Abstract
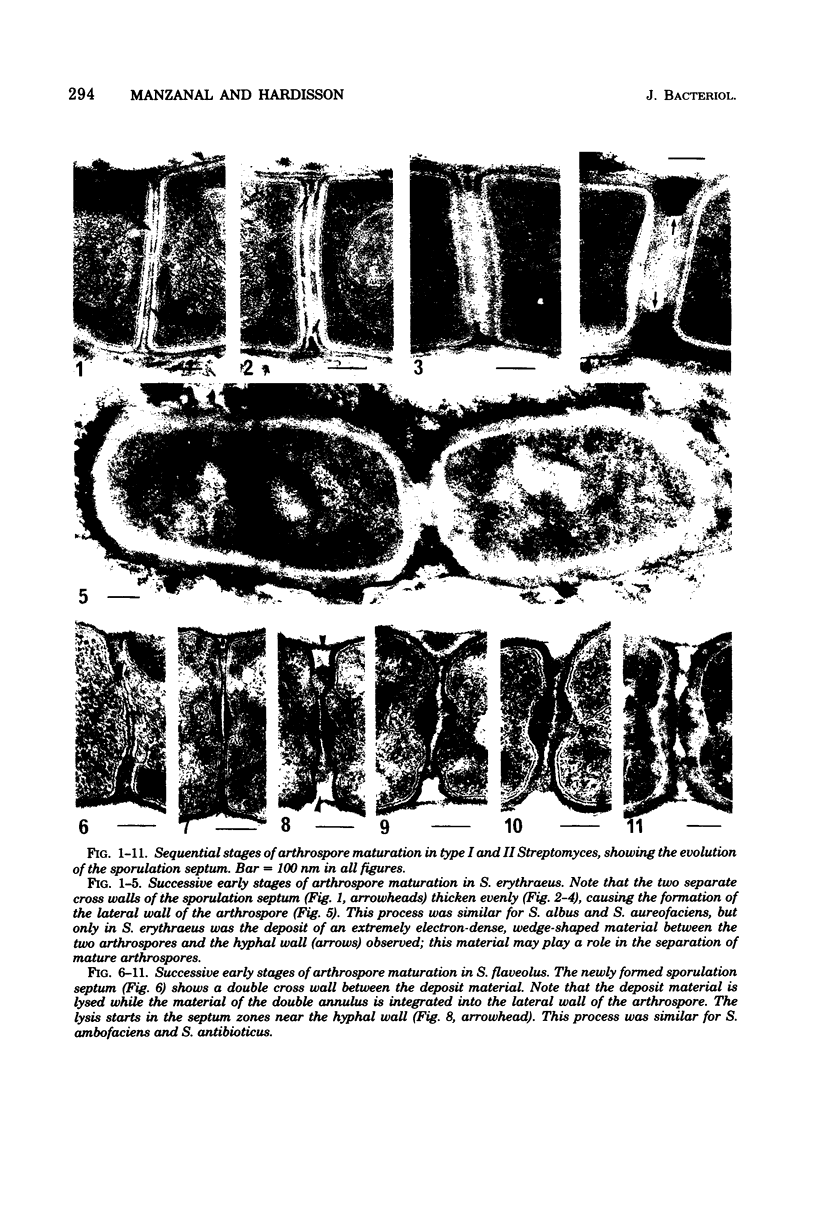
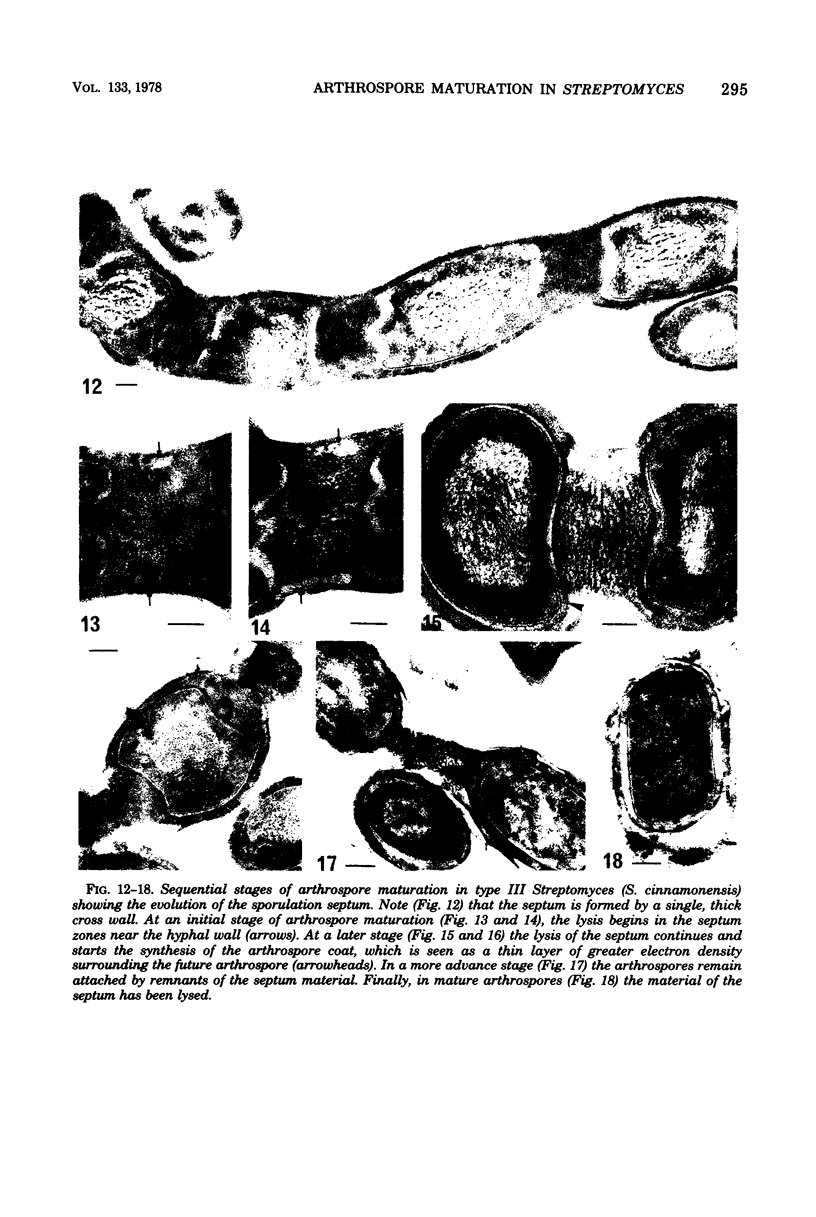
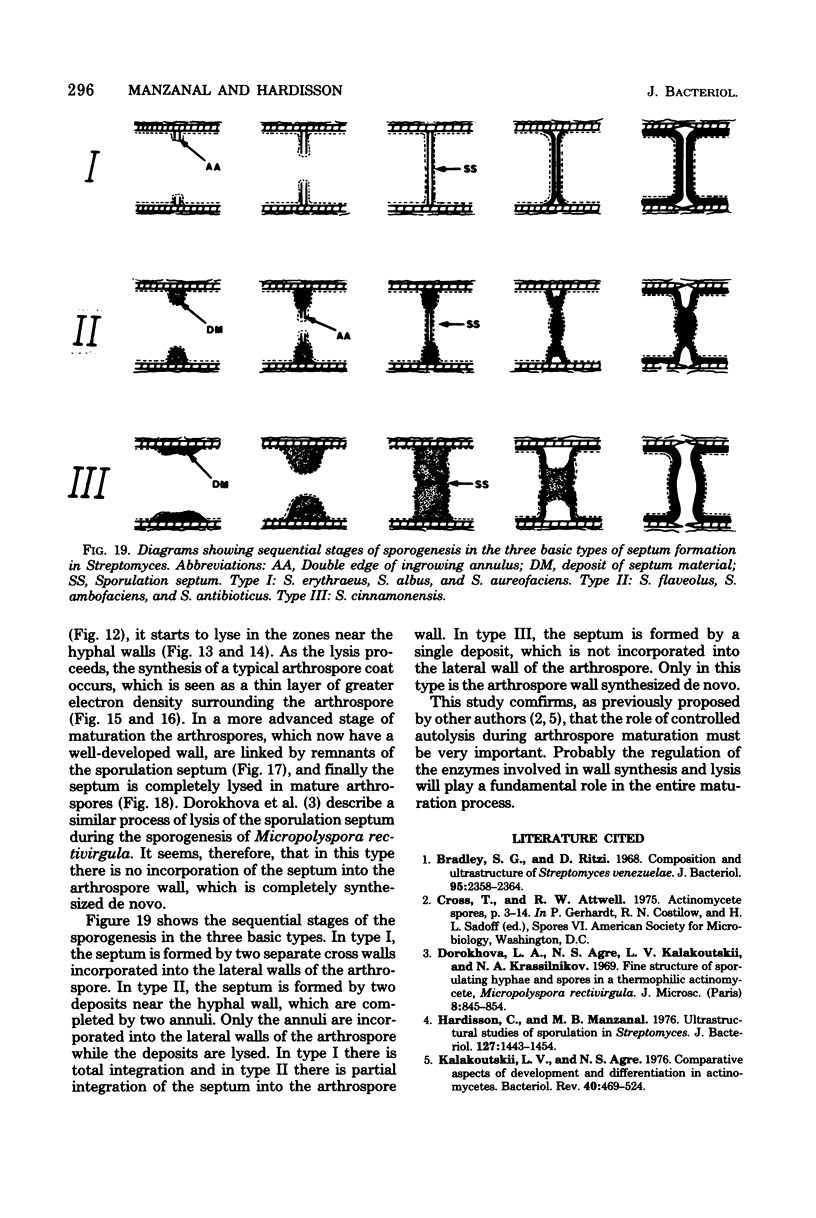
In the sporogenesis of Streptomyces, two basic stages can be considered: sporulation septum synthesis and arthrospore maturation. Most of the information about the ultrastructural changes accompanying the sporogenesis refer to the first stage of the process, but nothing has been published about the evolution of the sporulation septum during maturation. In a previous paper, proposed three basic types of sporulation septum formation in Streptomyces. Our ultrastructural study on the evolution of the sporulation septum during the early stages of arthrospore maturation in seven species of Streptomyces indicates correlation between the sporulation septum type and its evolution during the arthrospore maturation. In types I and II the material of the annuli was incorporated into the lateral walls of the arthrospore, whereas in types II and III the deposits were lysed during the maturation. Only in type III was the arthrospore wall synthesized de novo. In type I there was total integration and in type II there was partial integration of the septum into the arthrospore wall.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley S. G., Ritzi D. Composition and ultrastructure of Streptomyces venezuelae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2358–2364. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2358-2364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisson C., Manzanal M. B. Ultrastructural studies of sporulation in Streptomyces. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1443–1454. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1443-1454.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalakoutskii L. V., Agre N. S. Comparative aspects of development and differentiation in actinomycetes. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):469–524. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.469-524.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVittie A. Ultrastructural studies on sporulation in wild-type and white colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):291–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANCOURT M. W., LECHEVALIER H. A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF SPINY CONIDIA IN SPECIES OF STREPTOMYCES. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:311–316. doi: 10.1139/m64-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H., Hopwood D. A. Septation during sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):51–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Sharples G. P., Bradshaw R. M. The fine structure of the Actinomycetales. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1973 Jan;2:113–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]