Abstract
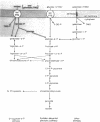
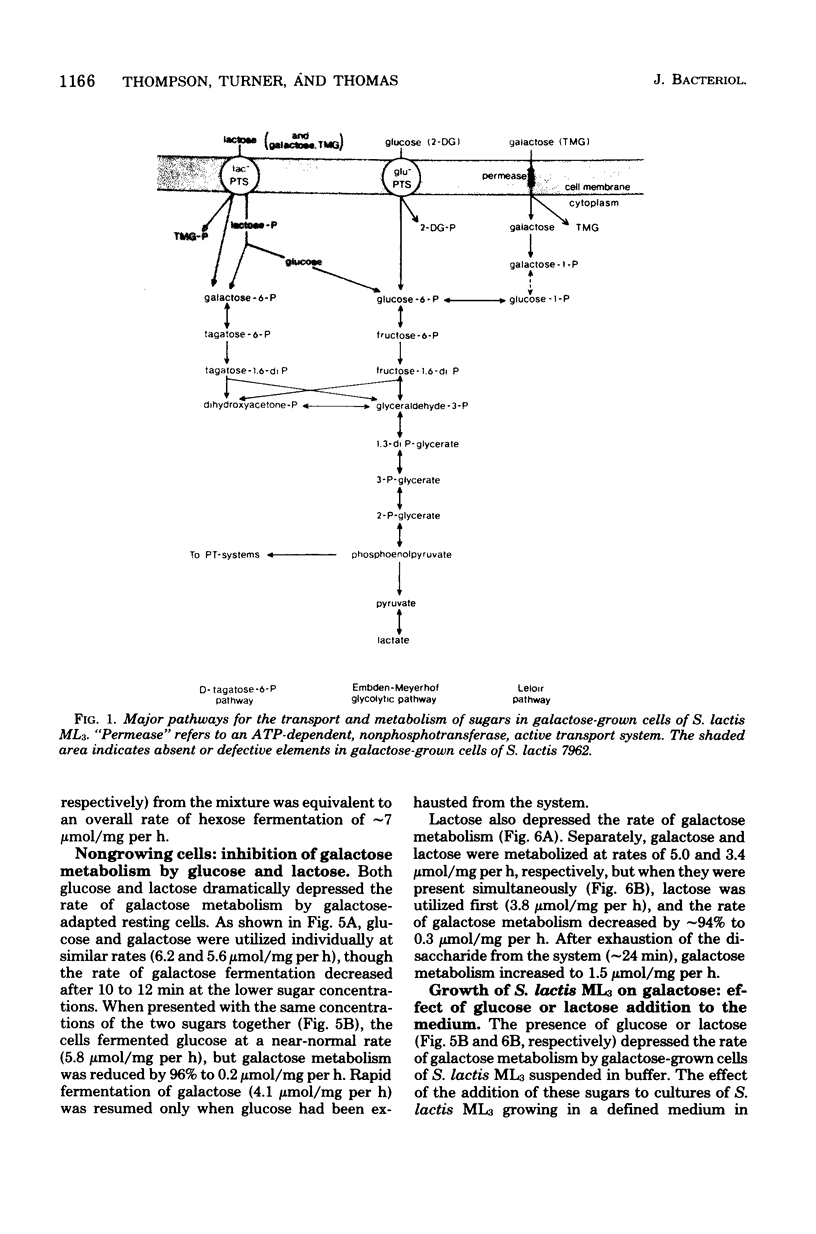
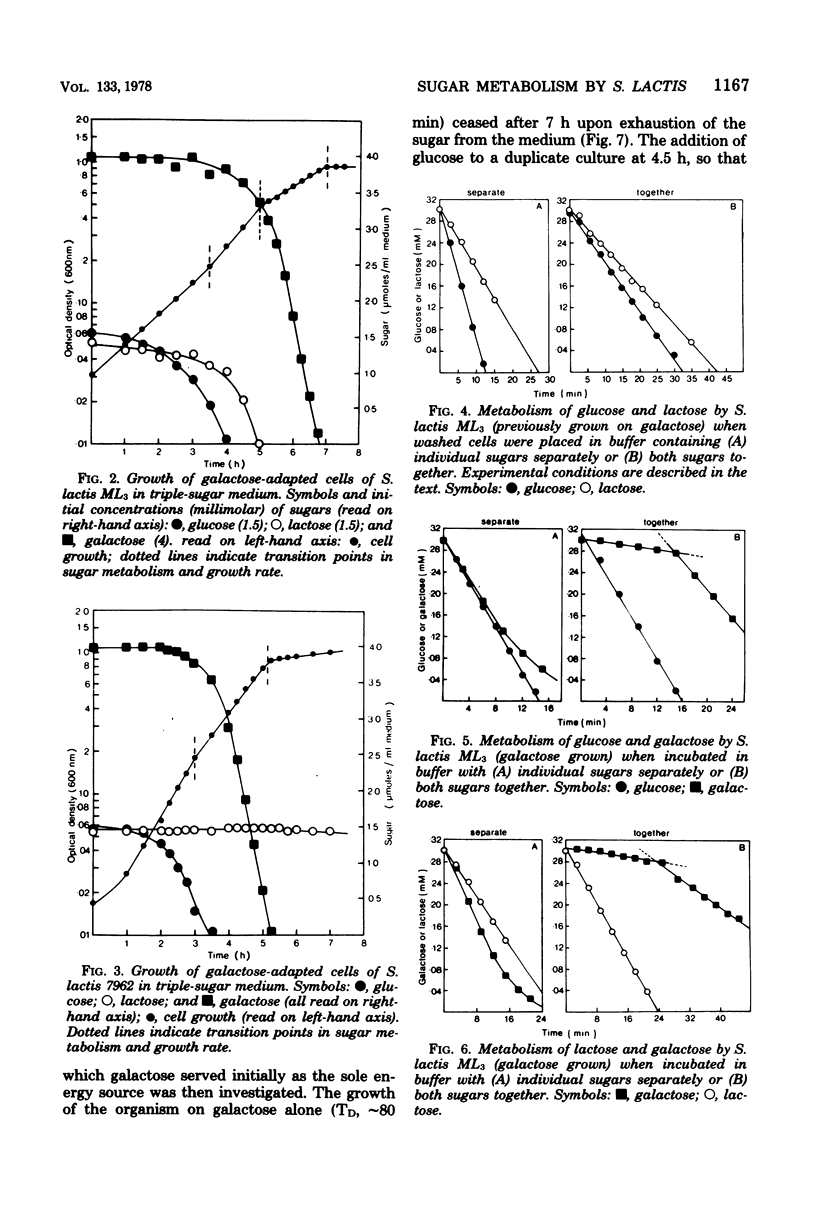
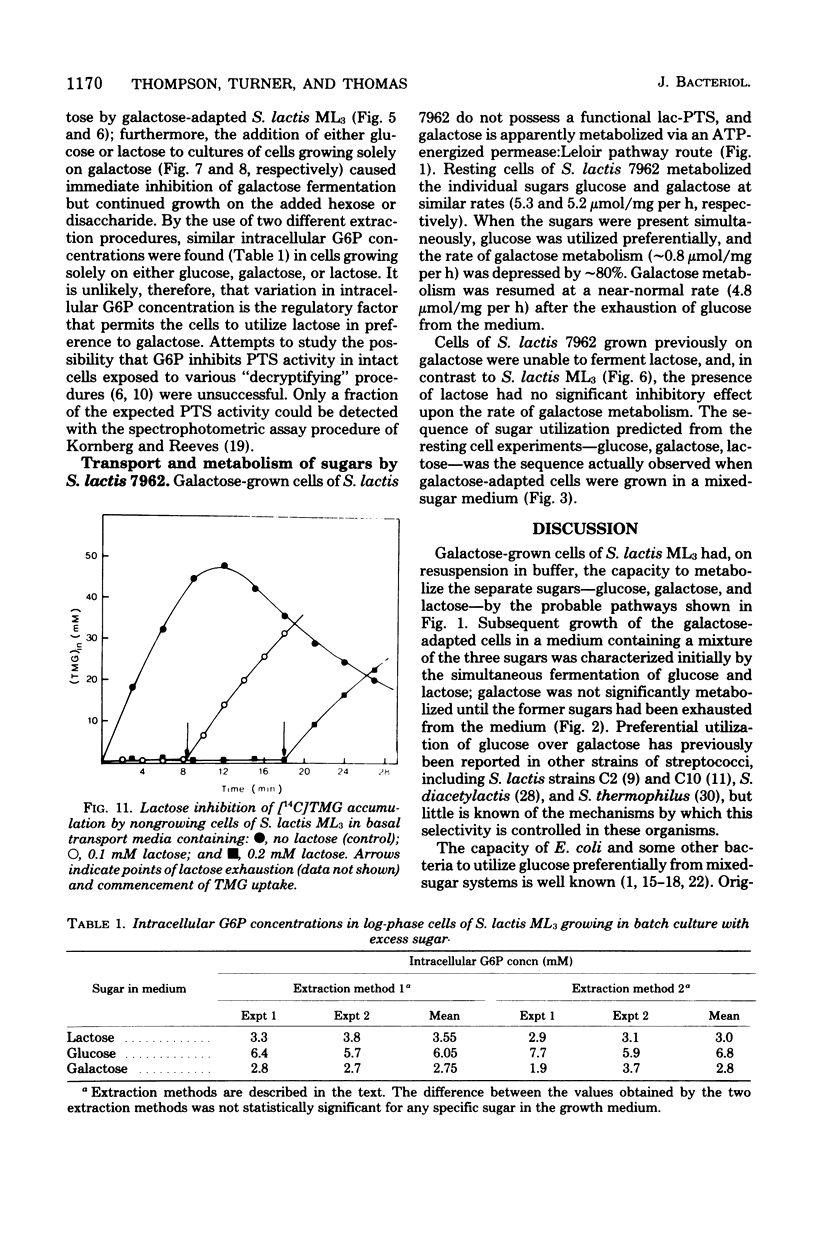
Growth of galactose-adapted cells of Streptococcus lactis ML3 in a medium containing a mixture of glucose, galactose, and lactose was characterized initially by the simultaneous metabolism of glucose and lactose. Galactose was not significantly utilized until the latter sugars had been exhausted from the medium. The addition of glucose or lactose to a culture of S. lactis ML3 growing exponentially on galactose caused immediate inhibition of galactose utilization and an increase in growth rate, concomitant with the preferential metabolism of the added sugar. Under nongrowing conditions, cells of S. lactis ML3 grown previously on galactose metabolized the three separate sugars equally rapidly. However, cells suspended in buffer containing a mixture of glucose plus galactose or lactose plus galactose again consumed glucose or lactose preferentially. The rate of galactose metabolism was reduced by ∼95% in the presence of the inhibitory sugar, but the maximum rate of metabolism was resumed upon exhaustion of glucose or lactose from the system. When presented with a mixture of glucose and lactose, the resting cells metabolized both sugars simultaneously. Lactose, glucose, and a non-metabolizable glucose analog (2-deoxy-d-glucose) prevented the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent uptake of thiomethyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (TMG), but the accumulation of TMG, like galactose metabolism, commenced immediately upon exhaustion of the metabolizable sugars from the medium. Growth of galactose-adapted cells of the lactose-defective variant S. lactis 7962 in the triple-sugar medium was characterized by the sequential metabolism of glucose, galactose, and lactose. Growth of S. lactis ML3 and 7962 in the triple-sugar medium occurred without apparent diauxie, and for each strain the patterns of sequential sugar metabolism under growing and nongrowing conditions were identical. Fine control of the activities of preexisting enzyme systems by catabolite inhibition may afford a satisfactory explanation for the observed sequential utilization of sugars by these two organisms.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Echols H. Glucose effect and the galactose enzymes of Escherichia coli: correlation between glucose inhibition of induction and inducer transport. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):601–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.601-608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bag J. Glucose inhibition of the transport and phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation of galactose and fructose in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):764–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.764-767.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Genetic evidence for the physiological significance of the D-tagatose 6-phosphate pathway of lactose and D-galactose degradation in staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):698–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.698-704.