Abstract
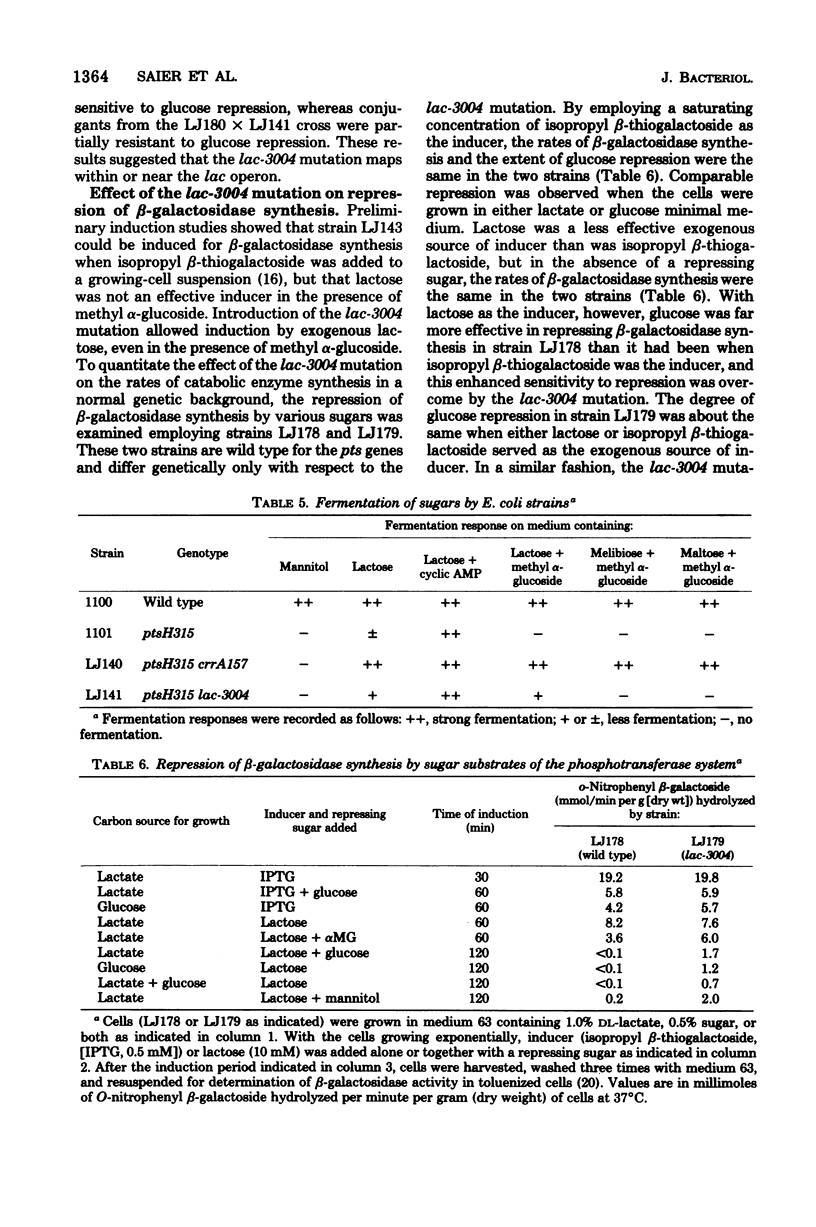
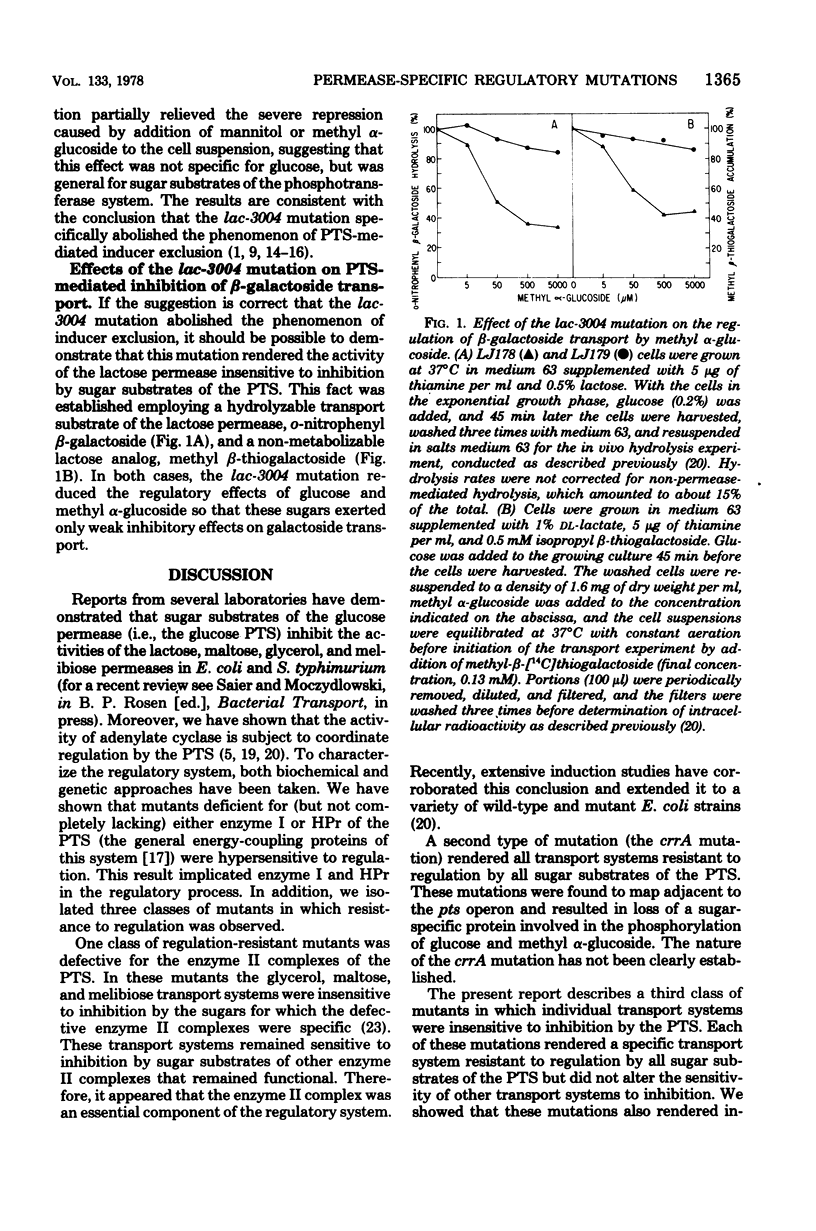
Several carbohydrate permease systems in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli are sensitive to regulation by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Mutant Salmonella strains were isolated in which individual transport systems had been rendered insensitive to regulation by sugar substrates of the phosphotransferase system. In one such strain, glycerol uptake was insensitive to regulation; in another, the maltose transport system was resistant to inhibition; and in a third, the regulatory mutation specifically rendered the melibiose permease insensitive to regulation. An analogous mutation in E. coli abolished inhibition of the transport of beta-galactosides via the lactose permease system. The mutations were mapped near the genes which code for the affected transport proteins. The regulatory mutations rendered utilization of the particular carbohydrates resistant to inhibition and synthesis of the corresponding catabolic enzymes partially insensitive to repressive control by sugar substrates of the phosphotransferase system. Studies of repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis in E. coli were conducted with both lactose and isopropyl beta-thiogalactoside as exogenous sources of inducer. Employing high concentrations of isopropyl beta-thiogalactoside, repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis was not altered by the lactose-specific transport regulation-resistant mutation. By contrast, the more severe repression observed with lactose as the exogenous source of inducer was partially abolished by this regulatory mutation. The results support the conclusions that several transport systems, including the lactose permease system, are subject to allosteric regulation and that inhibition of inducer uptake is a primary cause of the repression of catabolic enzyme synthesis.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Echols H. Glucose effect and the galactose enzymes of Escherichia coli: correlation between glucose inhibition of induction and inducer transport. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):601–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.601-608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman-Kurtz M., Lin E. C., Richey D. P. Promoter-like mutant with increased expression of the glycerol kinase operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):724–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.724-731.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Lin E. C. Glycerol-specific revertants of a phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase mutant: suppression by the desensitization of glycerol kinase to feedback inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):113–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.113-120.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Zwaig N., Lin E. C. Suppression of a pleiotropic mutant affecting glycerol dissimilation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro L., Feucht B. U., Morse M. L., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of carbohydrate permeases and adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli. Studies with mutant strains in which enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system is thermolabile. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5522–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E. Some improved methods in P22 transduction. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):625–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Hatfield D., Schwartz M. malB region in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of new mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.40-47.