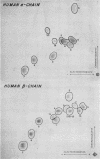
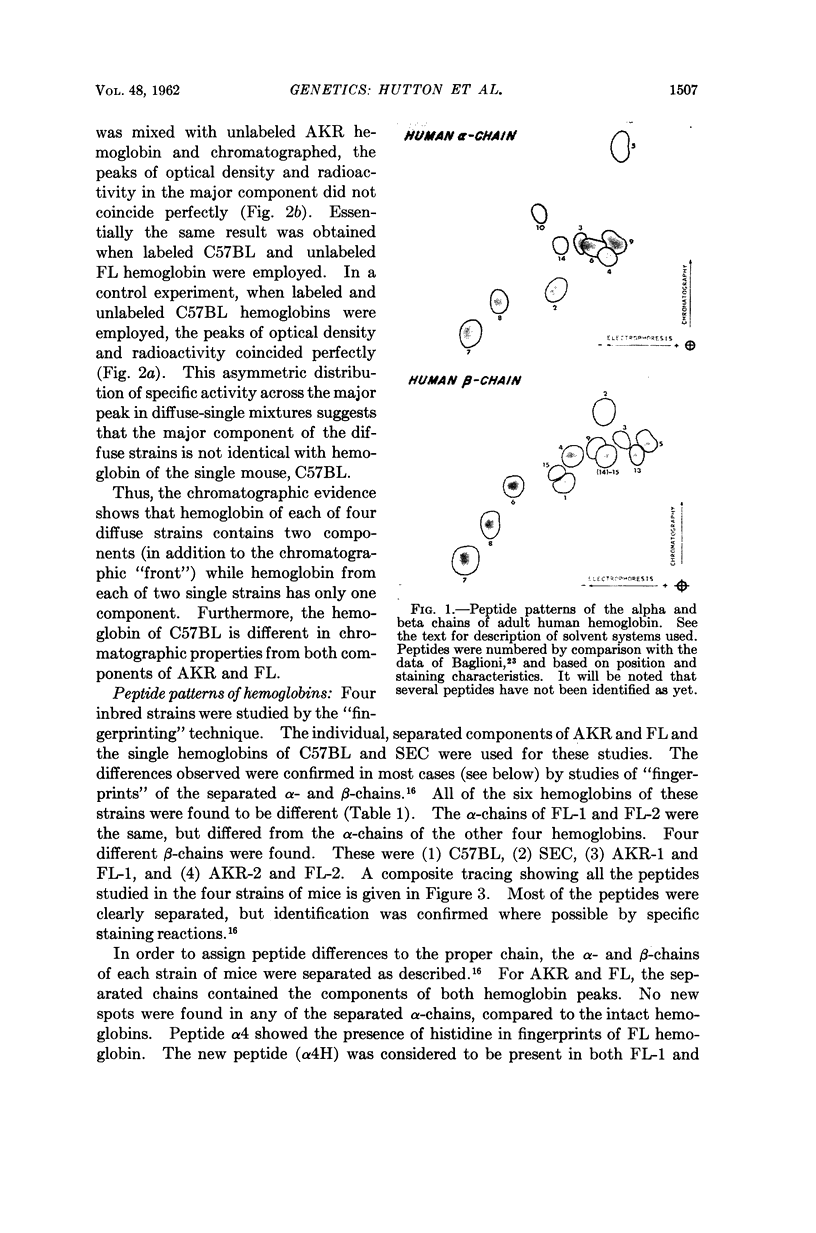
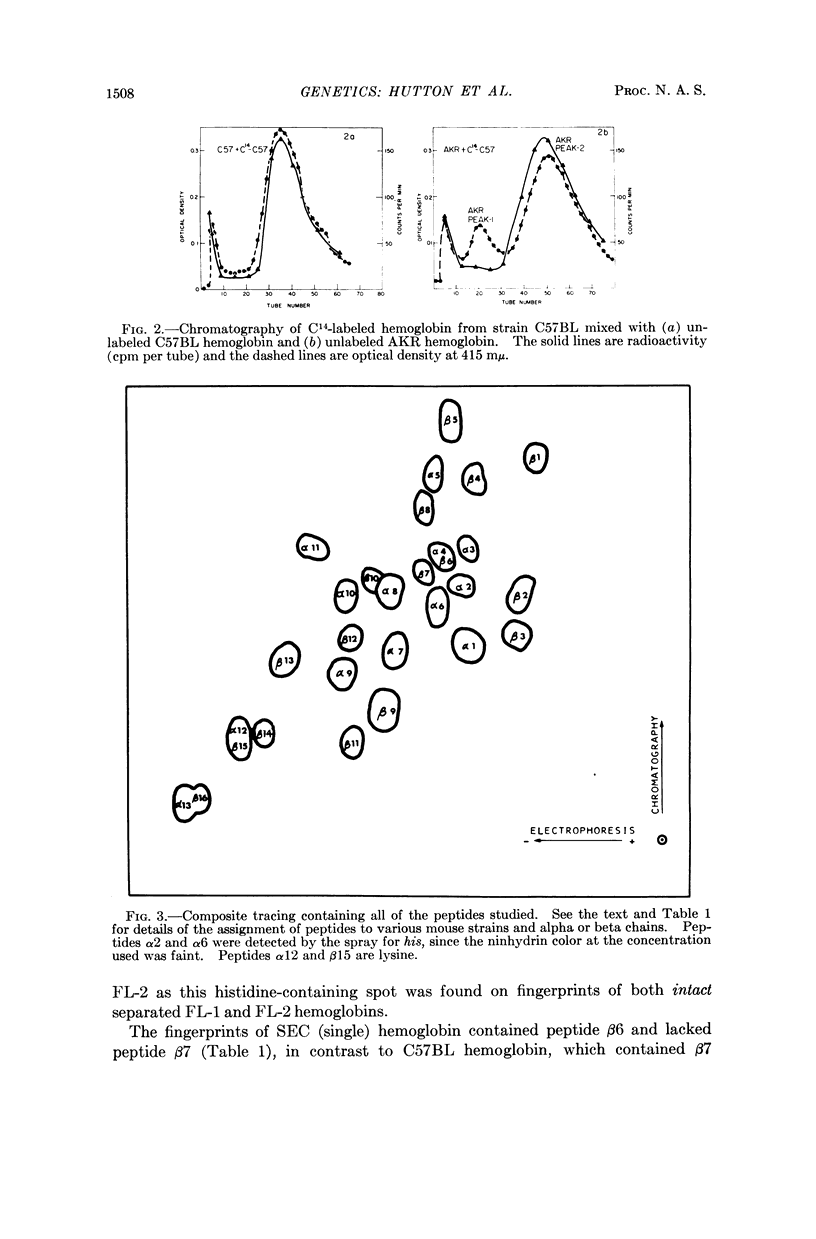
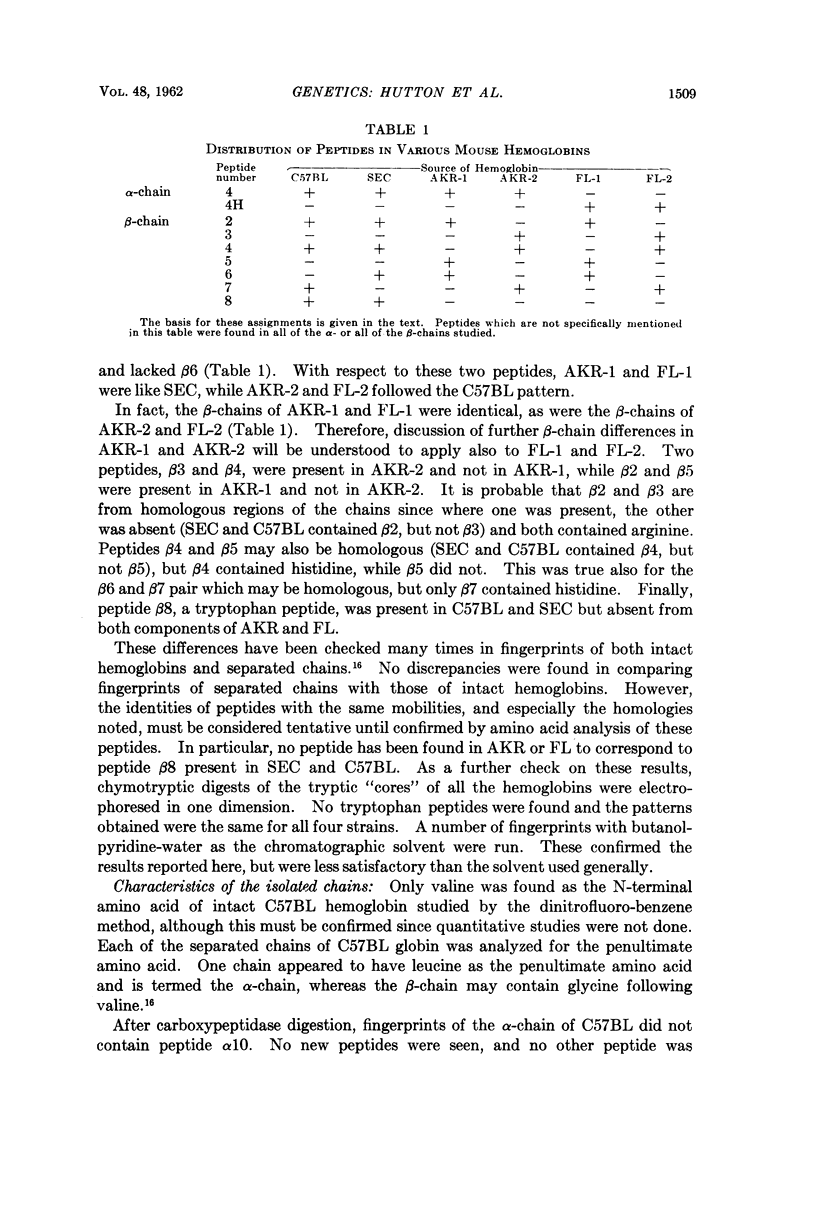
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAGLIONI C. An improved method for the fingerprinting of human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 1;48:392–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP J., FAVELUKES G., SCHWEET R., RUSSELL E. Control of specificity in haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1961 Sep 30;191:1365–1368. doi: 10.1038/1911365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J., Leahy J., Schweet R. FORMATION OF THE PEPTIDE CHAIN OF HEMOGLOBIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1030–1038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNOFF A. I., LIU J. C. The amino acid composition of hemoglobin. II. Analytical technics. Blood. 1961 Jan;17:54–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANELLI A. R., ANTONINI E., CAPUTO A. Studies on the structure of hemoglobin. I. Physicochemical properties of human globin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):608–615. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLUECKSOHN-WAELSCH S., RANNEY H. M., SISKEN B. F. The hereditary transmission of hemoglobin differences in mice. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jun;36(6 Pt 1):753–756. doi: 10.1172/JCI103479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIDOTTI G. The action of carboxypeptidases A and B on the separated alpha and beta chains of normal adult human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:177–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. L., SWENSON R. T., SCHWARTZ H. C. Characterization of a chemical abnormality in hemoglobin G. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3182–3187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. A., INGRAM V. M. Abnormal human haemoglobins. II. The chymotryptic digestion of the trypsin-resistant core of haemoglobins A and S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jun;28(3):546–549. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. A. Identity of the alpha-chains of adult and foetal human haemoglobins. Nature. 1959 May 16;183(4672):1373–1375. doi: 10.1038/1831373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM V. M. Gene evolution and the haemoglobins. Nature. 1961 Mar 4;189:704–708. doi: 10.1038/189704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM V. M., STRETTON A. O. Human haemoglobin A2: chemistry, genetics and evolution. Nature. 1961 Jun 17;190:1079–1084. doi: 10.1038/1901079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ A. M., DREYER W. J., ANFINSEN C. B. Peptide separation by two-dimensional chromatography and electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2897–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPP R. A., COSGROVE G. E. Solubility of hemoglobin as red cell marker in irradiated mouse chimeras. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:754–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANNEY H. M., GLUECKSOHN-WAELSCH S. Filter-paper electrophoresis of mouse haemoglobin: preliminary note. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):269–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSA J., SCHAPIRA G., DREYFUS J. C., DE GROUCH J., MATHE G., BERNARD J. Different heterogeneities of mouse haemoglobin according to strains. Nature. 1958 Oct 4;182(4640):947–948. doi: 10.1038/182947a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL E. S., GERALD P. S. Inherited electrophoretic hemoglobin patterns among 20 inbred strains of mice. Science. 1958 Dec 19;128(3338):1569–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3338.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. B., HAUG A., WILSON S. Physical and chemical studies on horse globin components. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):766–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON H. C., KENDREW J. C. The amino-acid sequence of sperm whale myoglobin. Comparison between the amino-acid sequences of sperm whale myoglobin and of human hemoglobin. Nature. 1961 May 20;190:670–672. doi: 10.1038/190670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLING W., VAN BEKKUM B. W. Different types of haemoglobin in two strains of mice. Nature. 1958 Oct 4;182(4640):946–947. doi: 10.1038/182946b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON S., SMITH D. B. Separation of the valyl-leucyl- and valyl-glutamyl-polypeptide chains of horse globin by fractional precipitation and column chromatography. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Mar;37(3):405–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E., Jones R. T., Pauling L. A COMPARISON OF ANIMAL HEMOGLOBINS BY TRYPTIC PEPTIDE PATTERN ANALYSIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Oct;46(10):1349–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.10.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]