Abstract
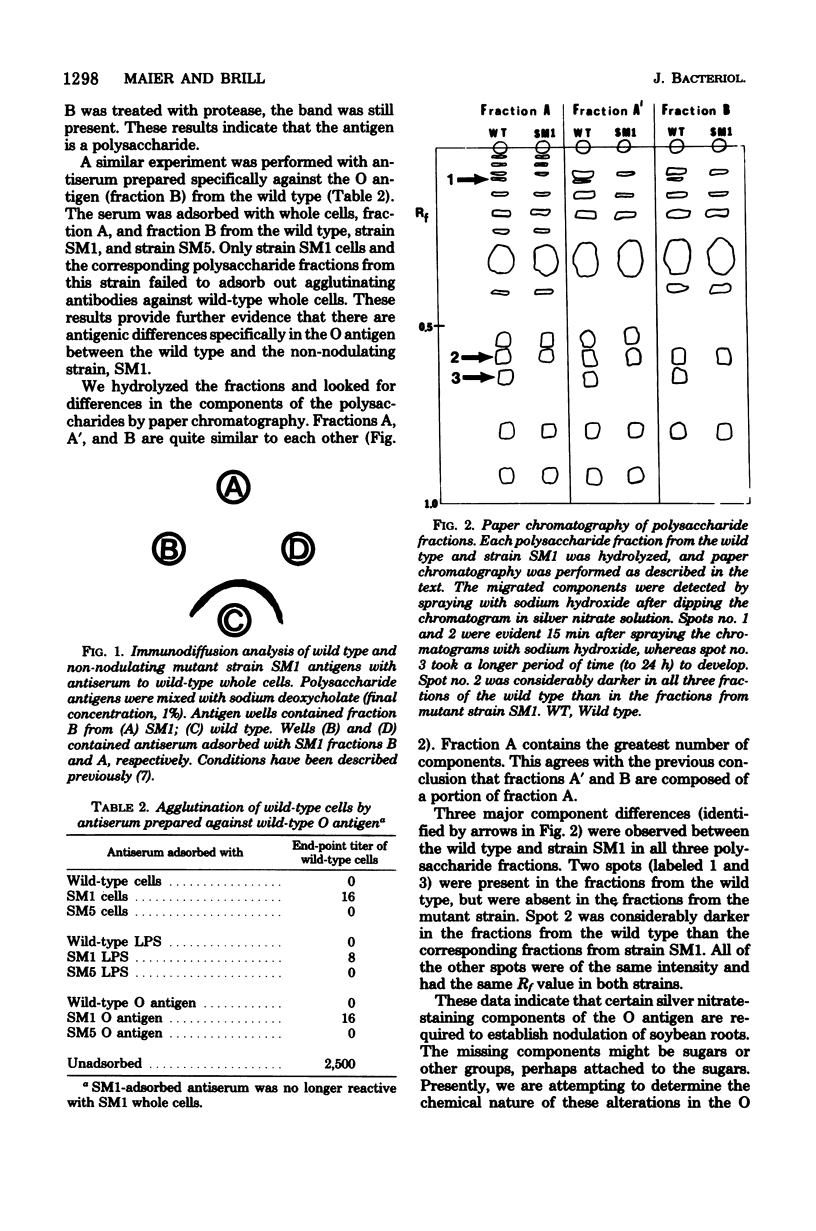
Non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum lacked a surface antigen that was present on the wild type. This surface antigen is associated with the O antigen portion of the lipopolysaccharide. Paper chromatography of hydrolyzed lipopolysaccharide and O antigen revealed three major component differences between the non-nodulating strains and the wild type.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W. D. Lectins as determinants of specificity in legume-Rhizobium symbiosis. Basic Life Sci. 1977;9:283–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0880-5_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Ingram L. O. Comparison of lipopolysaccharides from Agmenellum quadruplicatum to Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium by using thin-layer chromatography. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1566–1573. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1566-1573.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Brill W. J. Receptor site on clover and alfalfa roots for Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.132-136.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Antigenic differences between infective and noninfective strains of Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):172–177. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.172-177.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Cross-reactive antigens and lectin as determinants of symbiotic specificity in the Rhizobium-clover association. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1017–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1017-1033.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Napoli C. A., Hubbell D. H. Adsorption of bacteria to roots as related to host specificity in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.166-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K., Schmidt G., Orskov F., Orskov I. Comparative immunochemical studies of the surface antigens of Escherichia coli strains 08:K87(B?)H19 and (O32):K87(B?):H45. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 10;23(3):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K., Schmidt G., Orskov I., Orskov F. Immunochemical studies of polysaccharide surface antigens of Escherichia coli 0100:K?(B):H2. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;15(1):29–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Ineffective and non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.763-769.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Seitz E., Jann B., Jann K. Degradation studies on the lipopolysaccharide from E. coli 071:K?:H12. Separation and investigation of O-specific and core polysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1968 Oct;1(5):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planqué K., Kijne J. W. Binding of pea lectins to a glycan type polysaccharide in the cell walls of Rhizobium leguminosarum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarcsay L., Wang C. S., Li S. C., Alaupovic P. Composition and structure of the O-specific side chain of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens 08. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1948–1955. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang J. C., Wang C. S., Alaupovic P. Degradative effect of phenol on endotoxin and lipopolysaccharide preparations from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):786–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.786-795.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert J. S., Albersheim P. Host-symbiont interactions. I. The lectins of legumes interact with the o-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides of their symbiont Rhizobia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


