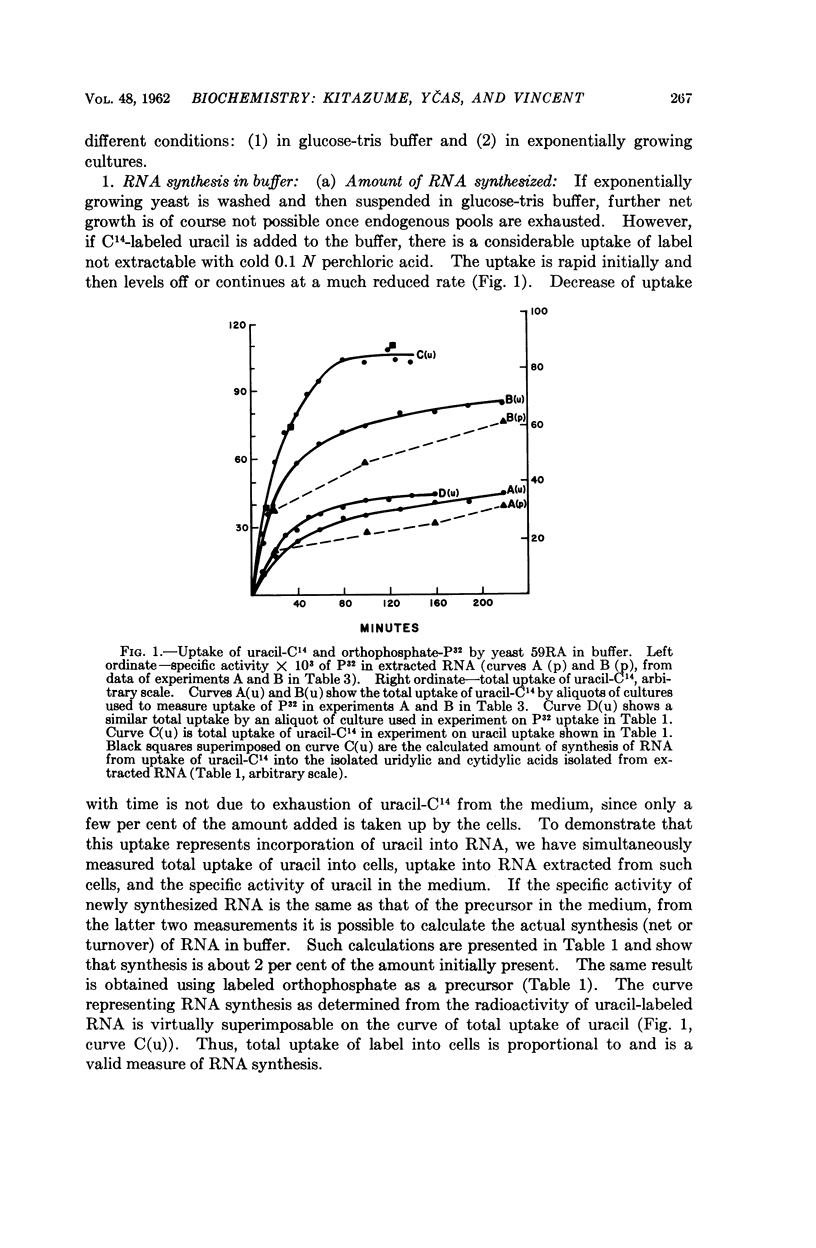
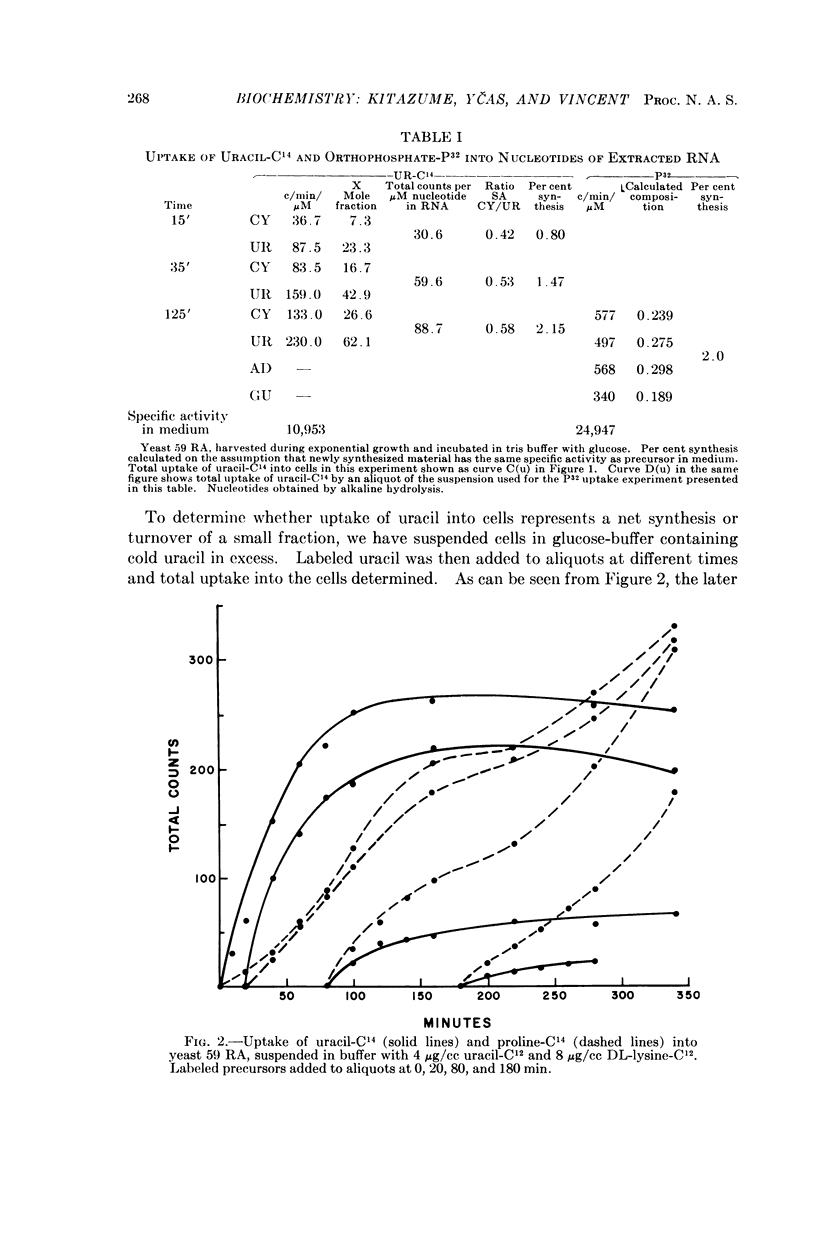
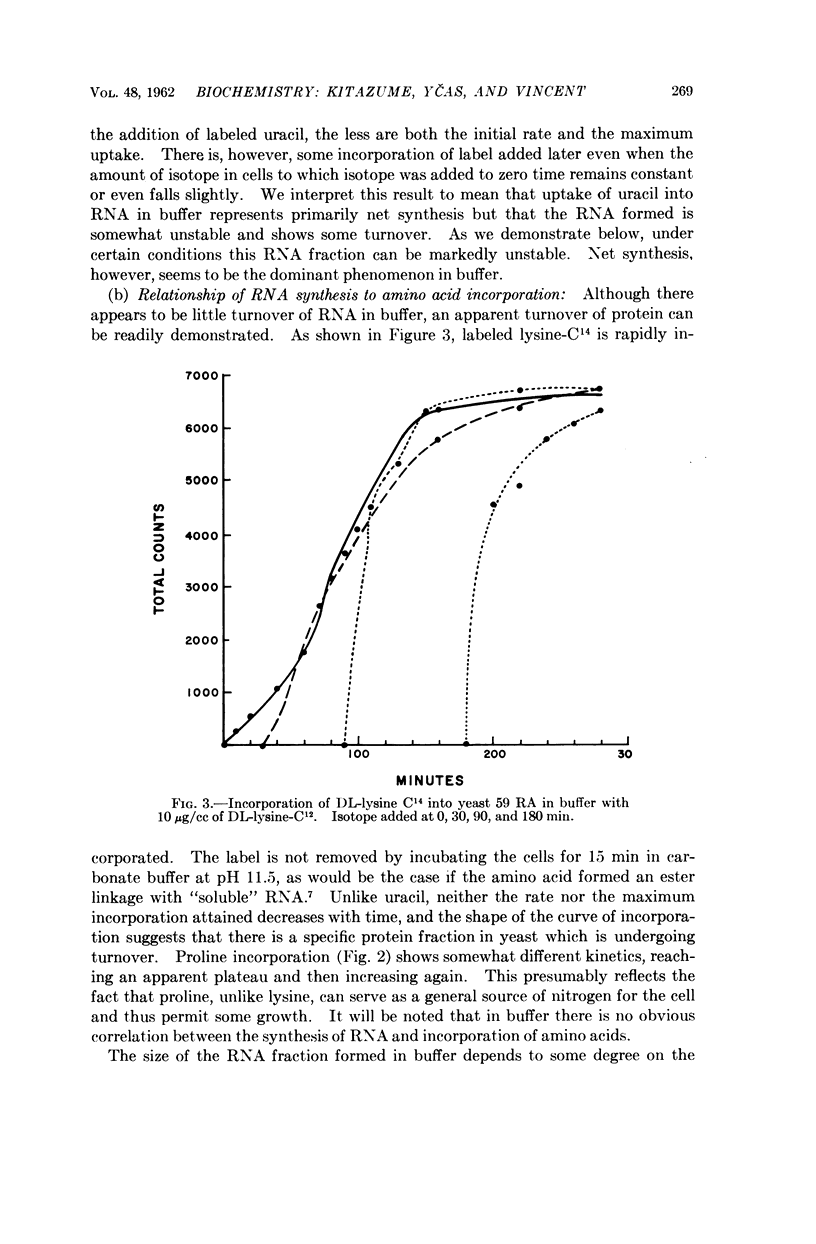
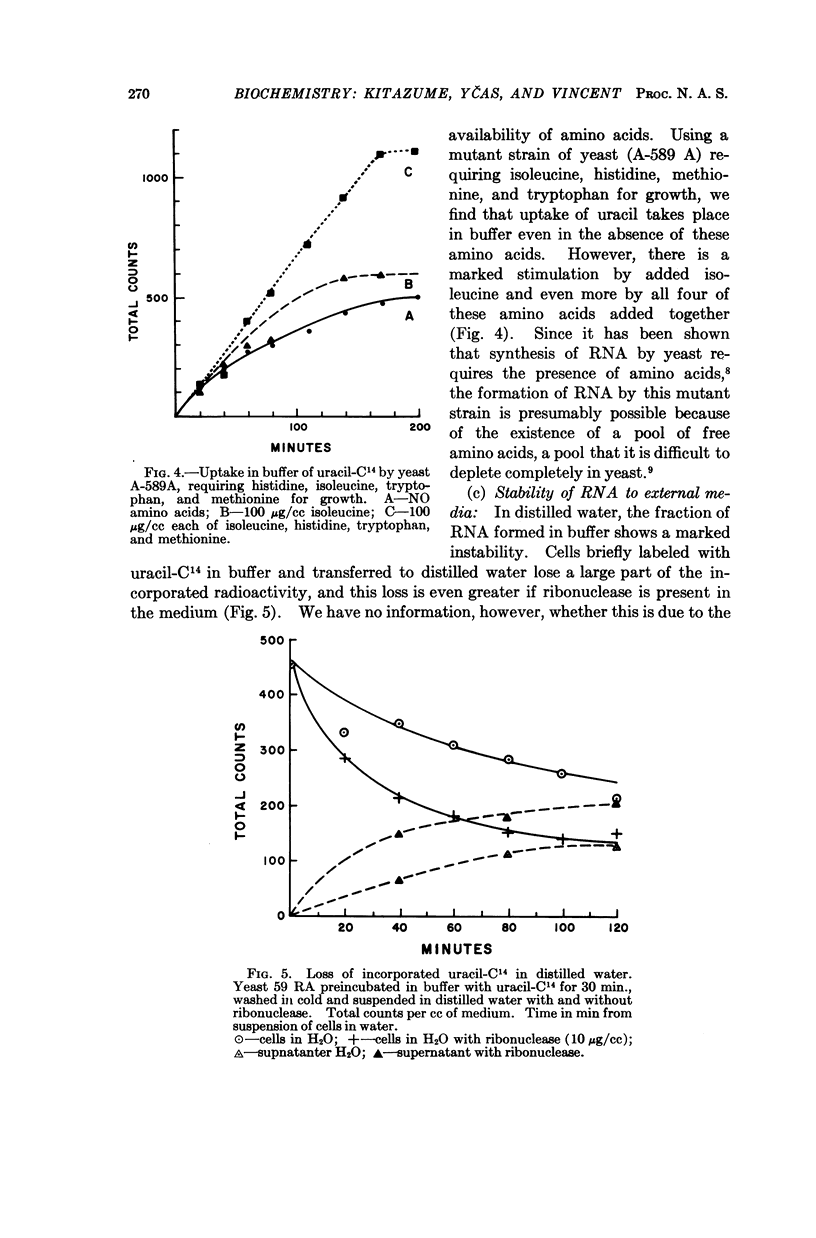
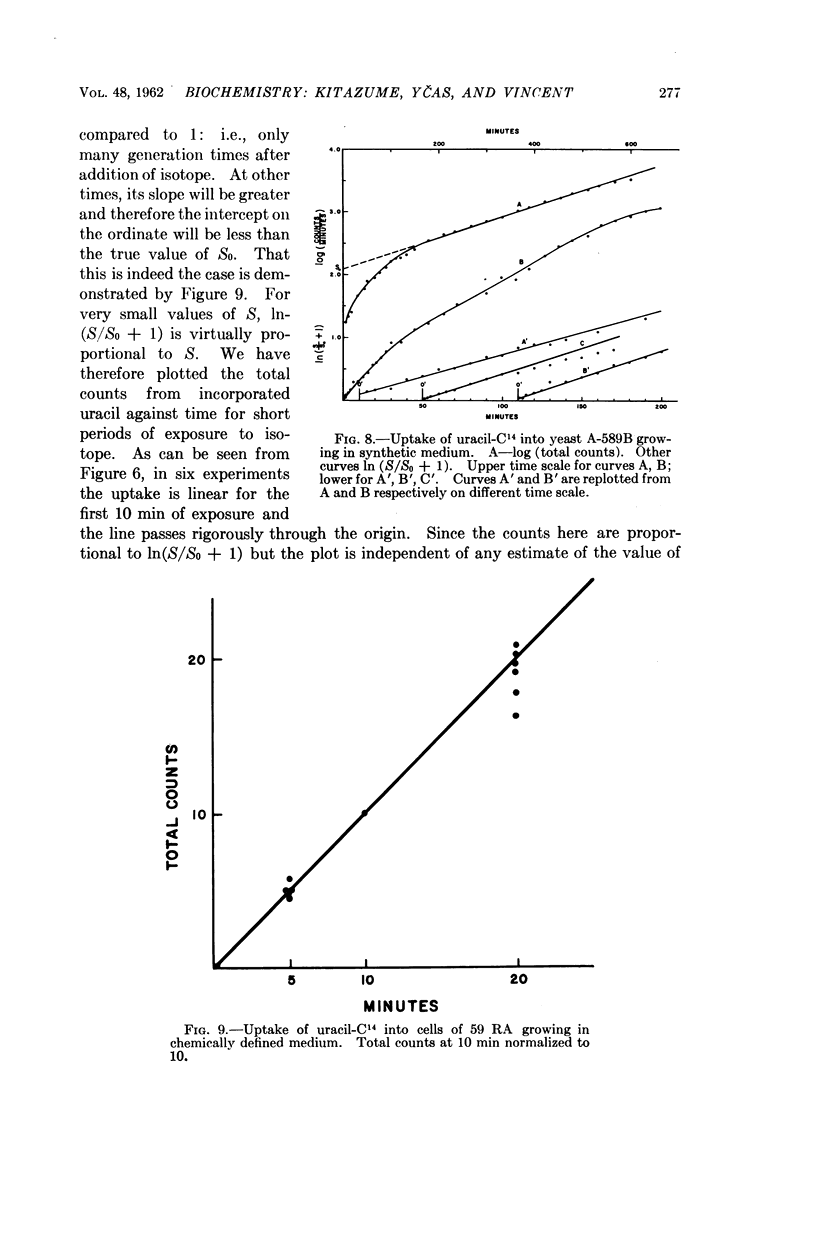
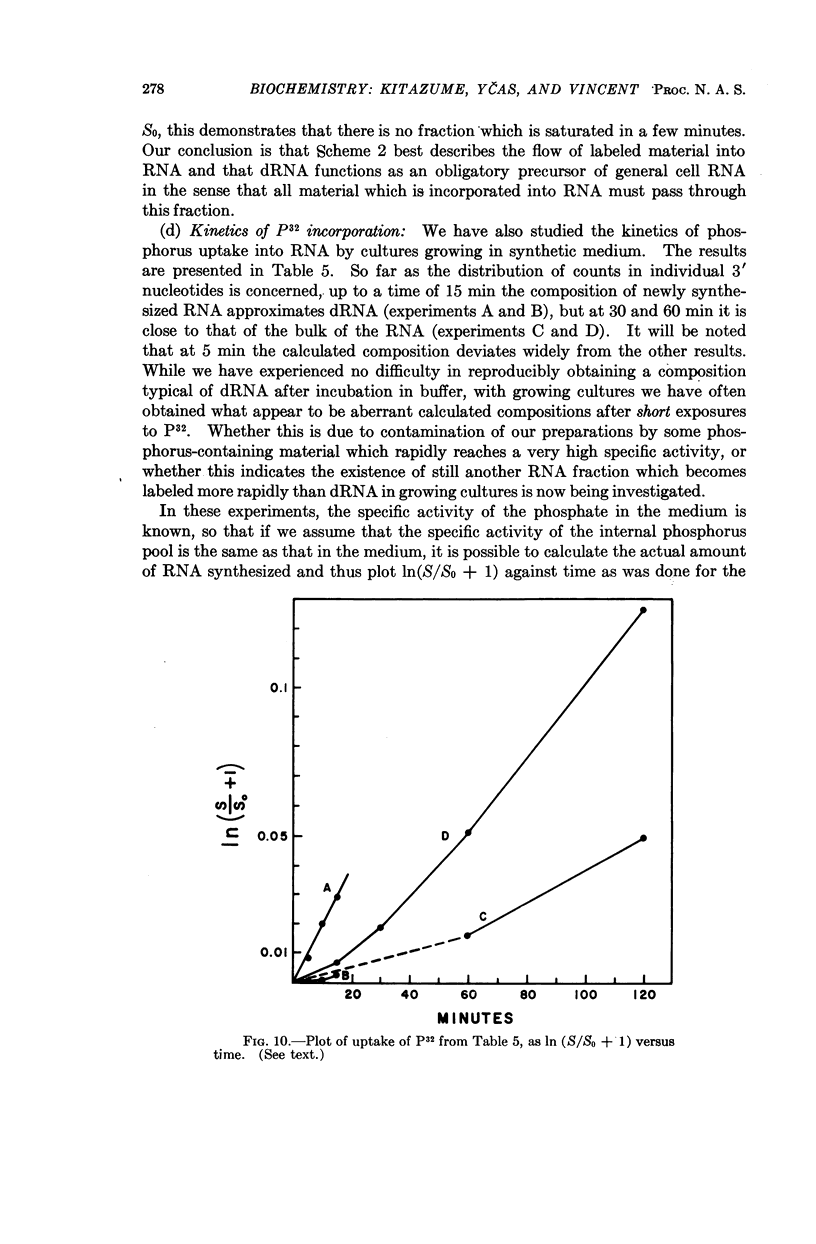
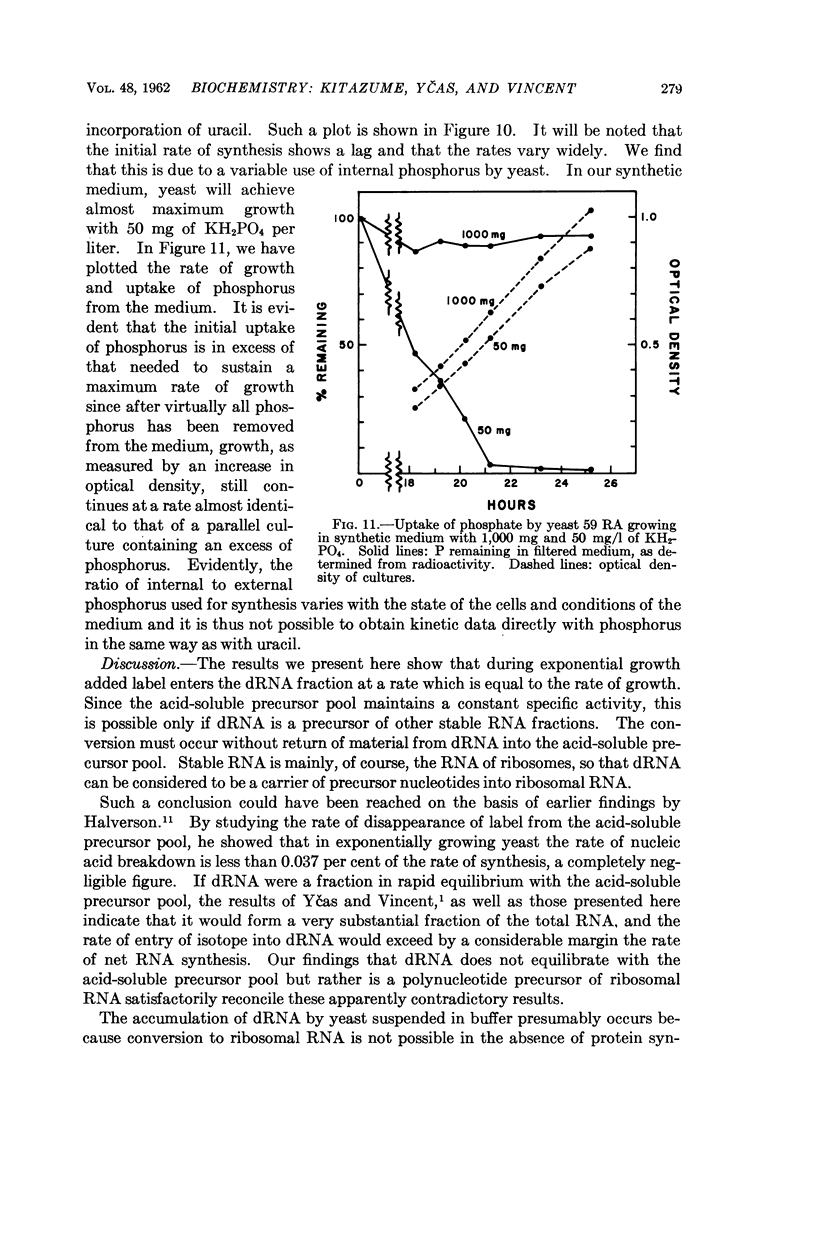
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISHOP J., FAVELUKES G., SCHWEET R., RUSSELL E. Control of specificity in haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1961 