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Local and non-local interactions of fluxes mediated by the glucose and galactoside permeases of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 12;249(1):197–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. I. Isolation of a phosphotransferase system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1393–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. II. Characterization of constitutive membrane-bound enzymes II of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinthal M. Biochemical studies of melibiose metabolism in wild type and mel mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1047–1052. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1047-1052.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinstry G., Koch A. L. Interaction of maltose transport with the transport of glucose and galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):455–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.455-458.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase systems: structural, functional, and evolutionary interrelationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):856–871. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.856-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U. Coordinate regulation of adenylate cyclase and carbohydrate permeases by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):7078–7080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Hofstadter L. J. Regulation of carbohydrate uptake and adenylate cyclase activity mediated by the enzymes II of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):883–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Roseman S. Sugar transport. 2nducer exclusion and regulation of the melibiose, maltose, glycerol, and lactose transport systems by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6606–6615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Roseman S. Sugar transport. The crr mutation: its effect on repression of enzyme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6598–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Roseman S. Inducer exclusion and repression of enzyme synthesis in mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):972–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition IV. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):558–586. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.558-586.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Saeed H. Insertion of the F factor into the cluster of rfa (rough A) genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):64–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.64-73.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R. Analysis of melibiose mutants deficient in alpha-galactosidase and thiomethylgalactoside permease II in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):462–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.462-471.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Hays J. B., Nakazawa T., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VI. Phosphoryl transfer in the lactose phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):957–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S., Saier M. H., Jr Sugar transport. Properties of mutant bacteria defective in proteins of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6584–6597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VII. Lactose transport in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. J., Morse H. G., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate Accumulation and Metabolism in Escherichia coli: Characteristics of the Reversions of ctr Mutations. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1318-1324.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. Inhibition of beta-galactoside transport by substrates of the glucose transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1030–1051. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


