Abstract
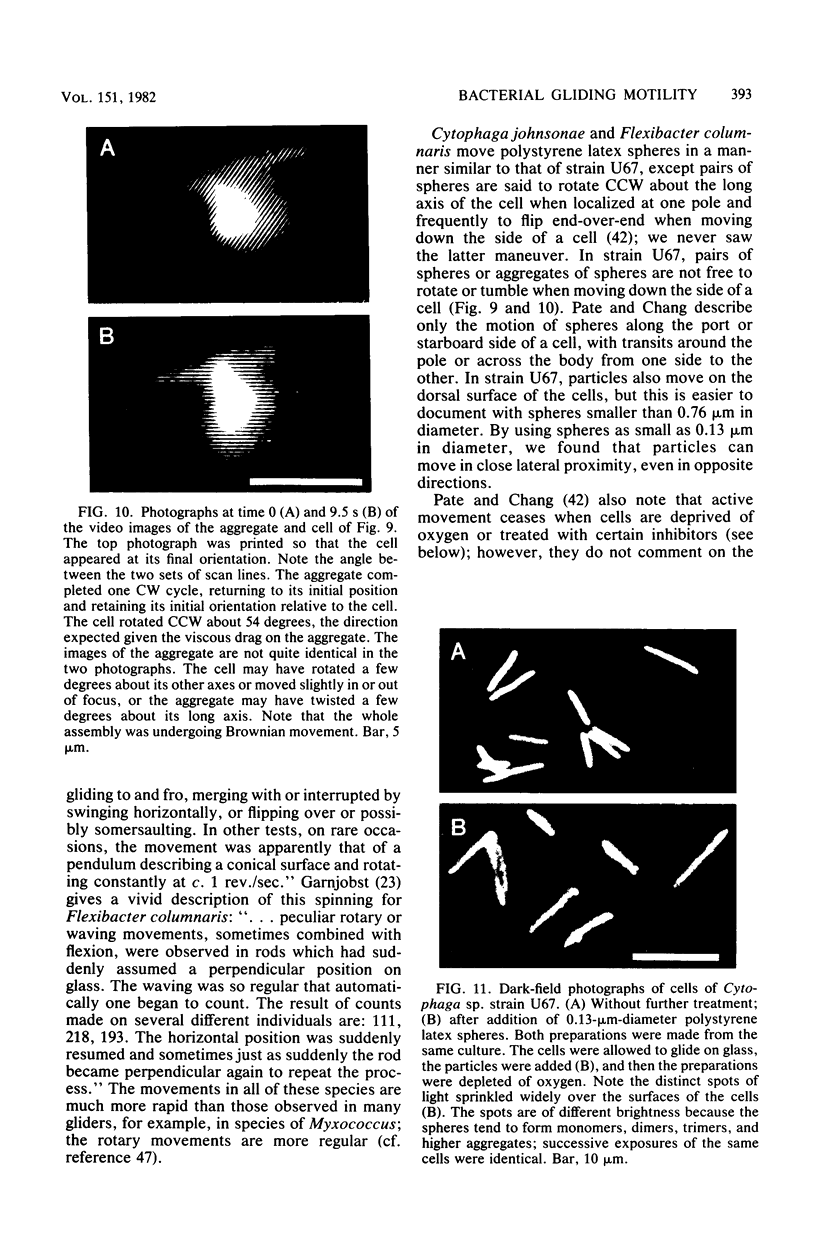
Video techniques were used to analyze the motion of the gliding bacterium Cytophaga sp. strain U67. Cells moved singly on glass along the long axis at a speed of about 2 micrometers/s, advancing, retreating, stopping, pivoting about a pole, or flipping over. They did not flex or roll. Cells of different lengths moved at about the same speed. Cells sometimes spun continuously about a pole at a frequency of about 2 HZ, the body moving in a plane parallel to that of the glass or on the surface of a cone having either a large or a small solid angle. Polystyrene latex spheres moved to and fro on the surfaces of cells, also at a speed of about 2 micrometers/s. They moved in the same fashion whether a cell was in suspension, gliding, or at rest on the glass. Two spheres on the same cell often moved in opposite directions, passing by one another in close proximity. Small and large spheres and aggregates of spheres all moved at about the same speed. An aggregate moved down the side of a cell with a fixed orientation, even when only one sphere was in contact with the cell. Spheres occasionally left one cell and were picked up by another. Cell pretreated with small spheres did not adhere to glass. When the cells were deprived of oxygen, they stopped gliding, and the spheres stopped moving on their surfaces. The spheres became completely immobilized; they no longer moved from cell to cell or exhibited Brownian movement. Cytophaga spp. are known to have a typical gram-negative cell envelope: an inner (cytoplasmic) membrane, a thin peptidoglycan layer, and an outer (lipopolysaccharide) membrane. Our data are consistent with a model for gliding in which sites to which glass and polystyrene strongly adsorb move within the fluid outer membrane along tracks fixed to the rigid peptidoglycan framework.