Sep 30;191:1365–1368. doi: 10.1038/1911365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAWERMAN G., YCAS M. Incorporation of the amino acid analog tryptazan into the protein of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 May;68(1):112–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROS F., HIATT H., GILBERT W., KURLAND C. G., RISEBROUGH R. W., WATSON J. D. Unstable ribonucleic acid revealed by pulse labelling of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1961 May 13;190:581–585. doi: 10.1038/190581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. O., SPIEGELMAN S. The effect of free amino acid pool levels on the induced synthesis of enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):496–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.496-504.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. Studies on protein and nucleic acid turnover in growing cultures of yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., SPIEGELMAN S. The selective synthesis of informational RNA in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1564–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Berg P., Ofengand E. J., Bergmann F. H., Dieckmann M. THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF THE RNA-AMINO ACID COMPOUND FORMED BY AMINO ACID-ACTIVATING ENZYMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Mar;45(3):319–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKIN E., ASTRACHAN L., COUNTRYMAN J. L. Metabolism of RNA phosphorus in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1958 Oct;6(2):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YCAS M., VINCENT W. S. The ribonucleic acid of Epanaphe moloneyi Druce. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Dec;21:513–522. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ycas M., Vincent W. S. A RIBONUCLEIC ACID FRACTION FROM YEAST RELATED IN COMPOSITION TO DESOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jun;46(6):804–811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.6.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZALOKAR M. Sites of protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis in the cell. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Apr;19:559–576. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


