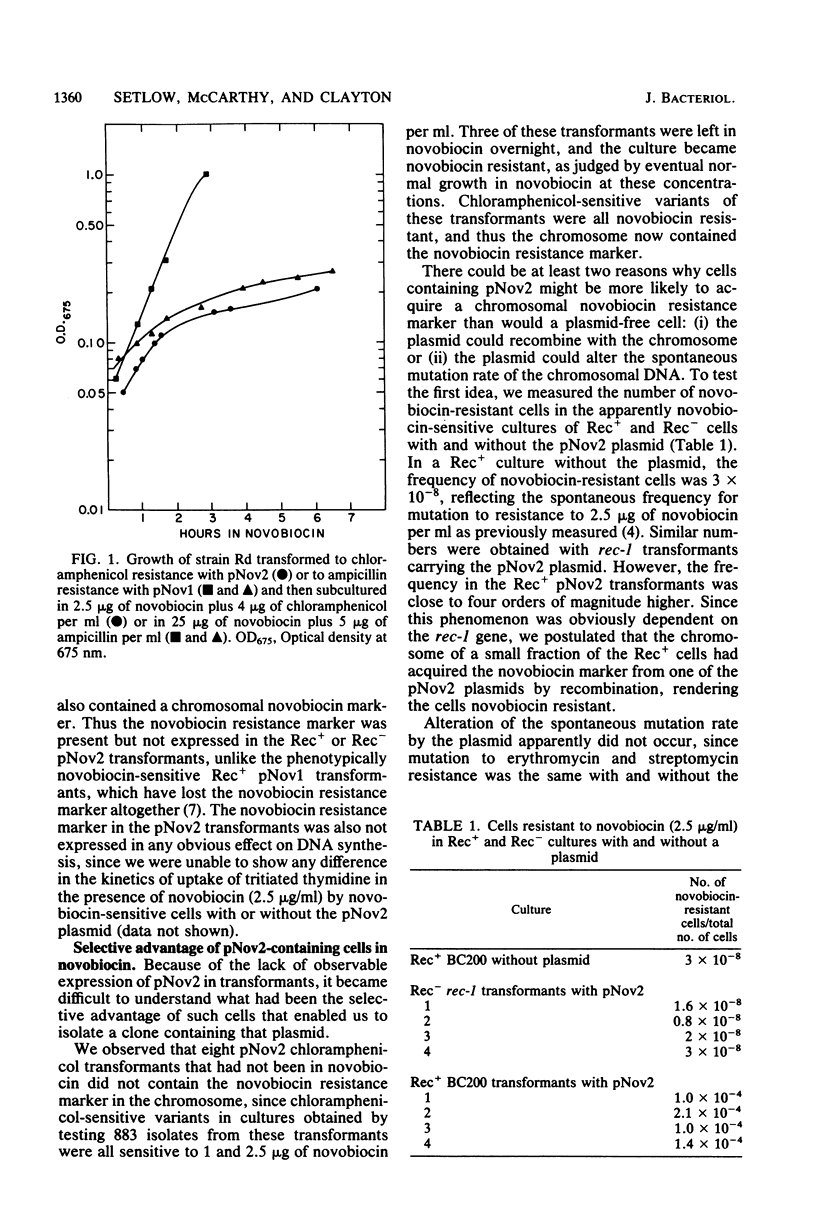
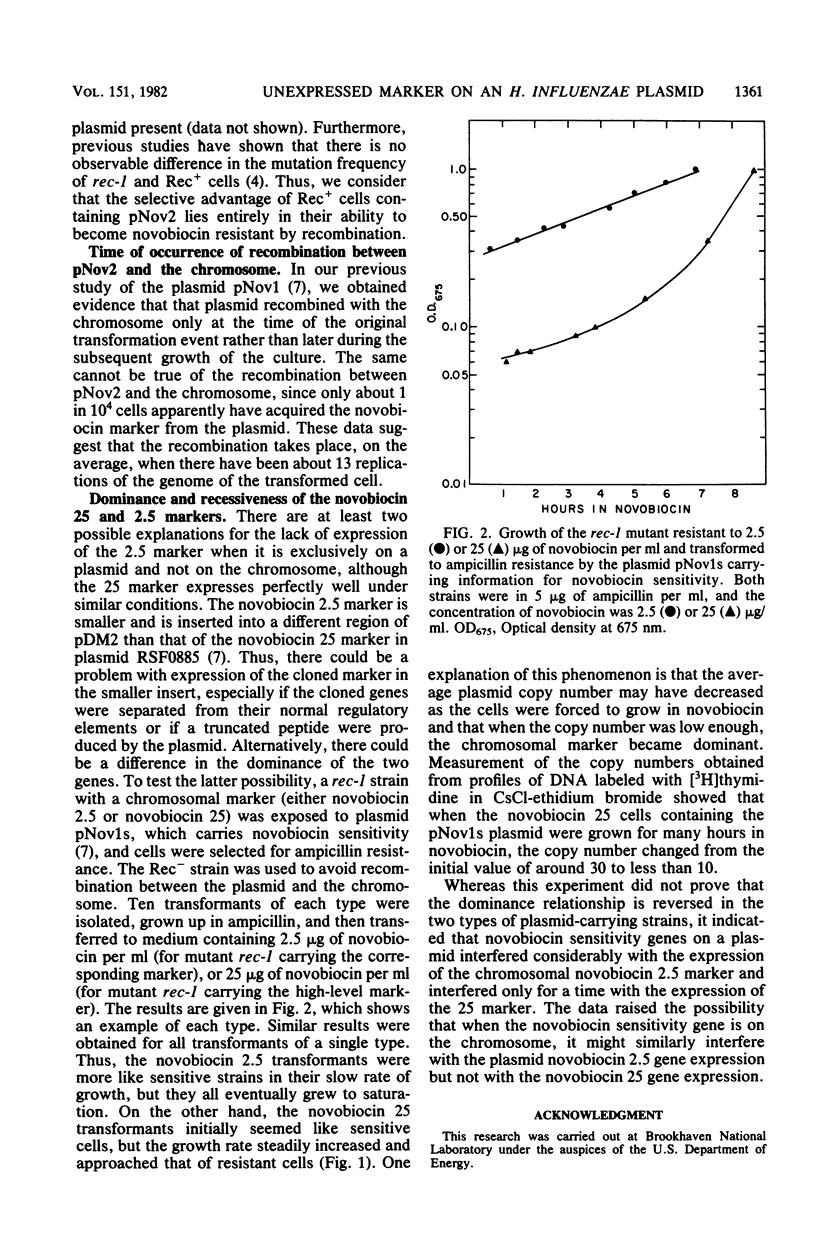
Abstract
The plasmid pNov2, carrying a cloned chromosomal marker conferring resistance to at least 2.5 micrograms of novobiocin per ml, was constructed with a new Haemophilus influenzae cloning vehicle, pDM2. The novobiocin marker of pNov2 was not normally expressed, but in Rec+ cells approximately one in 10(4) cells in a culture of a transformant became novobiocin resistant, a frequency about four orders of magnitude higher than the spontaneous mutation frequency. Variants of such cells that had lost the plasmid were also novobiocin resistant. Since Rec- cultures bearing pNov2 showed novobiocin resistance only at the normal mutation frequency, we concluded that the Rec+ novobiocin-resistant transformants arose because of a rare recombination between plasmid and chromosome in which the chromosome acquired the novobiocin marker from the plasmid. Evidence is presented that novobiocin sensitivity is dominant over this particular novobiocin resistance marker.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boling M. E., Allison D. P., Setlow J. K. Bacteriophage of Haemophilus influenzae. 3. Morphology, DNA homology, and immunity properties of HPlcl, S2, and the defective bacteriophage from strain Rd. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):585–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.585-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. S., 3rd, Rupert C. S. Ultraviolet sensitivity of Haemophilus influenzae transforming DNA. I. Effects of genetic mismatch and target size. Mutat Res. 1971 Mar;11(3):293–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball R. F., Setlow J. K., Liu M. The mutagenic and lethal effects of monofunctional methylating agents in strains of Haemophilus influenzae defective in repair processes. Mutat Res. 1971 May;12(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D., Clayton N. L., Setlow J. K. A plasmid cloning vehicle for Haemophilus influenzae and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1605–1607. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1605-1607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notani N. K., Setlow J. K., McCarthy D., Clayton N. L. Transformation of Haemophilus influenzae by plasmid RSF0885. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):812–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.812-816.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow J. K., Notani N. K., McCarthy D., Clayton N. L. Transformation of Haemophilus influenzae by plasmid RSF0885 containing a cloned segment of chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):804–811. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.804-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Goodgal S. H. Loss of activity of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid after uptake by Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):873–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.873-883.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


