Abstract
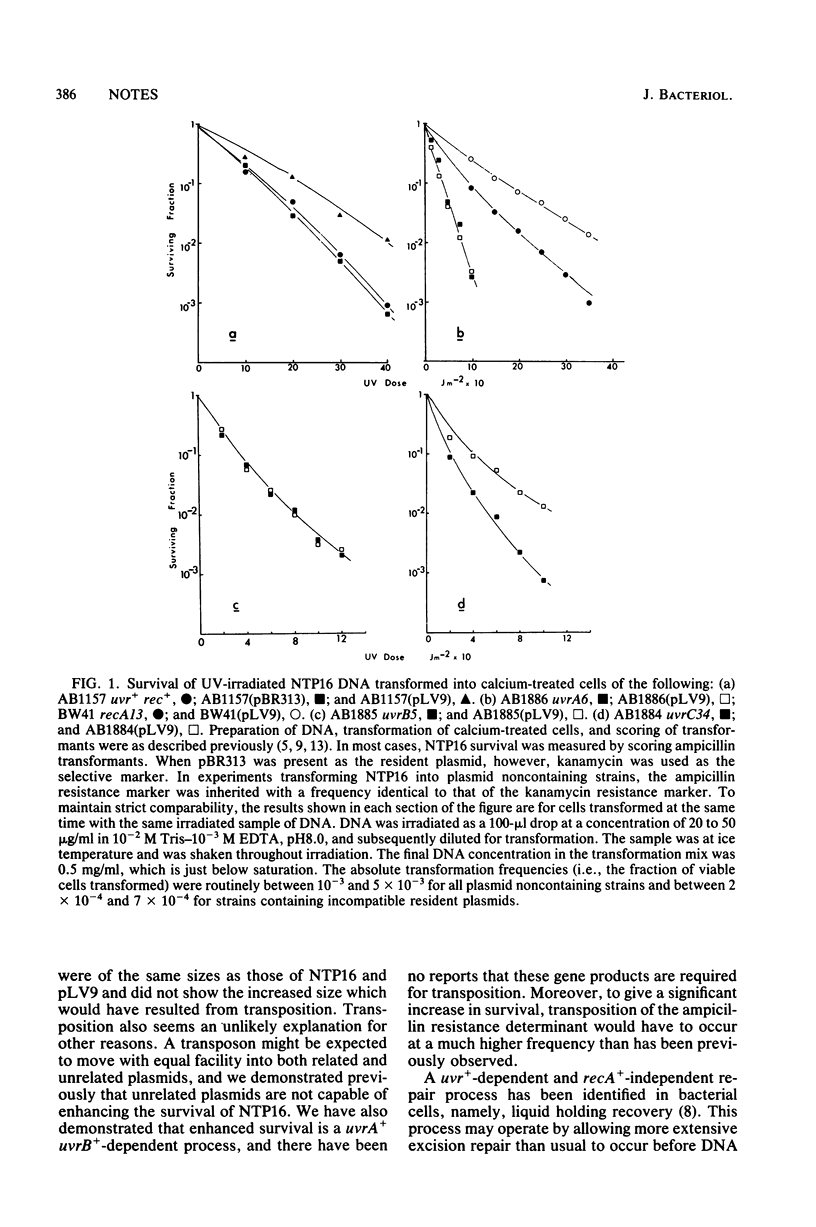
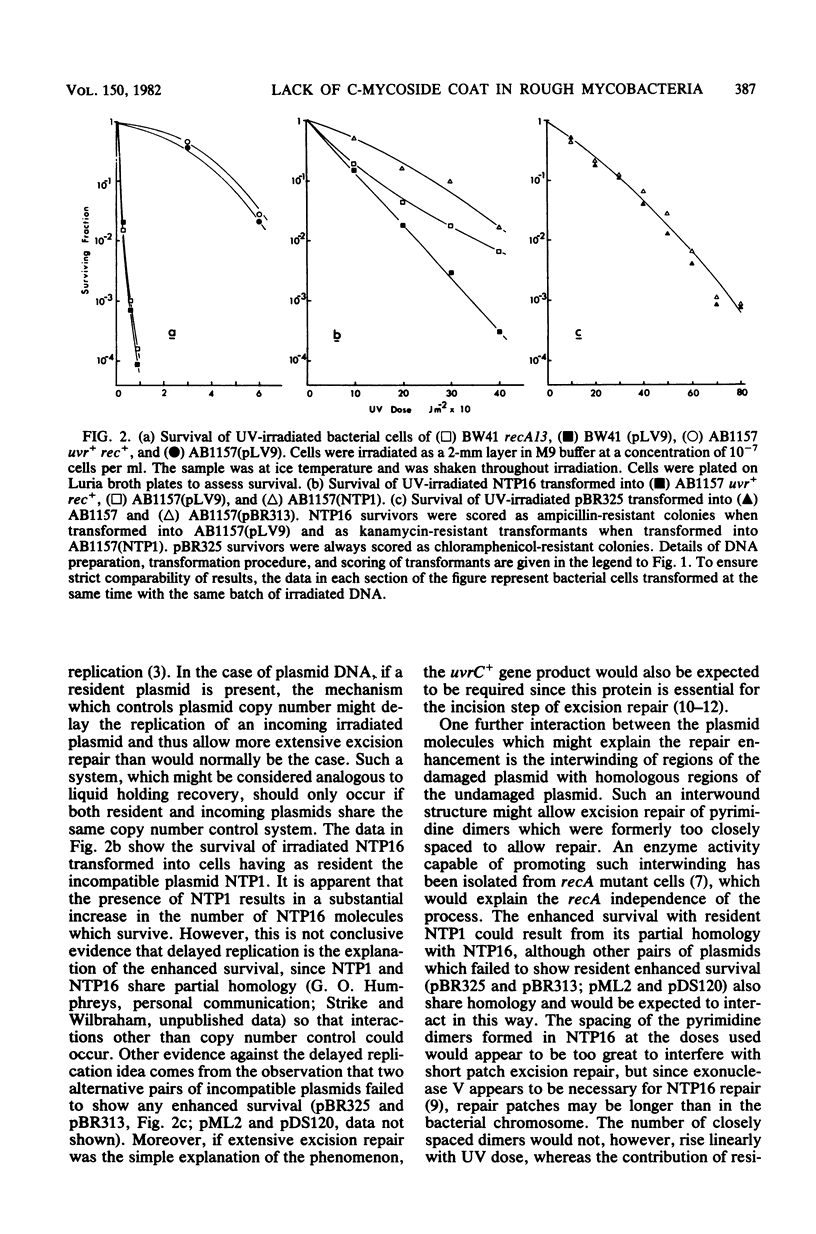
The survival of UV-irradiated DNA of plasmid NTP16 was monitored after its transformation into recipient cells containing an essentially homologous undamaged plasmid, pLV9. The presence of pLV9 resulted in a substantial increase in the fraction of damaged NTP16 molecules which survived in the recipient cells. This enhanced survival requires the host uvrA+ and uvrB+ gene products, but not the host recA+ gene product. The requirement for both homologous DNA and the uvrA+ and uvrB+ gene products suggests that a novel repair process may act on plasmid DNA. Possible mechanisms for this process are considered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Devoret R., Blanco M., George J., Radman M. Recovery of phage lambda from ultraviolet damage. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5A:155–171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2895-7_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K., Smith K. C. Dark recovery processes in Escherichia coli irradiated with ultraviolet light. II. Effect of uvr genes on liquid holding recovery. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1129–1133. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1129-1133.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibe A., Shimada K., Takagi Y. Repair of ultraviolet-light damaged ColE1 factor carrying Escherichia coli genes for guanine synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 11;168(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00271499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Dressler D. Biochemical assay designed to detect formation of recombination intermediates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1084–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B., Aldous E. RECOVERY FROM ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1949 Mar;57(3):363–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.3.363-375.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Strike P. Efficiency of Escherichia coli repair processes on uv-damaged transforming plasmid DNA. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg E., Nissen-Meyer J., Strike P. Incision of ultraviolet-irradiated DNA by extracts of E. coli requires three different gene products. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):524–526. doi: 10.1038/263524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg E. Reconstitution of an Escherichia coli repair endonuclease activity from the separated uvrA+ and uvrB+/uvrC+ gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg E., Rupp W. D., Strike P. Impaired incision of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid in uvrC mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):97–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.97-104.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strike P., Humphreys G. O., Roberts R. J. Nature of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid in calcium-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.1033-1035.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A., Humphreys G. O., Brown M. G., Saunders J. R. Simultaneous transformation of Escherichia coli by pairs of compatible and incompatible plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Apr 17;172(1):113–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00276222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


