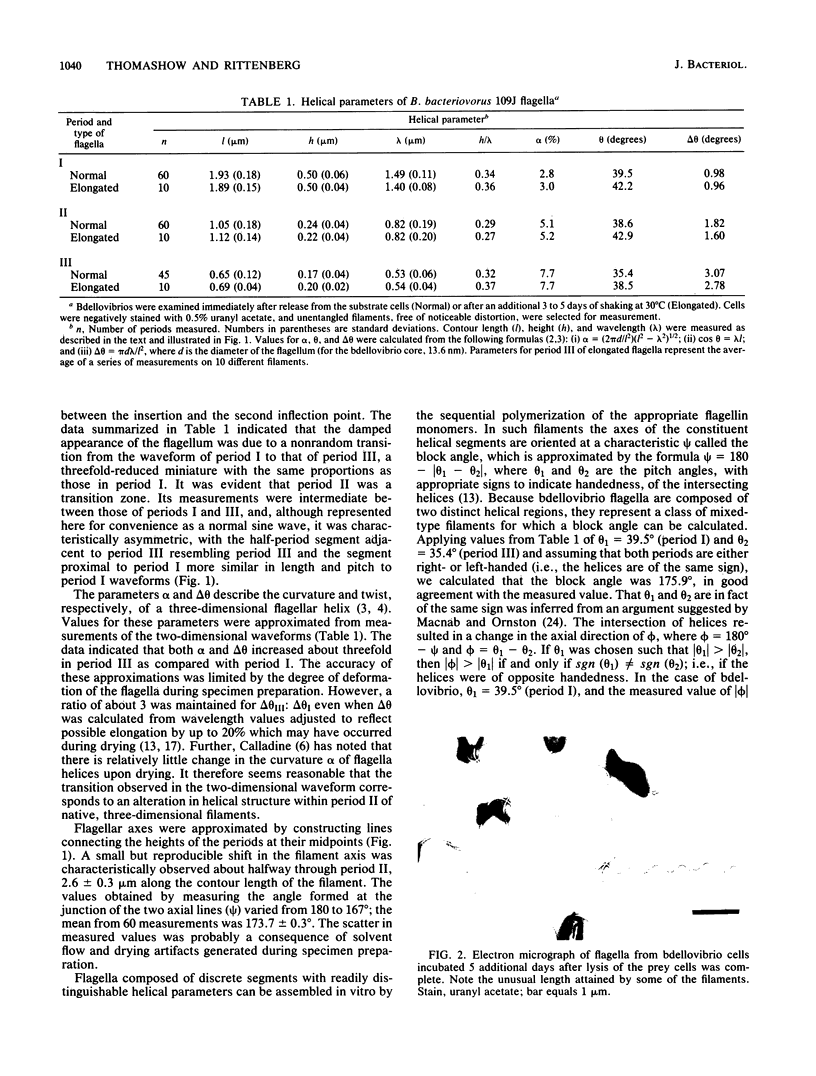
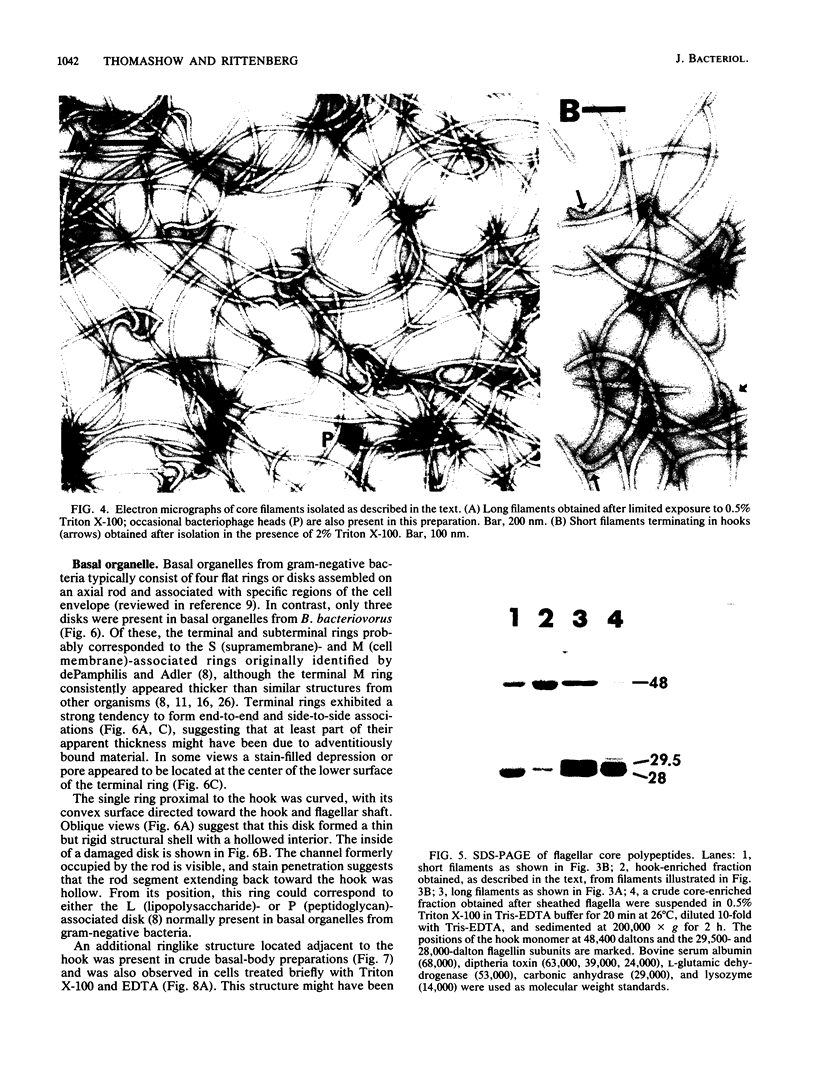
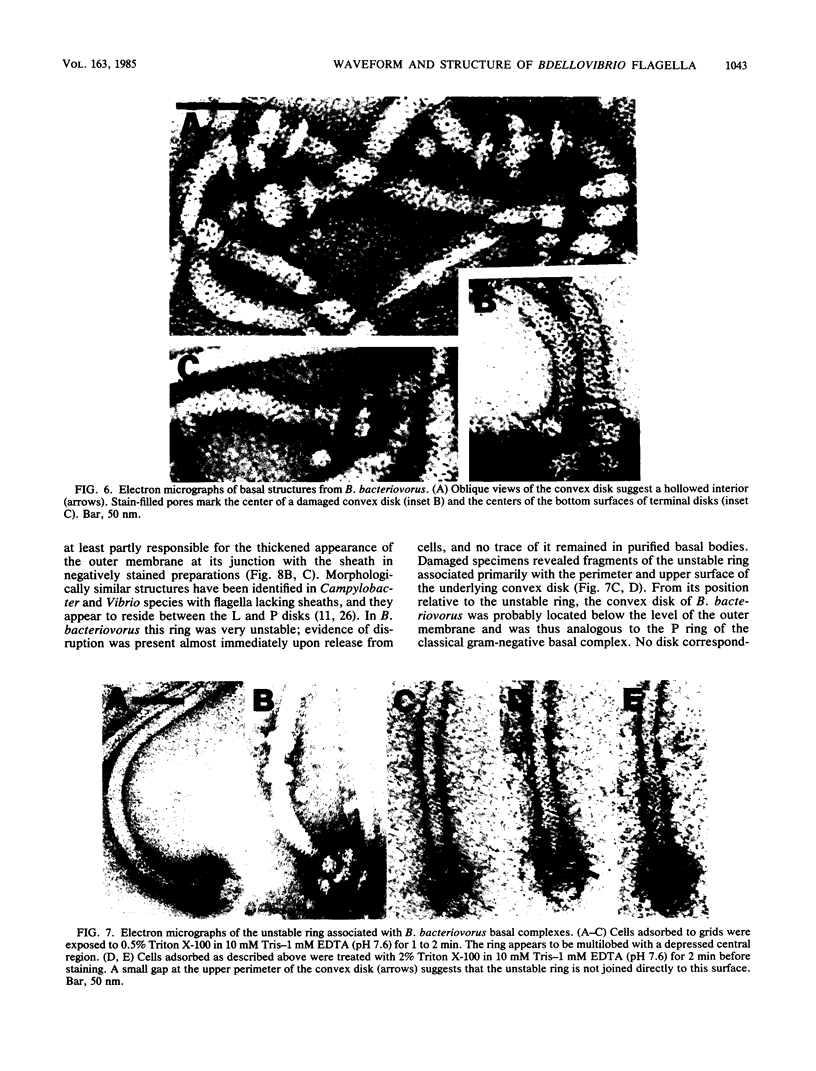
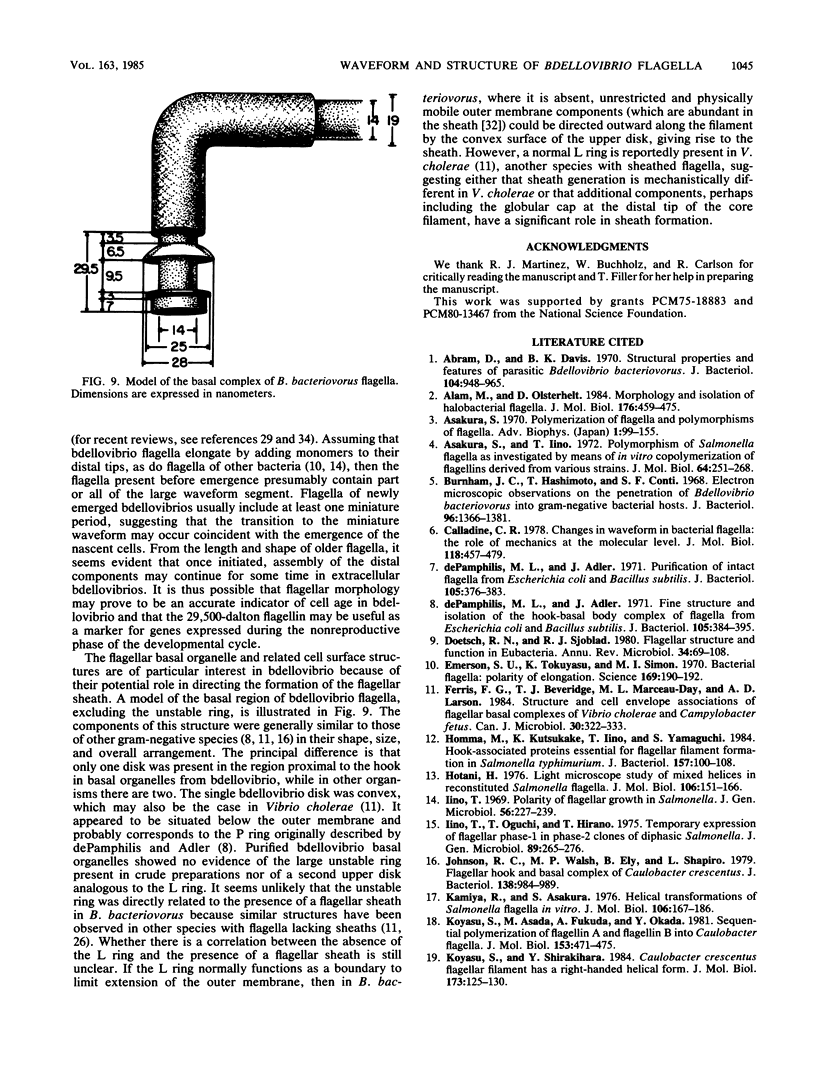
The structure of sheathed flagella from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus was investigated. The first three periods of these flagella were characterized by progressively smaller wavelengths and amplitudes in periods more distal to the cell. The damped appearance was due to a single nonrandom transition between two helical structures within each filament. The intersection of the two helices, one of which was a threefold-reduced miniature of the other, occurred at a fixed distance along the filament and resulted in a shift in the flagellar axis. Flagella increased in length as the cells aged and assumed a constant miniature waveform at their distal ends. The core filament was the principal determinant of flagellar morphology. It was composed of 28,000- and 29,500-dalton polypeptides. The 28,000-dalton subunits were located in the cell-proximal segment of the filament, and the 29,500-dalton subunits were located in the more distal region. The heteromorphous appearance of bdellovibrio flagella arose from the sequential assembly of these subunits. The basal complex associated with core filaments was examined because of its potential involvement in sheath formation. Bdellovibrio basal organelles were generally similar to those of other gram-negative species, but appeared to lack a disk analogous to the outer membrane-associated L ring which is a normal component of gram-negative basal complexes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Davis B. K. Structural properties and features of parasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):948–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.948-965.