Abstract
Histidine-containing protein (HPr) of gram-positive bacteria was found to be phosphorylated at a seryl residue (P-ser-HPr) in an ATP-dependent reaction catalyzed by a protein kinase (J. Deutscher and M. H. Saier, Jr., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80:6790-6794, 1983). Here we describe the purification and characterization of a soluble enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis which splits the phosphoryl bond in P-ser-HPr. The enzyme has a molecular weight of ca. 7.5 X 10(4), as determined by its migration behavior on a Sephacryl S-200 column. On native polyacrylamide gels the purified enzyme produced only one protein band. On sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels we found one major protein band of molecular weight 2.9 X 10(4) and two minor protein bands of molecular weights 2.3 X 10(4) and 7 X 10(4). Fructose 1,6-diphosphate, which stimulated the ATP-dependent, protein kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of HPr, had no effect on the phosphatase activity. Other glycolytic intermediates also had no effect. However, inorganic phosphate, which inhibited the ATP-dependent HPr kinase, stimulated the P-ser-HPr phosphatase. EDTA at a concentration of 0.1 mM completely inhibited the phosphatase. Divalent cations like Mg2+, Mn2+, and Co2+ overcame the inhibition by EDTA. Fe2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+ had no effect, whereas Ca2+ slightly inhibited the phosphatase. ATP was also found to inhibit the phosphatase. Under conditions in which ATP severely inhibited the phosphatase, ADP was found to have no effect on the enzyme activity. Besides P-ser-HPr of S. faecalis, the phosphatase was also able to hydrolyze the phosphoryl bond in P-ser-HPr of Streptococcus lactis, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Lactobacillus casei. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside phosphorylation, catalyzed by the S. aureus phosphoenolpyruvate:lactose phosphotransferase system, was about 150-fold decreased in the presence of P-ser-HPr of S. aureus, as compared with HPr. However, when P-ser-HPr was first incubated with P-ser-HPr phosphatase to allow complete hydrolysis of the phosphoryl bond, it had the same activity as HPr. Besides this cytoplasmic phosphoprotein phosphatase, we detected a membrane-bound phosphatase which also hydrolyzed the phosphoryl bond in P-ser-HPr.
Full text
PDF

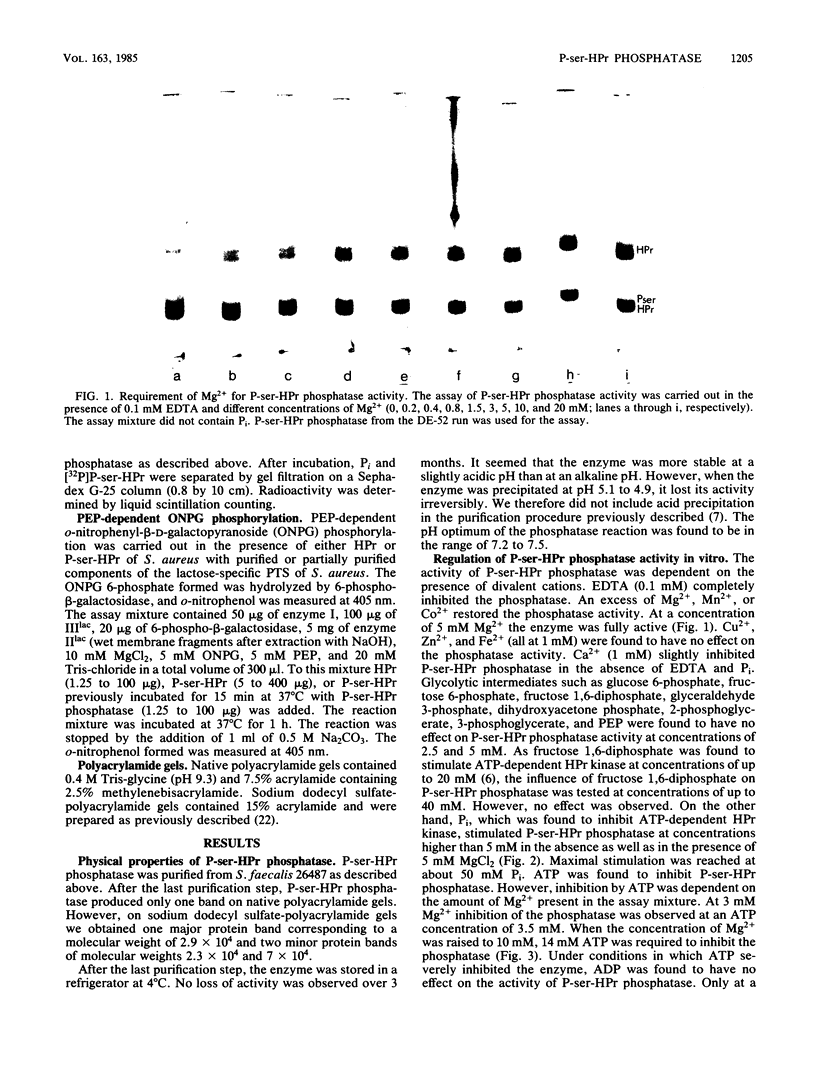

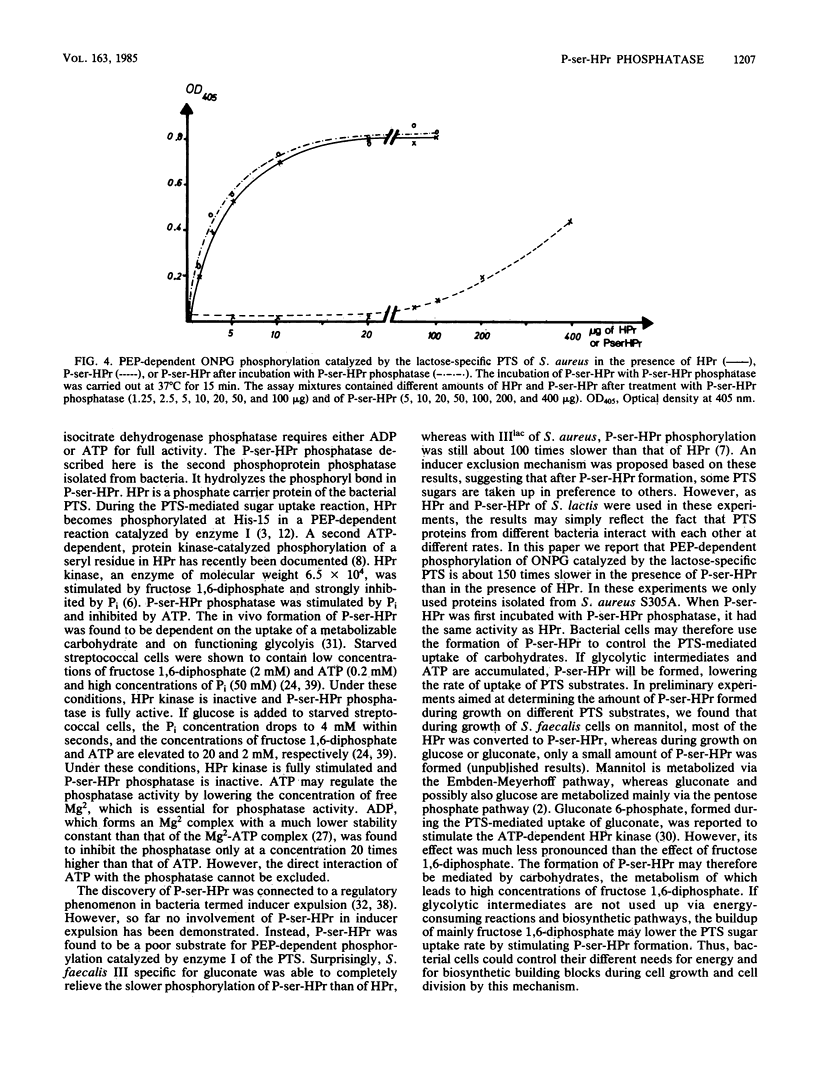


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Tung H. Y., Shenolikar S., Pilkis S. J., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Antibody to protein phosphatase-2A as a probe of phosphatase structure and function. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert C. A., Frank R., Stüber K., Deutscher J., Hengstenberg W. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent protein kinase enzyme I of Streptococcus faecalis: purification and properties of the enzyme and characterization of its active center. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):959–964. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernsmann P., Alpert C. A., Muss P., Deutscher J., Hengstenberg W. The bacterial PEP-dependent phosphotransferase system mechanism of gluconate phosphorylation in Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyreuther K., Raufuss H., Schrecker O., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. 