Abstract
Assays of intracellular ATP, ADP, and inorganic phosphate allowed calculation of the phosphorylation potential (delta G'ATP/F) maintained during glycolysis by Streptococcus lactis. At the same time, the electrochemical H+ gradient (delta mu-H+/F) was evaluated by distribution methods, using radioactive tetraphenylphosphonium bromide as a probe for the membrane potential and salicylic acid as a probe for the pH gradient. Detailed comparisons were made at pH 5, when the reaction mediated by the proton-translocating ATPase (BF0F1) was likely to have been poised near equilibrium; for those conditions, the ratio delta G'ATP/delta mu-H+ was used to estimate stoichiometry for BF0F1 during ATP hydrolysis. At an external pH of 5, in the presence or absence of valinomycin, this ratio was close to 3, over a range of 370 to 510 mV (8.5 to 11.7 kcal/mol) for delta G'ATP/F and a range of 128 to 167 mV for delta mu-H+/F. Other work suggested that delta G'ATP/delta mu-H+ increased from its minimum value of 3 to 4.3 as the external pH changed from pH 5 to 7.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anner B., Mossmayer M. Rapid determination of inorganic phosphate in biological systems by a highly sensitive photometric method. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
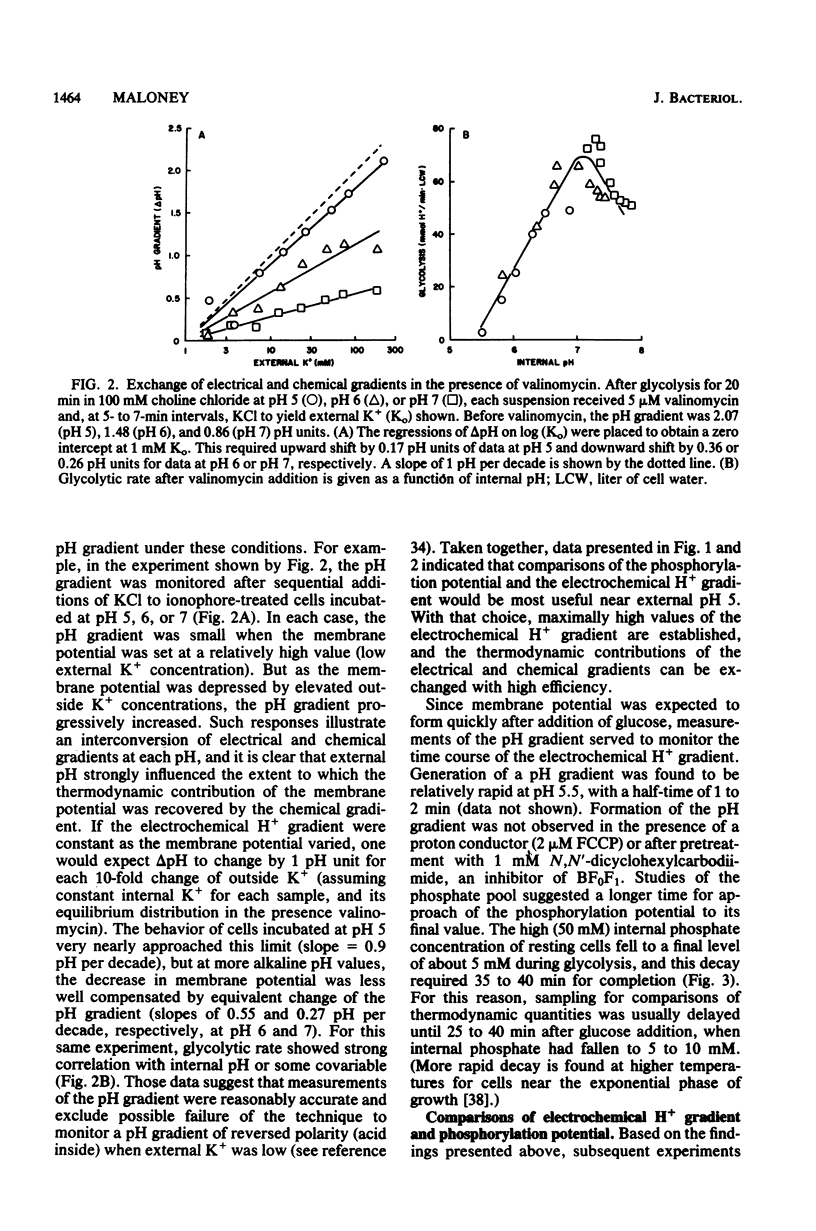
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Lehninger A. L. H+/ATP ratio during ATP hydrolysis by mitochondria: modification of the chemiosmotic theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport J. W., McCarty R. E. Quantitative aspects of adenosine triphosphate-driven proton translocation in spinach chloroplast thylakoids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8947–8954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey T. G., Hammes G. G. Steady state kinetics of ATP synthesis and hydrolysis catalyzed by reconstituted chloroplast coupling factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8941–8946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Porter J. S., Slayman C. L., Kaback H. R. Quantitative measurements of membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I., Kaback H. R. Electrochemical proton gradient in Micrococcus lysodeikticus cells and membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):651–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.651-658.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Blumenfeld H., Krulwich T. A. ATP synthesis by an uncoupler-resistant mutant of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8416–8421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Krulwich T. A. Oxidative phosphorylation by membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 13;635(3):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Susman P., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. The protonmotive force and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in an obligately alkalophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):708–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guynn R. W., Veech R. L. The equilibrium constants of the adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis and the adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase reactions. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):6966–6972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Levin E. Lactic acid translocation: terminal step in glycolysis by Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1141–1148. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1141-1148.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. I. The membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):27–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01868093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Pavlasová E., Baarda J. R. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Van Brunt J. Circulation of H+ and K+ across the plasma membrane is not obligatory for bacterial growth. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):372–373. doi: 10.1126/science.69317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Blanchard A. G., Metzger W. C. Proton motive force during growth of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.128-134.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.369-376.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Stoichiometry of the H+-ATPase of growing and resting, aerobic Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5534–5538. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., Ferguson S. J., John P. Measurement by a flow dialysis technique of the steady-state proton-motive force in chromatophores from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Comparison with phosphorylation potential. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 11;502(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., John P., Ferguson S. J. The protonmotive force in phosphorylating membrane vesicles from Paracoccus denitrificans. Magnitude, sites of generation and comparison with the phosphorylation potential. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):257–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1740257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J., Billica W. H. Non-equilibrium thermodynamics of oxidative phosphorylation by inverted inner membrane vesicles of rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12949–12957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Tsien R. Y., Miner C., Bookchin R. M. Physiological [Ca2+]i level and pump-leak turnover in intact red cells measured using an incorporated Ca chelator. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):478–481. doi: 10.1038/298478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Energy coupling to ATP synthesis by the proton-translocating ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Hansen F. C., 3rd Stoichiometry of proton movements coupled to ATP synthesis driven by a pH gradient in Streptococcus lactis. J Membr Biol. 1982;66(1):63–75. doi: 10.1007/BF01868482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. A protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Obligatory coupling between proton entry and the synthesis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.564-575.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty R. E., Portis A. R., Jr A simple, quantitative approach to the coupling of photophosphorylation to electron flow in terms of proton fluxes. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5110–5114. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Eisenberg M. Antibiotics and membrane biology. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):335–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. A chemiosmotic molecular mechanism for proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Proton translocation coupled to ATP hydrolysis in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):530–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. The Ninth Sir Hans Krebs Lecture. Compartmentation and communication in living systems. Ligand conduction: a general catalytic principle in chemical, osmotic and chemiosmotic reaction systems. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Sonnenberg A. S., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient in Streptococcus cremoris by lactate efflux. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Slater E. C. The value of G degrees for the hydrolysis of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 25;267(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld M., Neumann J. Proton conductance of the thylakoid membrane: modulation by light. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C., Boens C. C., Ogawa S. Steady state measurements of the internal phosphorylation potential and the cross membrane electrochemical potential for proton in respiring mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C. Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:1015–1026. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Equilibrium state of ATP-driven ion pumps in relation to physiological ion concentration gradients. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Feb;77(2):223–229. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient by lactate efflux in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. S., Hinkle P. C. Stoichiometry of adenosine triphosphate-driven proton translocation in bovine heart submitochondrial particles. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5395–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi B., Danforth W. H. Effect of pH on the kinetics of frog muscle phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):4110–4112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Rottenberg H., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of bioenergetics in wild-type and adenosinetriphosphatase(1-) Escherichia coli cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):1068–1075. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


