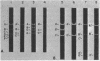
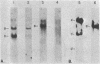
Abstract
Two clindamycin-erythromycin resistance transfer factors of Bacteroides fragilis, pBF4 and pBFTM10, were analyzed for regions of DNA homology. Although the plasmids were derived from different clinical isolates of B. fragilis and have different sizes, they showed homology in the clindamycin-erythromycin resistance region; no homology could be detected outside of this region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magot M., Fayolle F., Privitera G., Sebald M. Transposon-like structures in the Bacteroides fragilis MLS plasmid plP 410. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(4):559–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00428754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy M. H., Tally F. P. Mechanisms of drug-resistance transfer in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):59–75. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays T. D., Smith C. J., Welch R. A., Delfini C., Macrina F. L. Novel antibiotic resistance transfer in Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):110–118. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privitera G., Dublanchet A., Sebald M. Transfer of multiple antibiotic resistance between subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):97–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi V. O., Duerden B. I., Hafiz S. Transferable plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance in Bacteroides. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):359–370. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Snydman D. R., Gorbach S. L., Malamy M. H. Plasmid-mediated, transferable resistance to clindamycin and erythromycin in Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Snydman D. R., Shimell M. J., Malamy M. H. Characterization of pBFTM10, a clindamycin-erythromycin resistance transfer factor from Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.686-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Jones K. R., Macrina F. L. Transferable lincosamide-macrolide resistance in Bacteroides. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Macrina F. L. Physical characterization of Bacteroides fragilis R plasmid pBF4. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):867–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.867-872.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]