Abstract
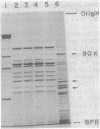
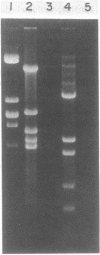
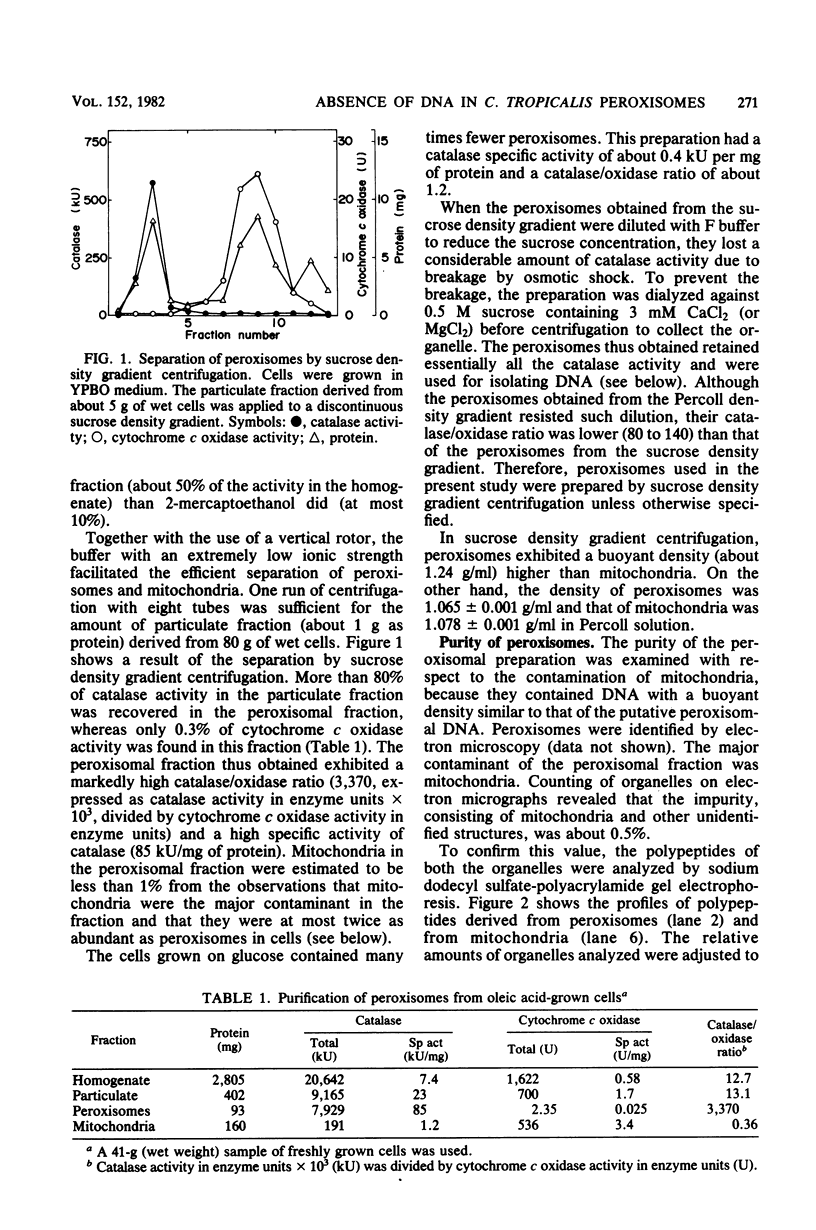
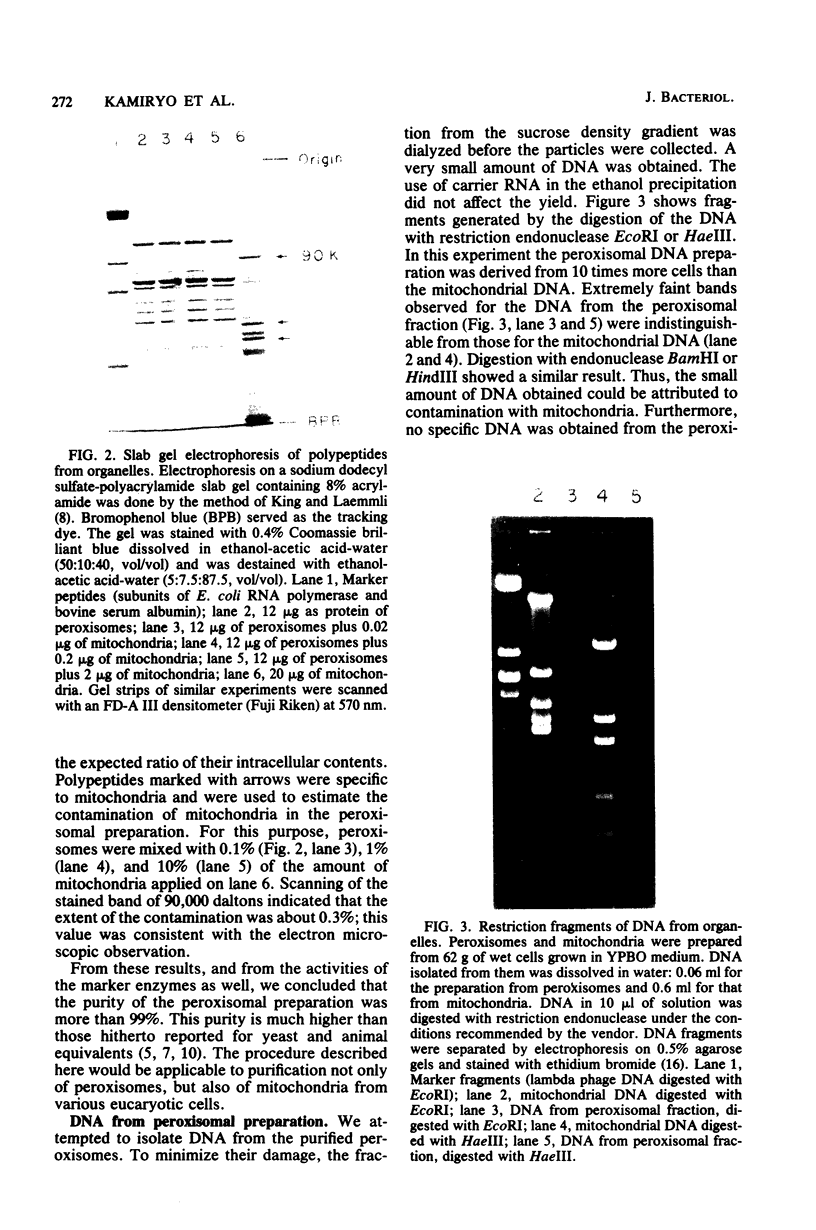
Yeast peroxisomes were purified to near homogeneity from cells of Candida tropicalis grown on oleic acid for the purpose of examining the possible presence of DNA in this organelle. The purification procedure includes the effective conversion of cells to spheroplasts with Zymolyase and sodium sulfite and the separation of the organelles at extremely low ionic strength. The mitochondrial contamination was less than 1%, based on several criteria, and the yield of peroxisomes was about 40%. The purified peroxisomal fraction contained a very small amount of DNA, which yielded restriction fragments indistinguishable from those of mitochondrial DNA. The absence of DNA in peroxisomes was also supported by cesium chloride density gradient centrifugation of the organelles lysed with a detergent, staining of the organelles with a fluorescent dye specific to DNA, and labeling of the DNA with [3H]adenine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiryo T., Mishina M., Tashiro S. I., Numa S. Candida lipolytica mutants defective in an acyl-coenzyme A synthetase: isolation and fatty acid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4947–4950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiryo T., Nishikawa Y., Mishina M., Terao M., Numa S. Involvement of long-chain acyl coenzyme A for lipid synthesis in repression of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in Candida lipolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4390–4394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Tanaka A., Yamamura M., Teranishi Y., Fukui S. Microbody of n-alkane-grown yeast. Enzyme localization in the isolated microbody. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00446647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisans S. K., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Acyl-CoA synthetase in rat liver peroxisomes. Computer-assisted analysis of cell fractionation experiments. