Abstract
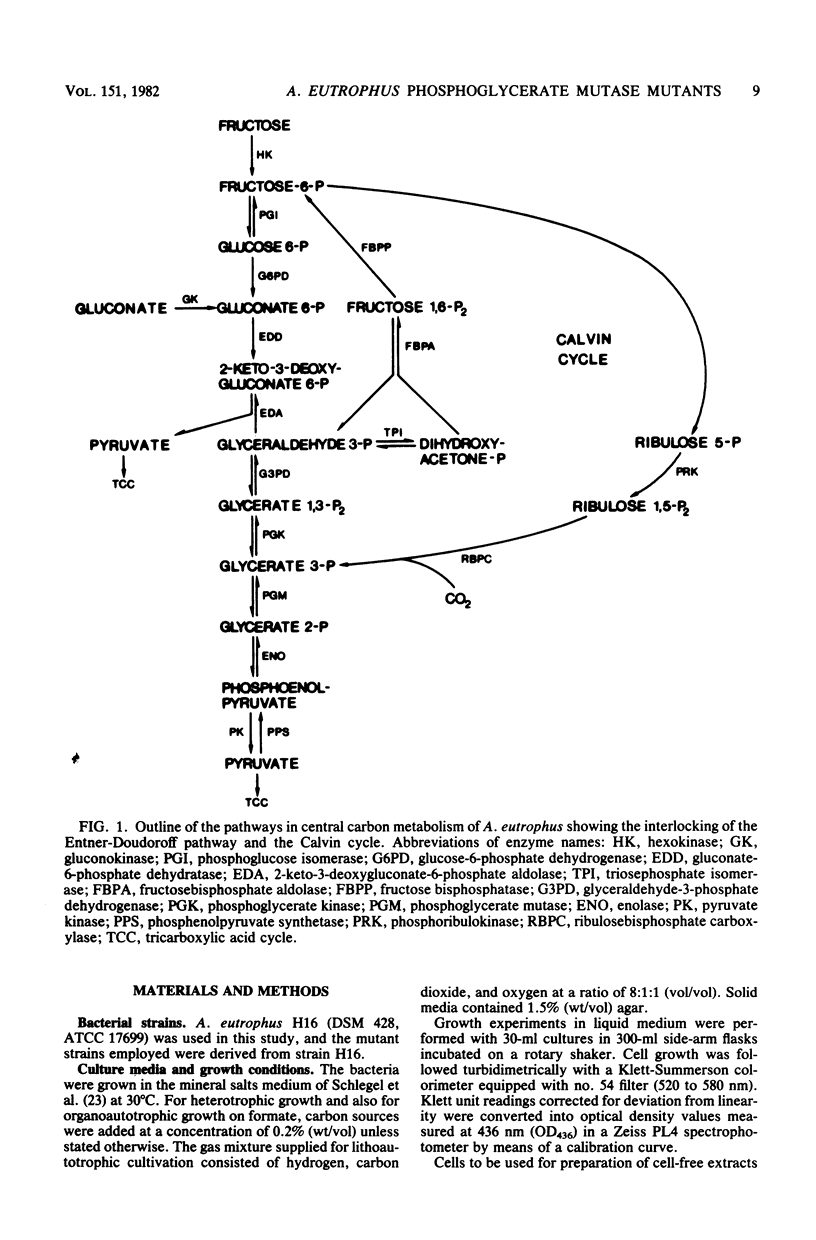
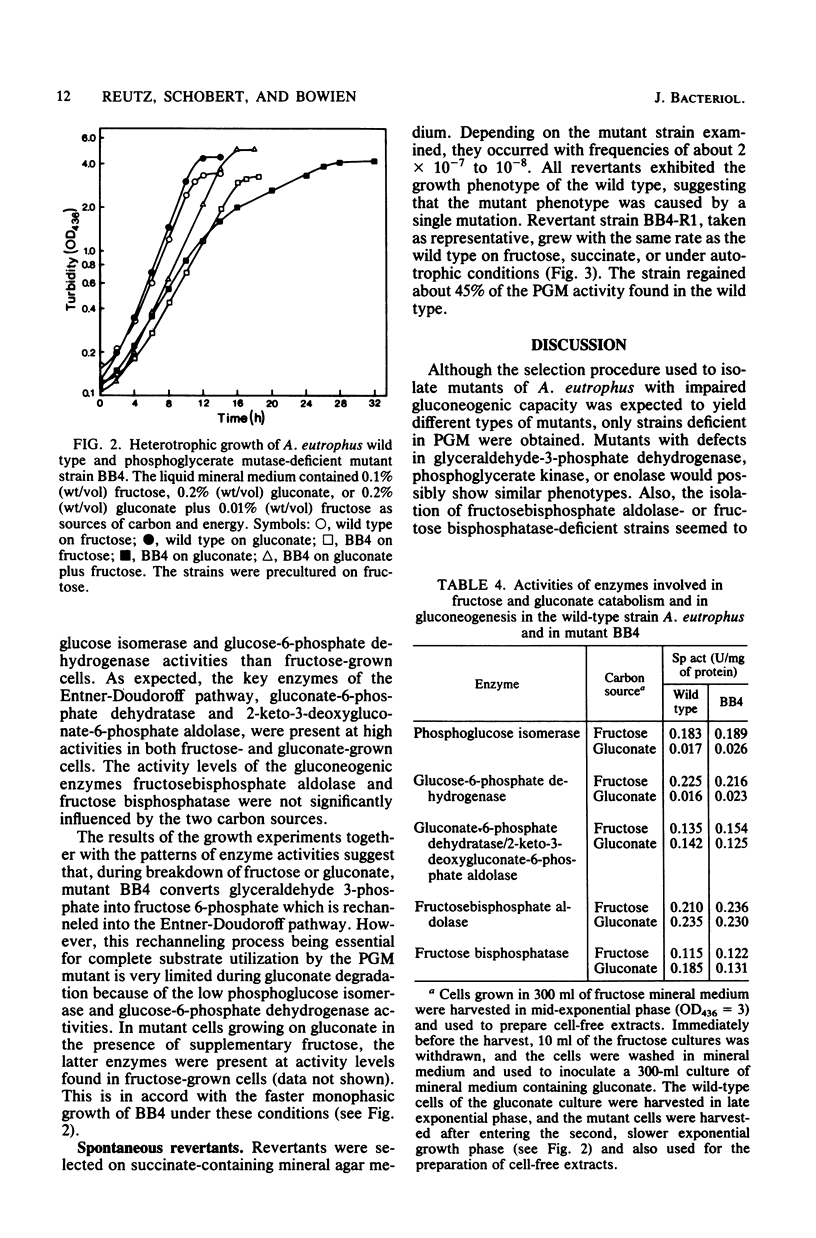
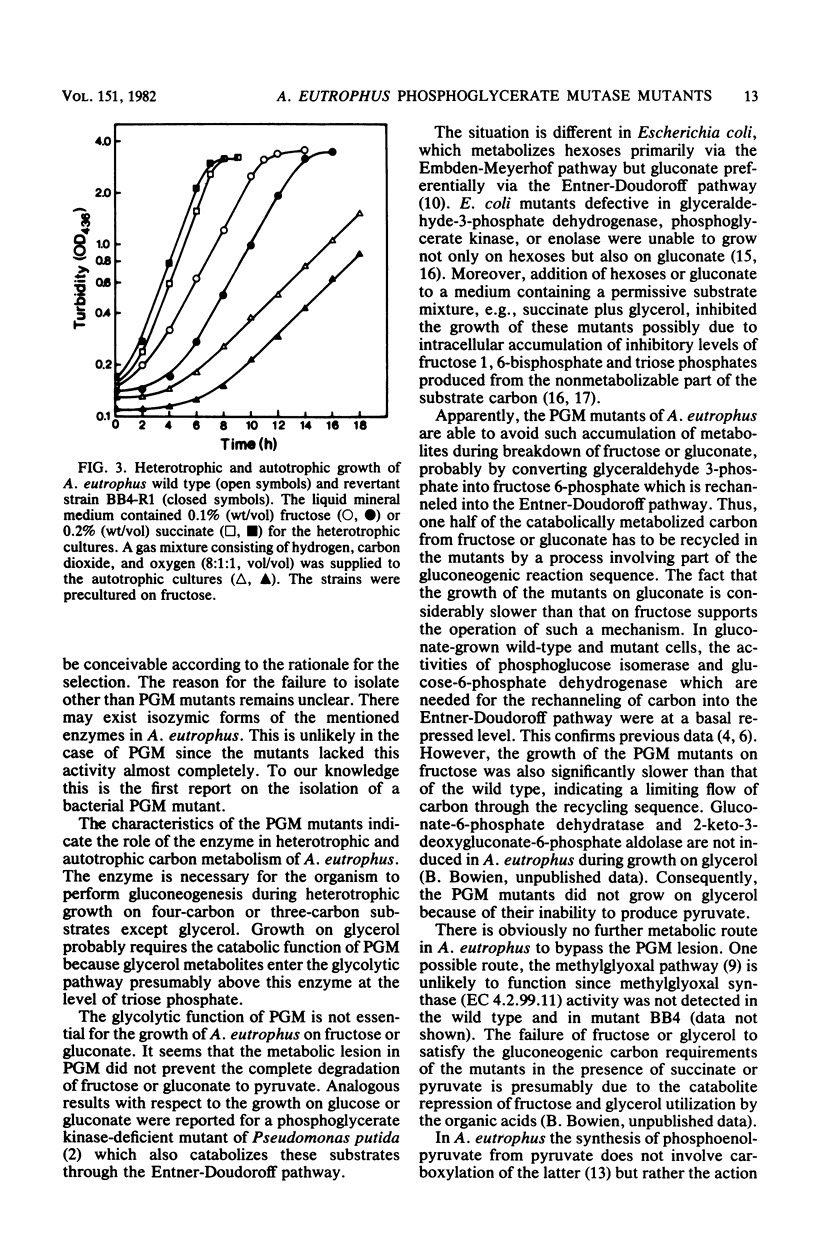
Mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus were isolated on the basis of their inability to grow on succinate as the sole source of carbon and energy. The mutants also failed to grow on other gluconeogenic substrates, including pyruvate, acetate, and citrate. Simultaneously, they had lost their capability for autotrophic growth. The mutants grew, but slower than the wild type, on fructose or gluconate. Growth retardation on gluconate was more pronounced. The mutants lacked phosphoglycerate mutase activity, and spontaneous revertants of normal growth phenotype had regained the activity. The physiological characteristics of the mutants indicate the role of phosphoglycerate mutase in heterotrophic and autotrophic carbon metabolism of A. eutrophus. Although the enzyme is necessary for gluconeogenesis during heterotrophic growth on three- or four-carbon substrates, its glycolytic function is not essential for the catabolism of fructose or gluconate via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. The enzyme is required during autotrophic growth as a catalyst in the biosynthetic route leading from glycerate 3-phosphate to pyruvate. It is suggested that the mutants accomplish the complete degradation of fructose and gluconate mutase lesion. The catabolically produced triose phosphates are converted to fructose 6-phosphate which is rechanneled into the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. This carbon recycling mechanism operates less effectively in mutant cells growing on gluconate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelal A. T., Schlegel H. G. Purification and regulatory properties of fructose 1,6-diphosphatase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):304–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.304-310.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio M. L., Ruiz-Amil M., Vicente M., Cánovas J. L. The role of phosphoglycerate kinase in the metabolism of Pseudomonas putida. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):326–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackkolb F., Schlegel H. G. Katabolische Repression und Enzymhemmung durch molekularen Wasserstoff bei Hydrogenomonas. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;62(2):129–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Mayer F., Codd G. A., Schlegel H. G. Purification, some properties and quaternary structure of the D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):157–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00690223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Der Biosyntheseweg der RNS-Ribose in Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H 16 und Pseudomonas facilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00409291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Isolierung und Charakterisierung katabolischer Defektmutanten von Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stemm H 16. I. Fructose-negative mutanten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(3):203–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Anderson A. The formation and catabolism of methylglyoxal during glycolysis in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 11;11(4):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80546-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Levisohn S. R. Glucose and gluconate metabolism in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1571-1578.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings W., Schlegel H. G. Zur Synthese von C 4 -Dicarbonsäuren aus Pyruvat durch Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H 16. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(3):204–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G., EBERHARDT U., SCHLEGEL H. G. VERWERTUNG VON FRUCTOSE DURCH HYDROGENOMONAS H 16. (I.) Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Apr 2;48:95–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. D., Fraenkel D. G. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1175–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1175-1179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Maitra P. K. Properties of Escherichia coli mutants deficient in enzymes of glycolysis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):398–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.398-410.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M., Maitra P. K. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants defective in enzymes of glycolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra P. K., Lobo Z. A kinetic study of glycolytic enzyme synthesis in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTREMOLI S., MANGIAROTTI G. A simple method for the preparation of D-ribulose 5-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:643–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reh M., Schlegel H. G. Anreicherung und Isolierung auxotropher Mutanten von Hydrogenomonas H 16. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;67(2):99–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Schlegel H. G. The membrane-bound hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. I. Solubilization, purification, and biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 12;567(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Cammack R., Schlegel H. G., Hall D. O. The iron-sulphur centres of soluble hydrogenase from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 19;578(2):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert K., Schobert P., Bowien B. Purification, some catalytic and molecular properties of phosphoribulokinase from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 13;658(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke D., Schlegel H. G. Regulation of the pyruvate kinase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H 16 in vitro and in vivo. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Oct 27;105(2):109–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00447123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


