Abstract
Selenomonas ruminantium, a strictly anaerobic, gram-negative bacterium isolated from sheep rumen, contains lysine decarboxylase (Y. Kamio et al., J. Bacteriol. 145:122-128, 1981). This report describes the synthesis, purification, and characterization of the enzyme. Lysine decarboxylase was synthesized in cells grown in chemically defined medium without lysine. The enzyme was purified approximately 1,800-fold to electrophoretic homogeneity. The native enzyme of approximate molecular weight 88,000 consisted of two identical subunits, each with a molecular weight of 44,000. Several properties of the enzyme were determined and compared with those of the lysine decarboxylases from Escherichia coli and Bacterium cadaverisis.
Full text
PDF

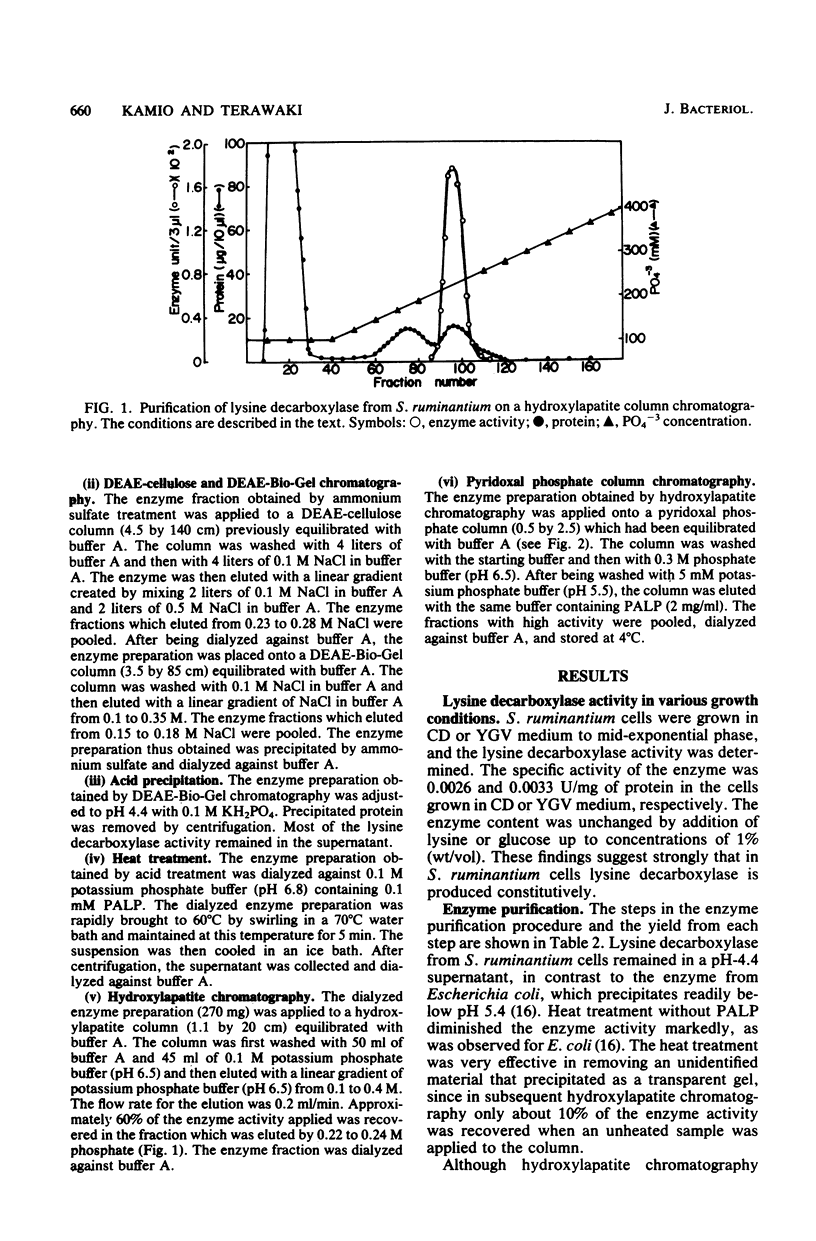
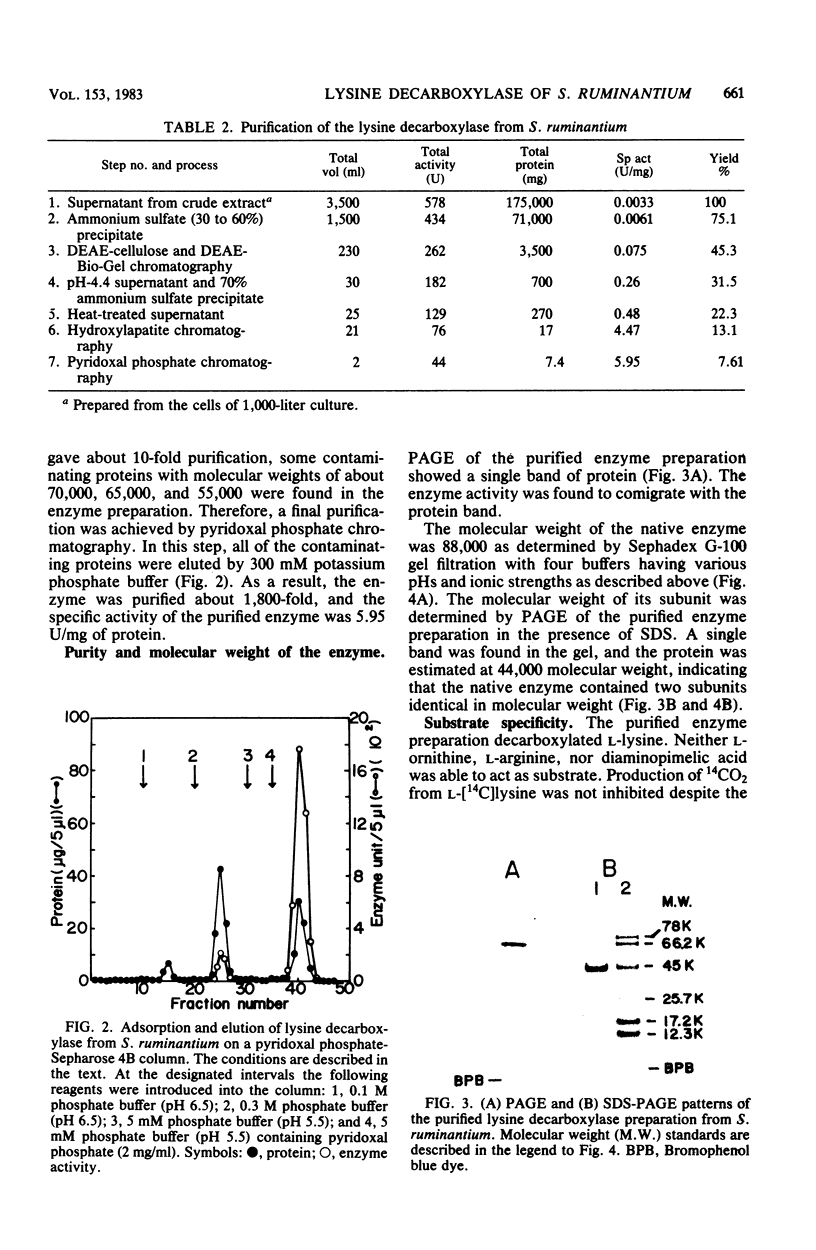



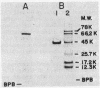
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeker E. A., Fischer E. H., Snell E. E. Arginine decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. 3. Subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5239–5245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeker E. A., Snell E. E. Arginine decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. II. Dissociation and reassociation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1678–1684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Itoh Y., Terawaki Y. Chemical structure of peptidoglycan in Selenomonas ruminantium: cadaverine links covalently to the D-glutamic acid residue of peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.49-53.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Itoh Y., Terawaki Y., Kusano T. Cadaverine is covalently linked to peptidoglycan in Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):122–128. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.122-128.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Takahashi H. Isolation and characterization of outer and inner membranes of Selenomonas ruminantium: lipid compositions. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):888–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.888-898.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Takahashi H. Outer membrane proteins and cell surface structure of Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.899-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Terawaki Y., Izaki K. Biosynthesis of cadaverine-containing peptidoglycan in Selenomonas ruminantium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3326–3333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Pardee A. B. A biosynthetic ornithine decarboxylase in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 22;20(6):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan E., Fottrell P. F. Interactions between an unusual aspartate aminotransferase from Rhizobium japonicum and pyridoxal-5'-phosphate studied by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80288-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabo D. L., Boeker E. A., Byers B., Waron H., Fischer E. H. Purification and physical properties of inducible Escherichia coli lysine decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):662–670. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Hespell R. B., Bryant M. P. Ammonia assimilation and glutamate formation in the anaerobe Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):593–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.593-602.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soda K., Moriguchi M. Crystalline lysine decarboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 6;34(1):34–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90524-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbauch P. H., Fischer E. H. Chemical and physical properties of Escherichia coli glutamate decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):226–233. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Isolation of ureolytic Peptostreptococcus productus from feces using defined medium; failure of common urease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):594–599. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.594-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]