1. Amino-acid sequence of the phosphocarrier protein HPr. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):275–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Beyreuther K., Sobek H. M., Stüber K., Hengstenberg W. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus: factor IIIlac, a trimeric phospho-carrier protein that also acts as a phase transfer catalyst. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4867–4873. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Saier M. H., Jr ATP-dependent protein kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation of a seryl residue in HPr, a phosphate carrier protein of the phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6790–6794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörschug M., Frank R., Kalbitzer H. R., Hengstenberg W., Deutscher J. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation site in enzyme IIIglc of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enami M., Ishihama A. Protein phosphorylation in Escherichia coli and purification of a protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):526–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnak M., Reeves H. C. Purification and properties of phosphorylated isocitrate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7915–7920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassner M., Stehlik D., Schrecker O., Hengstenberg W., Maurer W., Rüterjans H. The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. 2. 1H and 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies on the phosphocarrier protein HPr, phosphohistidines and phosphorylated HPr. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):287–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W. Enzymology of carbohydrate transport in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;77:97–126. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66740-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Hill K. L., Morse M. L. Phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus: its requirement for the accumulation and metabolism of galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.383-388.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Blair J., Guy P., Witters L., Hardie D. G. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 3. Fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 2. Glycogen metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalbitzer H. R., Deutscher J., Hengstenberg W., Rösch P. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus: 1H nuclear magnetic resonance studies on phosphorylated and unphosphorylated factor IIIlac and its interaction with the phosphocarrier protein HPr. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6178–6185. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalbitzer H. R., Hengstenberg W., Rösch P., Muss P., Bernsmann P., Engelmann R., Dörschug M., Deutscher J. HPr proteins of different microorganisms studied by hydrogen-1 high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance: similarities of structures and mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):2879–2885. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein with kinase and phosphatase activities involved in regulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):458–460. doi: 10.1038/300458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo G. A., Borthwick A. C., Holms W. H., Nimmo H. G. Partial purification and properties of isocitrate dehydrogenase kinase/phosphatase from Escherichia coli ML308. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoraro V. L., Hermes J. D., Cleland W. W. Stability constants of Mg2+ and Cd2+ complexes of adenine nucleotides and thionucleotides and rate constants for formation and dissociation of MgATP and MgADP. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5262–5271. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S., Cohen P., Fisher M. J., Pogson C. I., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis and aromatic amino acid breakdown in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):39–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Hengstenberg W., Saier M. H., Jr Properties of ATP-dependent protein kinase from Streptococcus pyogenes that phosphorylates a seryl residue in HPr, a phosphocarrier protein of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.333-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Panos C., Saier M. H., Jr Mechanism of inducer expulsion in Streptococcus pyogenes: a two-step process activated by ATP. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):354–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.354-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Panos C. Regulation of beta-galactoside phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus pyogenes by an expulsion mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T. The enzymology of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar transport systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Jul 7;46(1):3–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00215577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer A., Schrecker O., Hengstenberg W. The staphylococcal phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Purification and characterisation of the galactoside-specific membrane-component enzyme II. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(2):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of methyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside-6-phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus lactis by exclusion and expulsion mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.885-894.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Torchia D. A. Use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 14C fluorography in studies of glycolysis and regulation of pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.791-800.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Identification of the inhibitor-2 phosphatases in rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Mattoo R. L., Peri K. G. Phosphoproteins and the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: evidence for IIImannose, IIIfructose, IIIglucitol, and the phosphorylation of enzyme IImannitol and enzyme IIN-acetylglucosamine. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(3):139–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N., Kukuruzinska M. A., Nakazawa A., Waygood E. B., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Phosphoryl transfer reactions catalyzed by enzyme I of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14477–14491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]