Full text
PDF


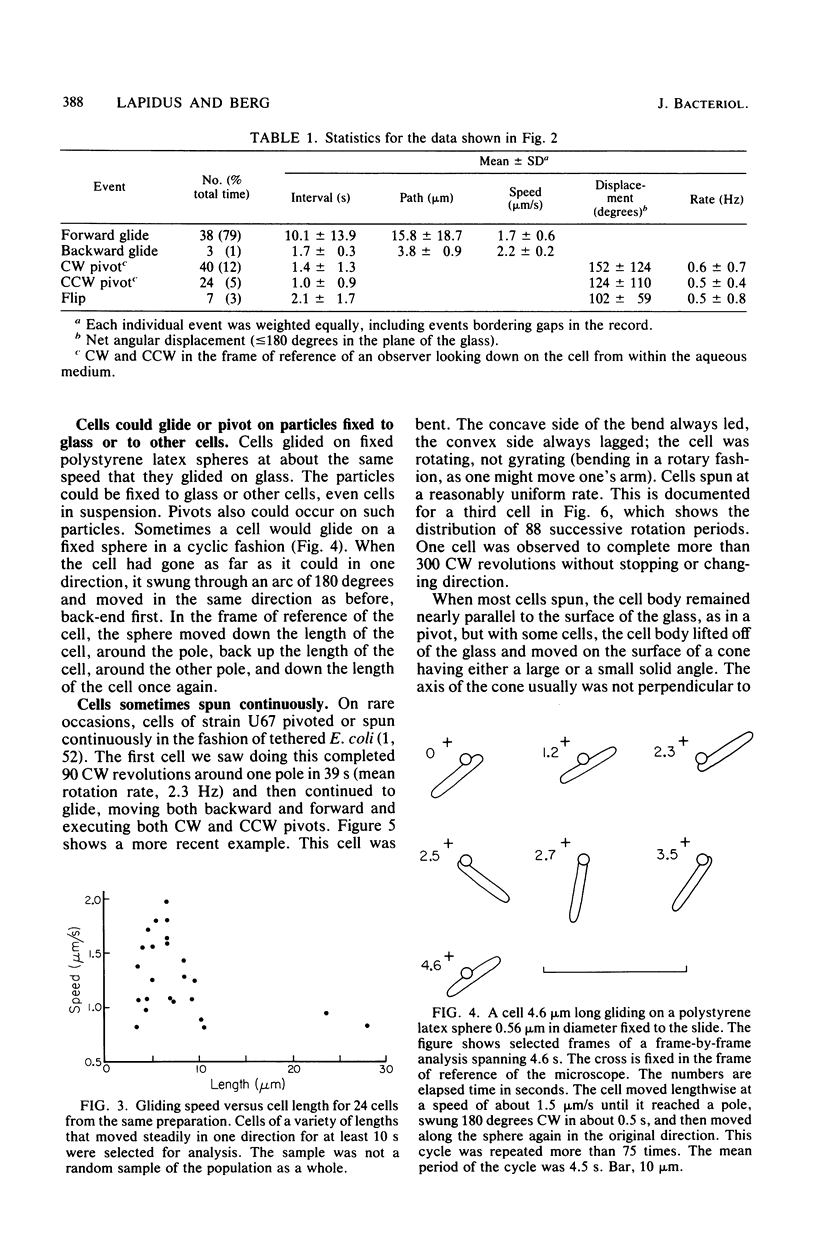
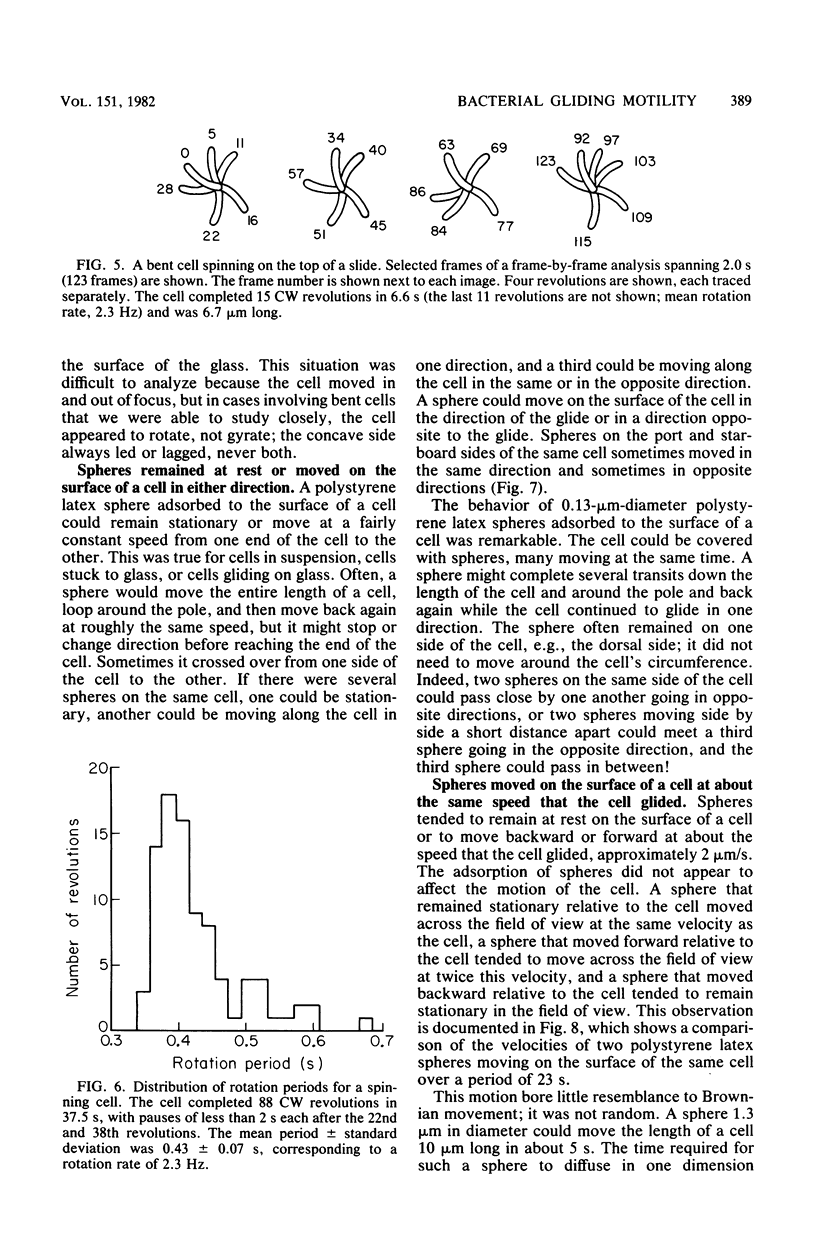

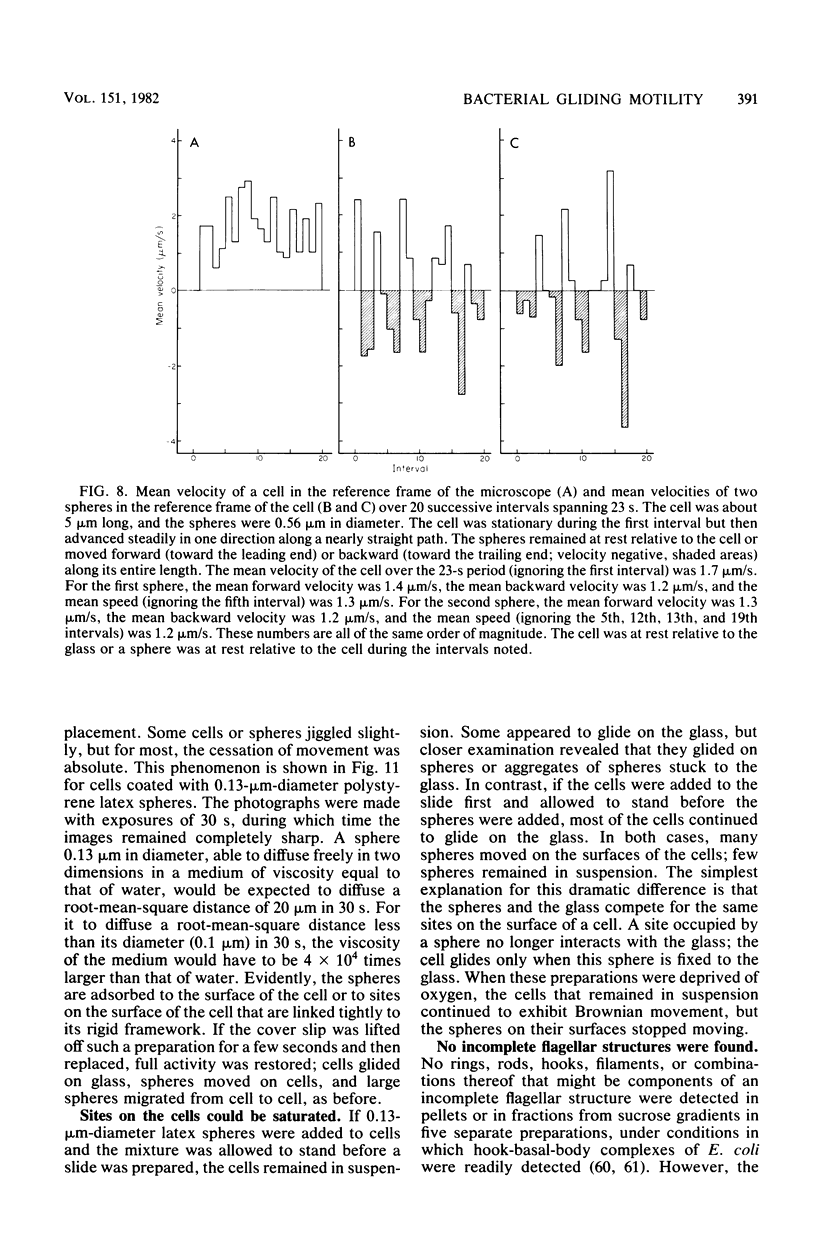
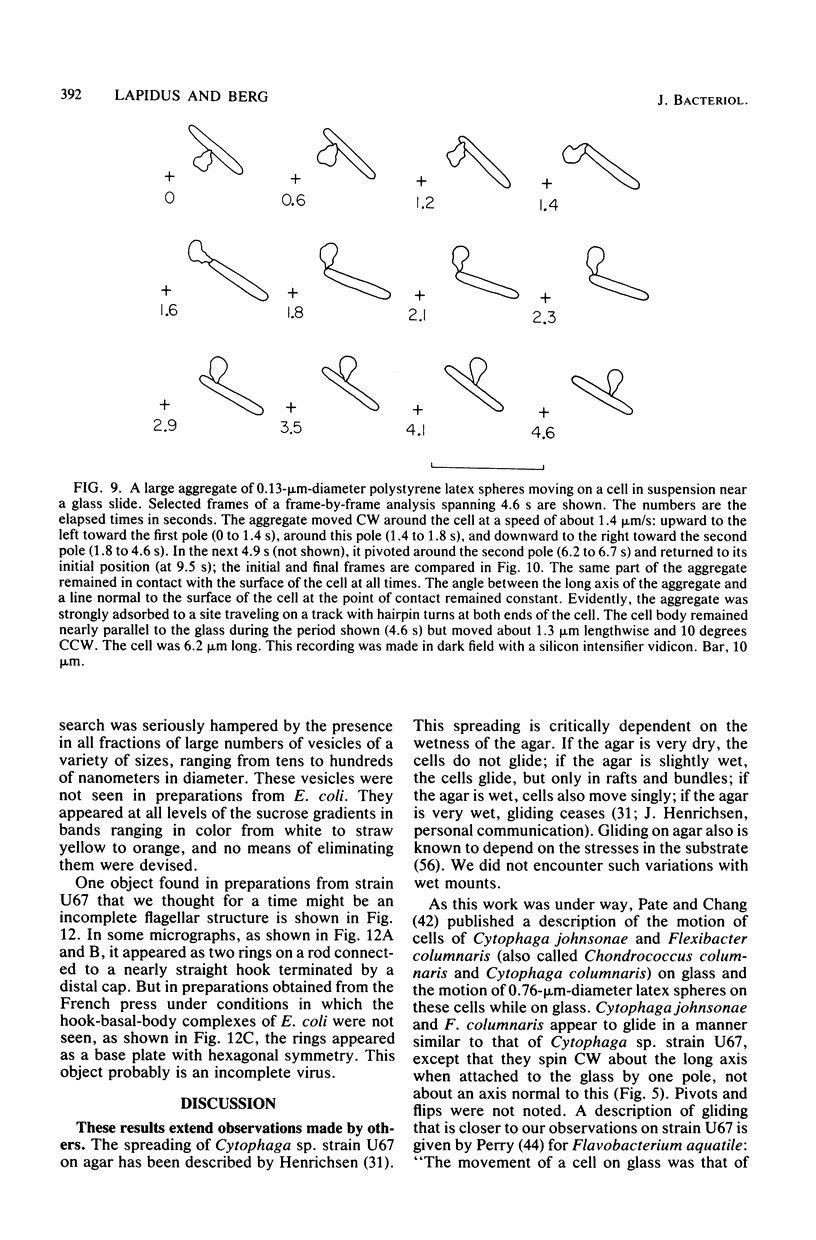





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Bacterial behaviour. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):389–392. doi: 10.1038/254389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Dynamic properties of bacterial flagellar motors. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):77–79. doi: 10.1038/249077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. How spirochetes may swim. J Theor Biol. 1976 Feb;56(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Tedesco P. M. Transient response to chemotactic stimuli in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Brown D. T. Surface structure of gliding bacteria after freeze-etching. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1351–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1351-1355.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P. Gliding motility of prokaryotes: ultrastructure, physiology, and genetics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:497–529. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E. Motility and chemotaxis of spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P. J. The history, biology, and taxonomy of the Cytophaga group. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1599–1653. doi: 10.1139/m77-236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayrell-Hart B., Burchard R. P. Association of flexing and gliding in Flexibacter. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1417–1420. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1417-1420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Hageage G. J. Motility in procaryotic organisms: problems, points of view, and perspectives. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Aug;43(3):317–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb00963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duxbury T. A microperfusion chamber for studying the growth of bacterial cells. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):247–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Webley D. M. An electron microscope study of the cell surface of Cytophaga johnsonii and some observations on related organisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1965;31(4):361–382. doi: 10.1007/BF02045916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnjobst L. Cytophaga columnaris (Davis) in Pure Culture: A Myxobacterium Pathogenic to Fish. J Bacteriol. 1945 Feb;49(2):113–128. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.2.113-128.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J., Pate J. L. Isolation and characterization of gliding motility mutants of Cytophaga columnaris. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Nov 19;93(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00427927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne E. A., Jr, Greenberg E. P. Relationship between proton motive force and motility in Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1450–1457. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1450-1457.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfen L. N., Castenholz R. W. Gliding in a blue-green alga: a possible mechanism. Nature. 1970 Mar 21;225(5238):1163–1165. doi: 10.1038/2251163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics of structure and function of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. B. Gliding motility in some non-spreading flexibacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;36(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1973.tb04095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Phototrophic green and purple bacteria: a comparative, systematic survey. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:275–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringsheim E. G. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BACTERIA AND MYXOPHYCEAE. Bacteriol Rev. 1949 Jun;13(2):47–98. doi: 10.1128/br.13.2.47-98.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbach H. Taxonomy of the gliding bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:339–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F. Source of energy for gliding motility in Flexibacter polymorphus: effects of metabolic and respiratory inhibitors on gliding movement. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):544–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.544-556.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULZ G. Bewegungsstudien sowie elektronenmikroskopische Membranuntersuchungen an Cyanophyceen. Arch Mikrobiol. 1955;21(4):335–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Genetic analysis of flagellar mutants in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.105-113.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano S. Flexibacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:155–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. A Note on Elasticotaxis in Myxobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1942 Oct;44(4):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.4.405-412.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Cohen-Bazire G. Phototrophic prokaryotes: the cyanobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:225–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. THE CYTOPHAGA GROUP: A CONTRIBUTION TO THE BIOLOGY OF MYXOBACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1942 Sep;6(3):143–196. doi: 10.1128/br.6.3.143-196.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Iino T., Horiguchi T., Yamaguchi S. Incomplete flagellar structures in nonflagellate mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):904–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.904-915.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Komeda Y. Incomplete flagellar structures in Escherichia coli mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1036–1041. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1036-1041.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]