Abstract
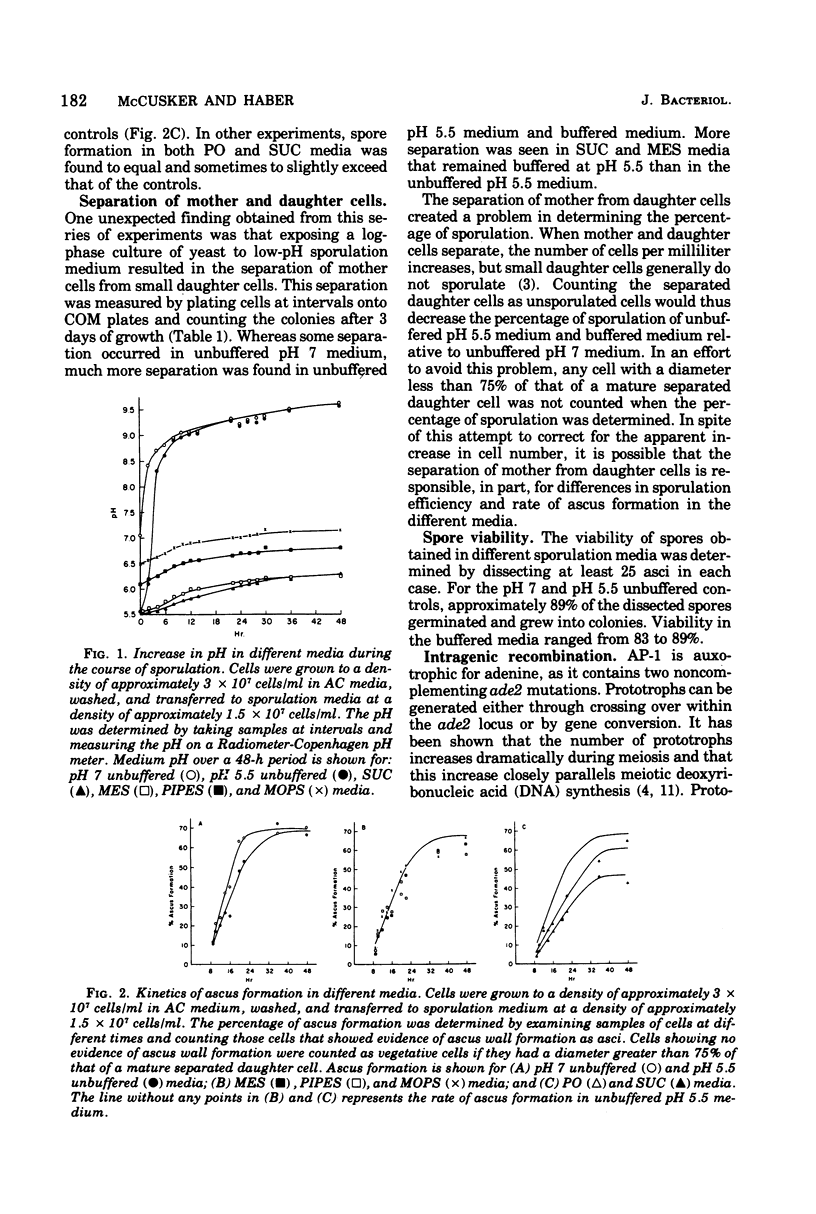
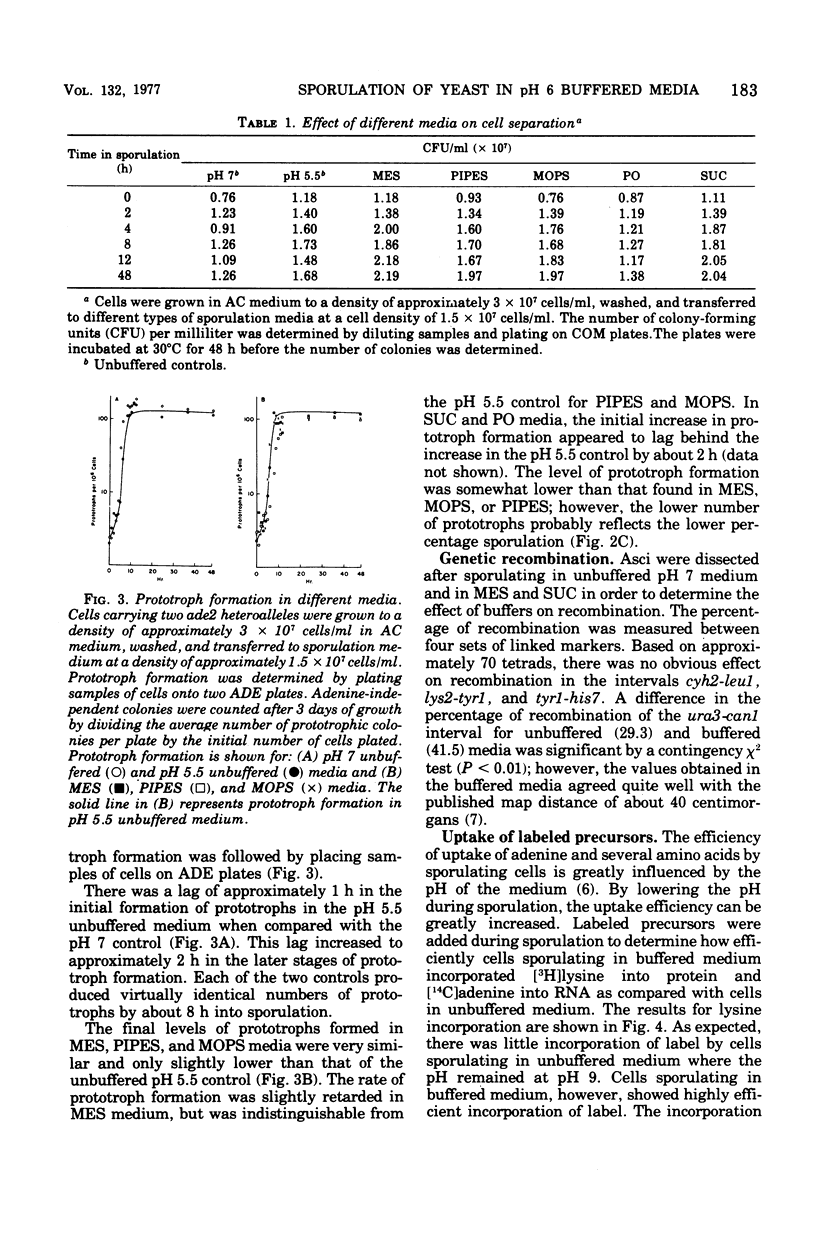
Diploid cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae underwent meiosis and sporulation when placed in 1% potassium acetate sporulation medium. In unbuffered sporulation medium the pH rose very rapidly, reaching pH 8.4 after 2 h of sporulation. Under these conditions, the uptake of radioactive adenine and lysine was extremely limited, and ascus formation was insensitive to inhibitors such as 5-fluorouracil and canavanine. By using several different buffers, we showed that an increase in the pH of sporulation media was not necessary for sporulation to occur. Spore viability and the kinetics of ascus and prototroph formation were normal for cells sporulated in several types of media buffered as low as pH 5.5. Incubation of sporulating cells below pH 6.5 did cause separation of small but viable buds from their mother cells. With sporulating cells buffered below pH 6.5, the incorporation of radioactive adenine and lysine was greatly enhanced and cells became sensitive to inhibition by 5-fluorouracil and canavanine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Haber J. E., Halvorson H. O. Cell cycle dependency of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1027-1033.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küenzi M. T., Tingle M. A., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the absence of a functional mitochondrial genome. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.80-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. Effect of pH on adenine and amino acid uptake during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.519-526.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Fogel S. A system selective for yeast mutants deficient in meiotic recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(4):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00334431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Halvorson H. O. Sporulation of yeast harvested during logarithmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):831–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.831-832.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., ROMAN H. Evidence for two types of allelic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Feb;48:255–261. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wejksnora P., Haber J. E. Influence of pH on the rate of ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.128-134.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kloet S. R. Effects of 5-fluorouracil and 6-azauracil on the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):167–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1060167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