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S., Iino T. Polymorphism of Salmonella flagella as investigated by means of in vitro copolymerization of flagellins derived from various strains. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S. Polymerization of flagellin and polymorphism of flagella. Adv Biophys. 1970;1:99–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham J. C., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Electron microscopic observations on the penetration of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus into gram-negative bacterial hosts. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1366–1381. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1366-1381.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Sjoblad R. D. Flagellar structure and function in eubacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:69–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Tokuyasu K., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella: polarity of elongation. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J., Marceau-Day M. L., Larson A. D. Structure and cell envelope associations of flagellar basal complexes of Vibrio cholerae and Campylobacter fetus. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):322–333. doi: 10.1139/m84-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Iino T., Yamaguchi S. Hook-associated proteins essential for flagellar filament formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.100-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotani H. Light microscope study of mixed helices in reconstituted Salmonella flagella. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Oguchi T., Hirano T. Temporary expression of flagellar phase-1 in phase-2 clones of diphasic Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):265–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Polarity of flagellar growth in salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 May;56(2):227–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Walsh M. P., Ely B., Shapiro L. Flagellar hook and basal complex of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):984–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.984-989.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya R., Asakura S. Helical transformations of Salmonella flagella in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):167–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Asada M., Fukuda A., Okada Y. Sequential polymerization of flagellin A and flagellin B into Caulobacter flagella. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Shirakihara Y. Caulobacter crescentus flagellar filament has a right-handed helical form. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagenaur C., Agabian N. Caulobacter flagellar organelle: synthesis, compartmentation, and assembly. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1062-1069.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagenaur C., Agabian N. Caulobacter flagellins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):731–733. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.731-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagenaur C., Agabian N. Physical characterization of Caulobacter crescentus flagella. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):435–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.435-444.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEZ R. J. A METHOD FOR THE PURIFICATION OF BACTERIAL FLAGELLA BY ION EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:115–120. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Morphological differences in flagella in Campylobacter fetus subsp. intestinalis and C. fetus subsp. jejuni. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(8):655–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Sheffery M., Newton A. Regulation of flagellin synthesis in the cell cycle of caulobacter: dependence on DNA replication. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Mayer F., Edelbluth C., Schmitt R. Structure of plain and complex flagellar hooks of Pseudomonas rhodos. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):679–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.679-688.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Structure of the flagellum of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1952–1955. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1952-1955.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjoblad R. D., Emala C. W., Doetsch R. N. Invited review: bacterial flagellar sheaths: structures in search of a function. Cell Motil. 1983;3(1):93–103. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Rittenberg S. C. Isolation and composition of sheathed flagella from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1047–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1047-1054.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Penicillin-induced formation of osmotically stable spheroplasts in nongrowing Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1484–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1484-1491.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]