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9599–9607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Kamiryo T., Tashiro S., Hagihara T., Tanaka A., Fukui S., Osumi M., Numa S. Subcellular localization of two long-chain acyl-coenzyme-A synthetases in Candida lipolytica. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Kamiryo T., Tashiro S., Numa S. Separation and characterization of two long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases from Candida lipolytica. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi M., Kazama H. Microbody-associated DNA in Candida tropicalis pK 233 cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80393-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi M., Miwa N., Teranishi Y., Tanaka A., Fukui S. Ultrastructure of Candida yeasts grown on n-alkanes. Appearance of microbodies and its relationship to high catalase activity. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):181–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00696234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis E. S., Bartley W., Meek G. A. Changes in the structure and enzyme activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to changes in the environment. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj0900369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder P. High capacity gel preparative electrophoresis for purification of fragments of genomic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggenkamp R., Sahm H., Wagner F. Microbial assimilation of methanol induction and function of catalase in Candida boidinii. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigenaka Y., Roth L. E., Pihlaja D. J. Microtubules in the heliozoan axopodium. 3. Degradation and reformation after dilute urea treatment. J Cell Sci. 1971 Jan;8(1):127–151. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. The use of fluorescent DNA-binding agent for detecting and separating yeast mitochondrial DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:335–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]