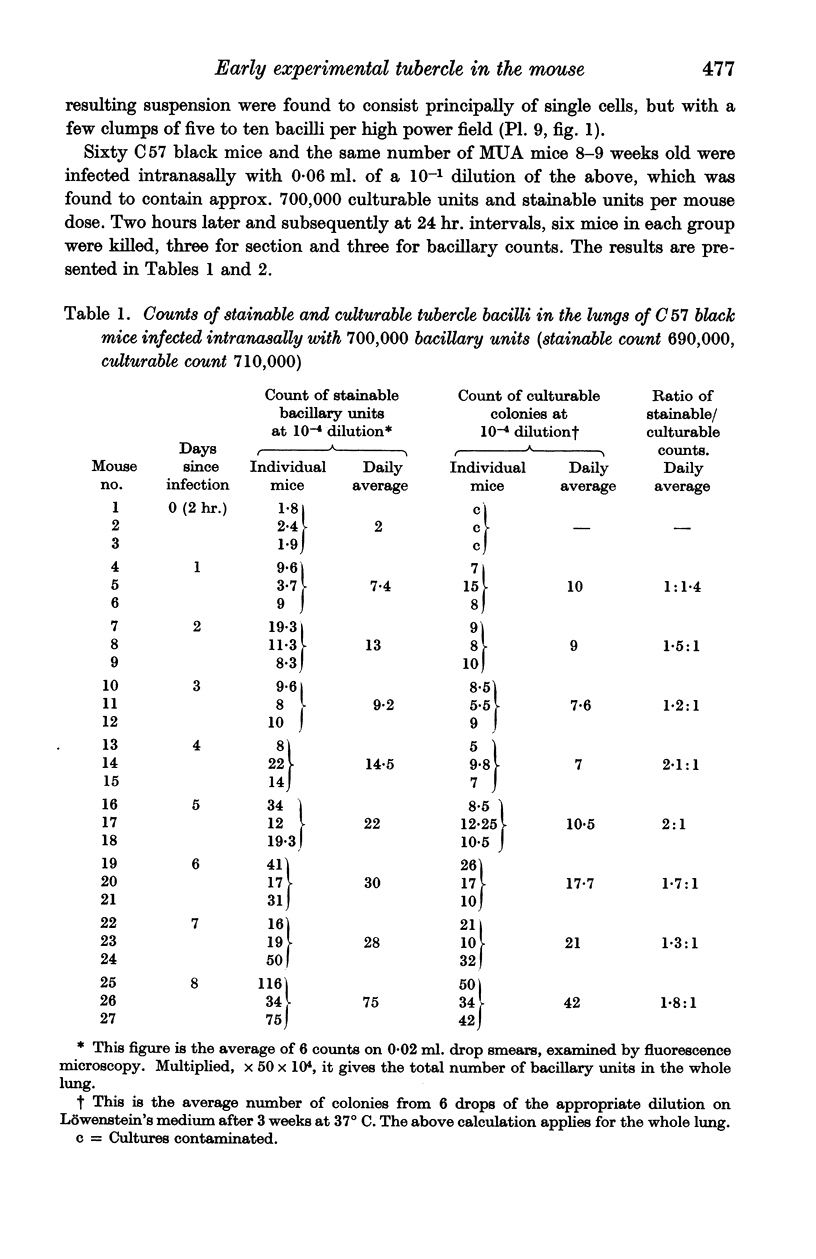
Full text
PDF



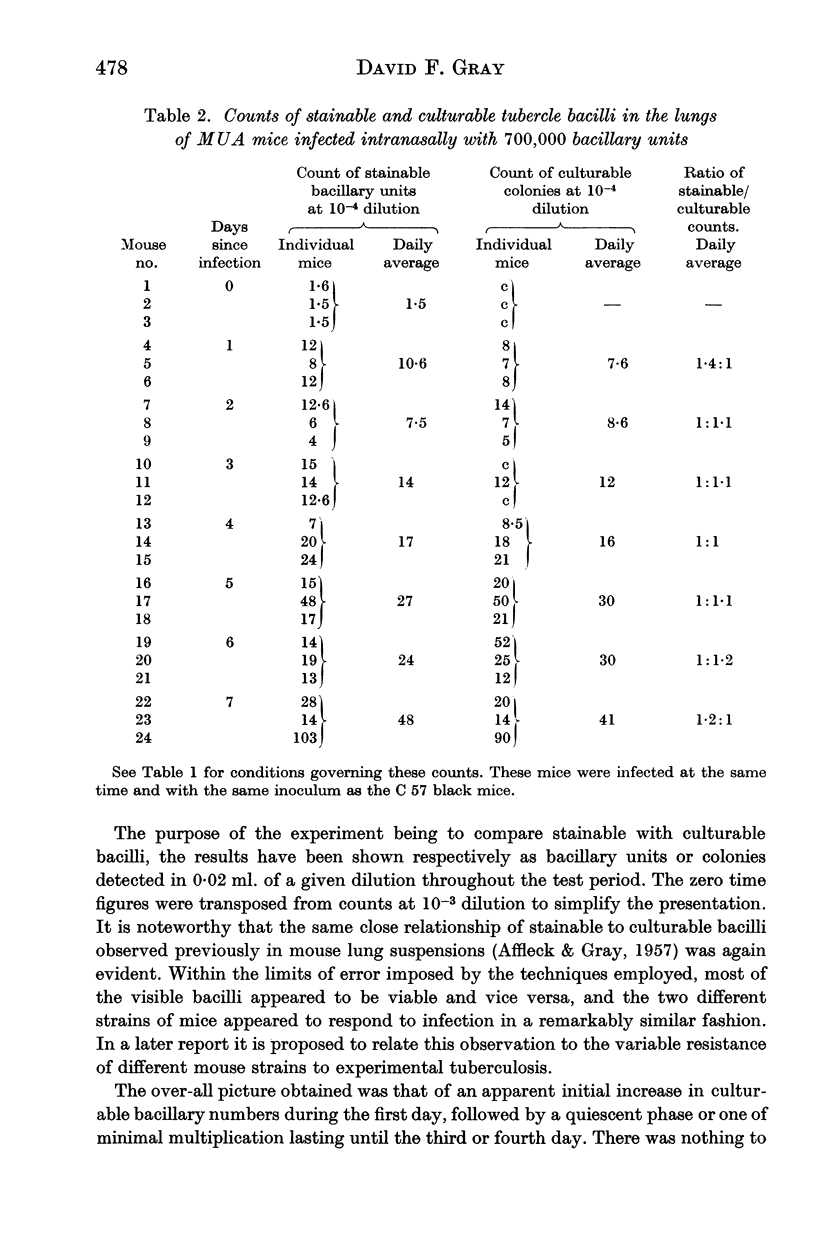




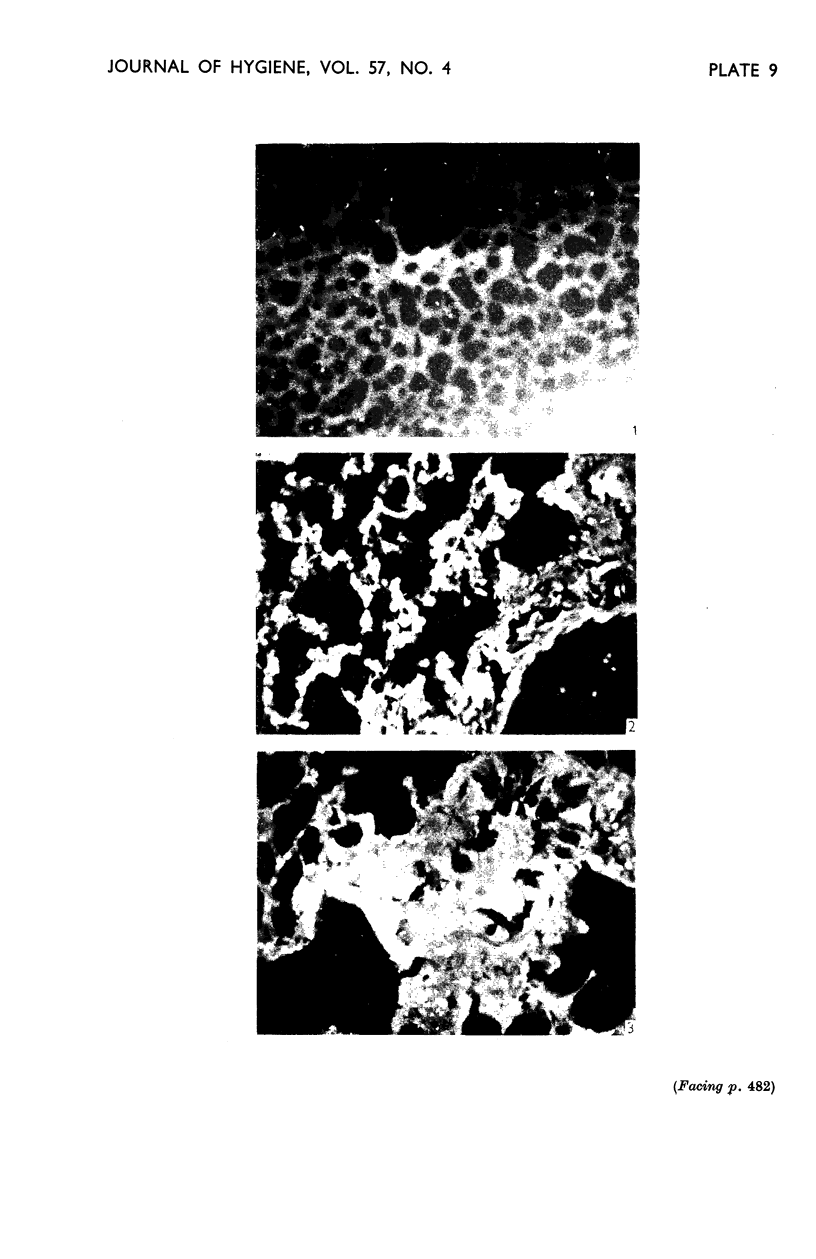
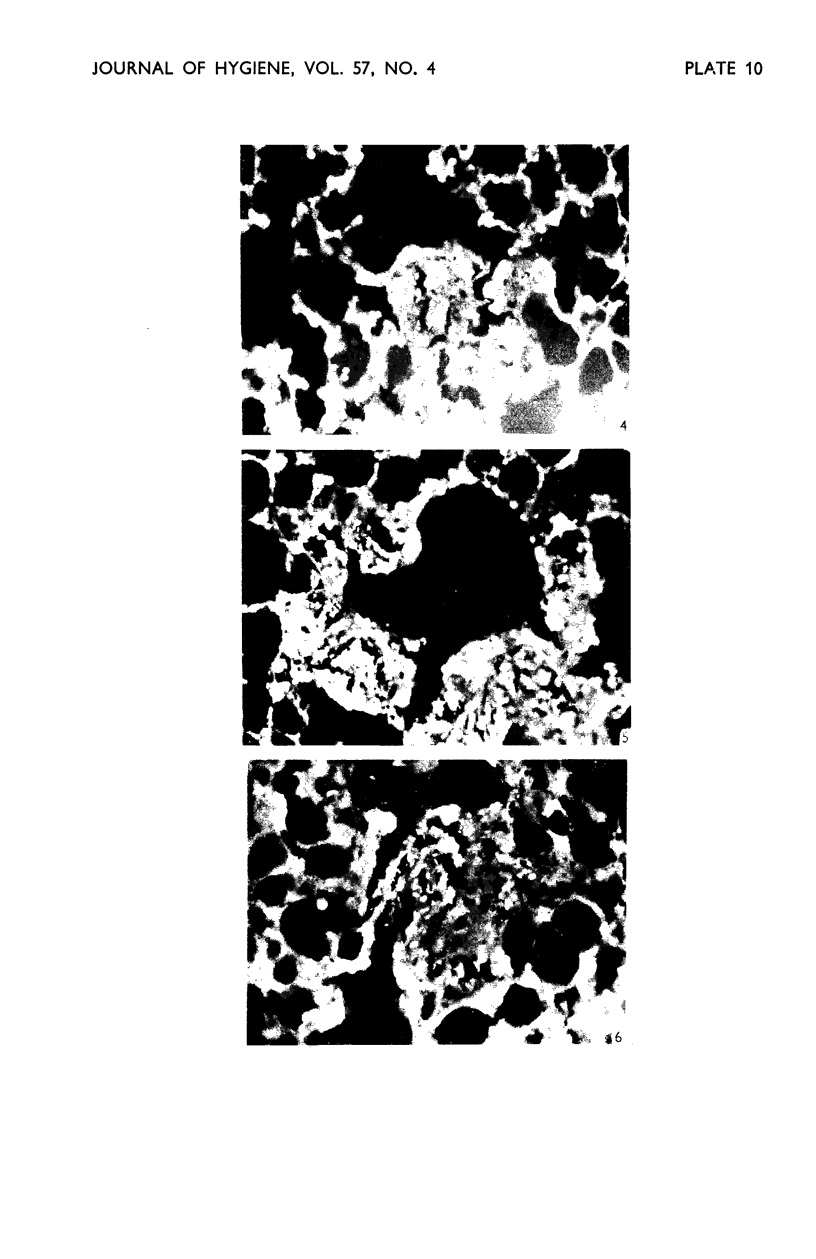
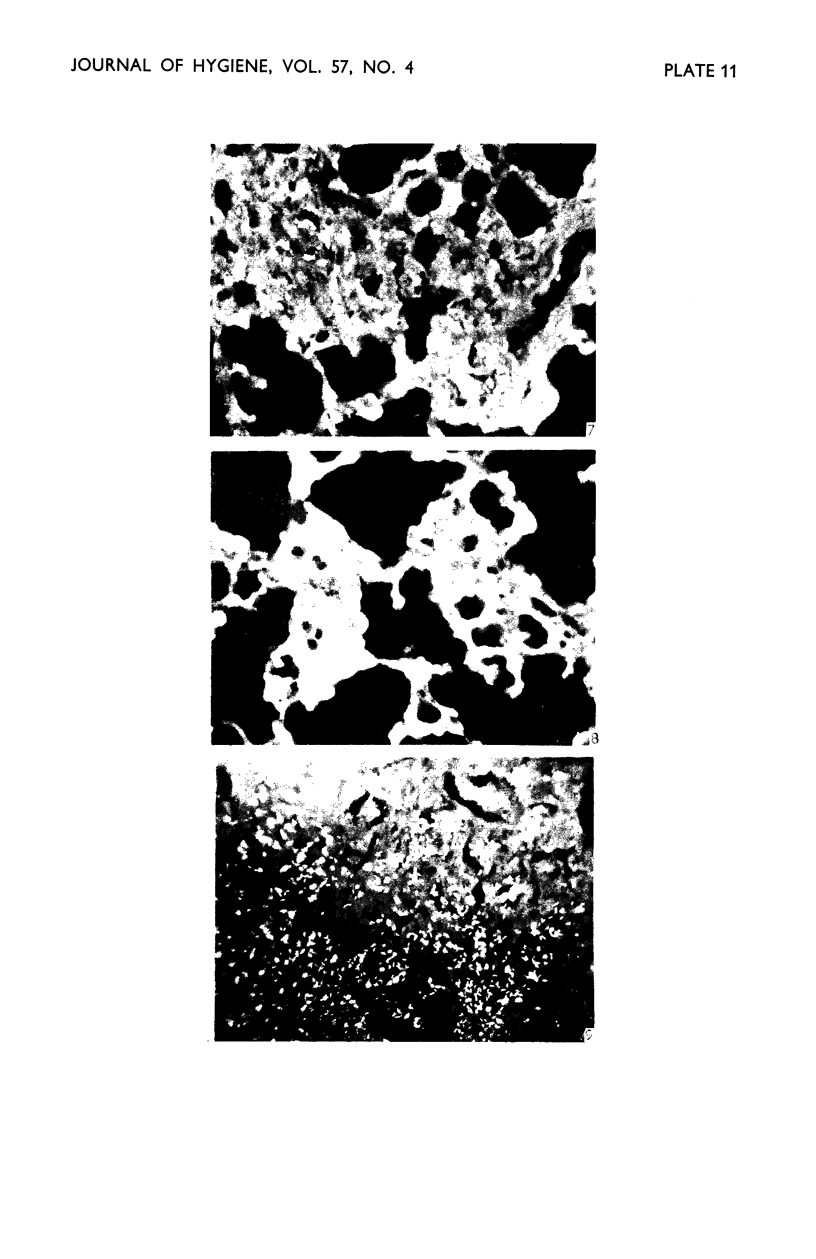

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOCH H. Studies on the virulence of tubercle bacilli; the relationship of the physiological state of the organisms to their pathogenicity. J Exp Med. 1950 Dec;92(6):507–526. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., AFFLECK M. N. Relationship of allergy to gross lung disease and culturable bacilli in tuberculous mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1958 Aug;78(2):226–234. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1958.78.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F. Detection of small numbers of mycobacteria in sections by fluorescence microscopy. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Jul;68(1):82–95. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F. Immunity, natural anergy, and artificial desensitization in experimental tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1958 Aug;78(2):235–250. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1958.78.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., JENNINGS P. A. Allergy in experimental mouse tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Aug;72(2):171–195. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY D. F., MATTINSON M. W. Detection of small numbers of tubercle bacilli from dispersed cultures, using mice, guinea pigs, and artificial media. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 May;65(5):572–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B., SMITH N., WELLS A. Q. The growth of intracellular tubercle bacilli in relation to their virulence. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Apr;69(4):479–494. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER E., JACKSON E. R., WHITESIDE E. S., ALVERSON C. Experimental embolic pulmonary tuberculosis in mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Mar;69(3):419–442. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART G. T. The pathogenesis of tuberculosis in mice infected intravenously with human tubercle bacilli; the use of mice in chemotherapeutic tests. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Feb;31(1):5–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]