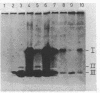
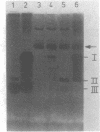
Abstract
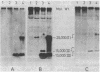
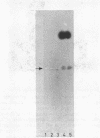
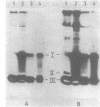
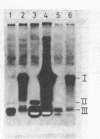
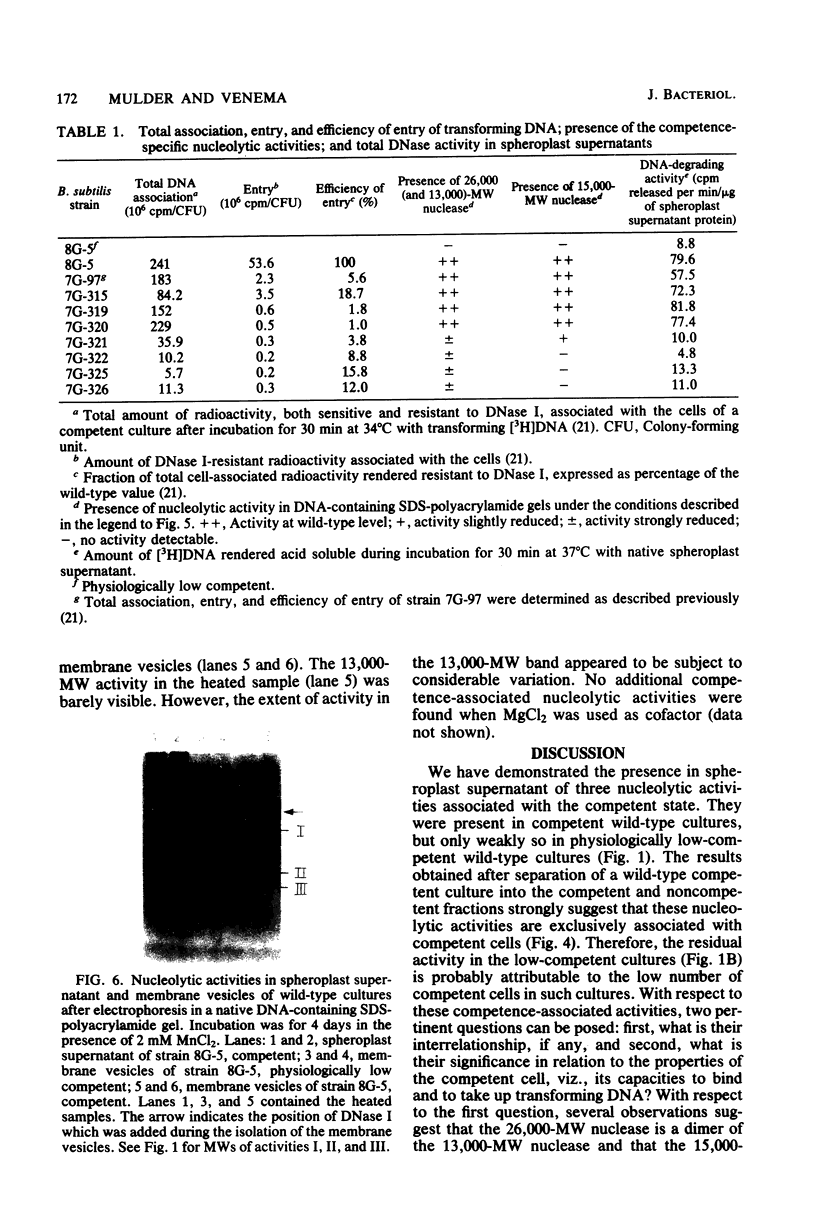
A comparison of the nucleolytic activities in competent and physiologically low-competent wild-type cultures of Bacillus subtilis in DNA-containing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels revealed the existence of three competence-associated nuclease activities with apparent molecular weights of 13,000, 15,000, and 26,000. The three activities, which were dependent on manganese or magnesium ions, were specifically present in the competent fraction of a competent culture. The competence-associated nucleolytic activities of eight transformation-defective mutant strains were assayed, resulting in the following three classes of mutants: (i) four strains which, according to this assay, were not impaired in any of the nucleolytic activities mentioned above; (ii) one strain which was strongly impaired in the 13,000- and 26,000-molecular-weight activities, but showed a considerable level of the 15,000-molecular-weight activity; and (iii) three strains which were severely impaired in all three activities. The results indicated that the 26,000-molecular-weight activity was a dimer of the 13,000-molecular-weight activity and that this nuclease was involved in the entry of DNA.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bron S., Venema G. Ultraviolet inactivation and excision-repair in Bacillus subtilis. I. Construction and characterization of a transformable eightfold auxotrophic strain and two ultraviolet-sensitive derivatives. Mutat Res. 1972 May;15(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(72)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buitenwerf J., Venema G. Transformation in bacillus subtilis: fate of transforming DNA in transformation deficient mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):203–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00338696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W. F., Jr, Spizizen J. Isolation, characterization, and activation of the magnesium dependent endodeoxyribonuclease from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):403–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff-Abelson R., Dubnau D. Conditions affecting the isolation from transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis of high-molecular-weight single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid of donor origin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):146–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.146-153.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff-Abelson R., Dubnau D. Kinetic analysis of the products of donor deoxyribonucleate in transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):154–162. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.154-162.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doly J., Sasarman E., Anagnostopoulos C. ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease in Bacillus subtilis and a mutant deficient in this activity. Mutat Res. 1974 Jan;22(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Cirigliano C. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. Formation and properties of products isolated from transformed cells which are derived entirely from donor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):9–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Konings W. N., Venema G. Interactions between exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and membrane vesicles isolated from competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):771–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.771-776.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Venema G. Different nuclease activities in competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):25–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.25-33.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Bisschop A., Veenhuis M., Vermeulen C. A. New procedure for the isolation of membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis and an electron microscopy study of their ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1456–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1456-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Competence for deoxyribonucleic acid uptake and deoxyribonuclease action external to cells in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):152–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.152-163.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Identification of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.222-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Neuberger M. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1321–1329. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1321-1329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C., Nester E. W. Heat-activated endonuclease in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1426–1430. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1426-1430.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Early intermediate state of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid during uptake by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.38-44.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Breakage prior to entry of donor DNA in Pneumococcus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder J. A., Venema G. Isolation and partial characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants impaired in DNA entry. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):260–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.260-268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechowska M., Fox M. S. Fate of transforming deoxyribonucleate in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):680–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.680-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. L., Lacks S. A. Nuclease detection in SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 15;80(1):76–90. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher B., Dubnau D. A manganese-stimulated endonuclease from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher B., Dubnau Purification and properties of a manganese-stimulated endonuclease from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):429–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.429-438.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Tomasz A. Early stages in DNA binding and uptake during genetic transformation of pneumococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]