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in group N streptococci: presence of enzymes for both the D-galactose 1-phosphate and D-tagatose 6-phosphate pathways. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):318–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.318-320.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D0galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus: pathway of D-galactose 6-phosphate degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90761-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITTI J. E., SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R. BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:937–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.937-942.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B., Holms W. H. Control of the sequential utilization of glucose and fructose by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Aug;96(2):191–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. B., Thomas T. D. Pyruvate kinase of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.52-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cords B. R., McKay L. L. Characterization of lactose-fermenting revertants from lactose-negative Streptococcus lactis C2 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):830–839. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.830-839.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. A new assay of the phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland S. E., Speck M. L., Woodard J. R., Jr Stimulation of lactic streptococci in milk by -galactosidase. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.21-25.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., McDonald I. J. Beta-D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase from Streptococcus cremoris HP: purification and enzyme properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.667-674.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Protonmotive force in fermenting Streptococcus lactis 7962 in relation to sugar accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):879–886. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L. Fine control of sugar uptake by Escherichia coli. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:175–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Reeves R. E. Inducible phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent hexose phosphotransferase activities in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1042/bj1281339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L. The nature and control of carbohydrate uptake by Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R., Molskness T., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Carbohydrate metabolism in lactic streptococci: fate of galactose supplied in free or disaccharide form. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):951–958. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.951-958.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B., NEIDHARDT F. C. Inhibitory effect of glucose on enzyme formation. Nature. 1956 Oct 13;178(4537):801–802. doi: 10.1038/178801b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. F., Paigen K. Catabolite inhibition: a general phenomenon in the control of carbohydrate utilization. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):902–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.902-913.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. F., Paigen K. Site of catabolite inhibition of carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):885–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.885-887.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L., Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Mechanisms of lactose utilization by lactic acid streptococci: enzymatic and genetic analyses. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):804–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.804-809.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molskness T. A., Lee D. R., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. -D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase of lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.373-380.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa H. H., Collins E. B. Role of galactose or glucose-1-phosphate in preventing the lysis of Streptococcus diacetilactis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):592–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.592-602.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'leary V. S., Woychik J. H. Utilization of Lactose, Glucose, and Galactose by a Mixed Culture of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus in Milk Treated with Lactase Enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):89–94. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.89-94.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opheim D., Bernlohr R. W. Purification and regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1150–1159. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1150-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Roseman S. Sugar transport. 2nducer exclusion and regulation of the melibiose, maltose, glycerol, and lactose transport systems by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6606–6615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F. Glucose transport in Streptococcus mutans: preparation of cytoplasmic membranes and characteristics of phosphotransferase activity. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Mayo J. A. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose transport in oral streptococci. J Dent Res. 1973 Nov-Dec;52(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520060801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Nakazawa T., Hays J. B., Roseman S. Sugar transport. IV. Isolation and characterization of the lactose phosphotransferase system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):932–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VII. Lactose transport in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Regulation of lactose fermentation in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):474–478. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.474-478.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Characteristics and energy requirements of an alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport system in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):719–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.719-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]