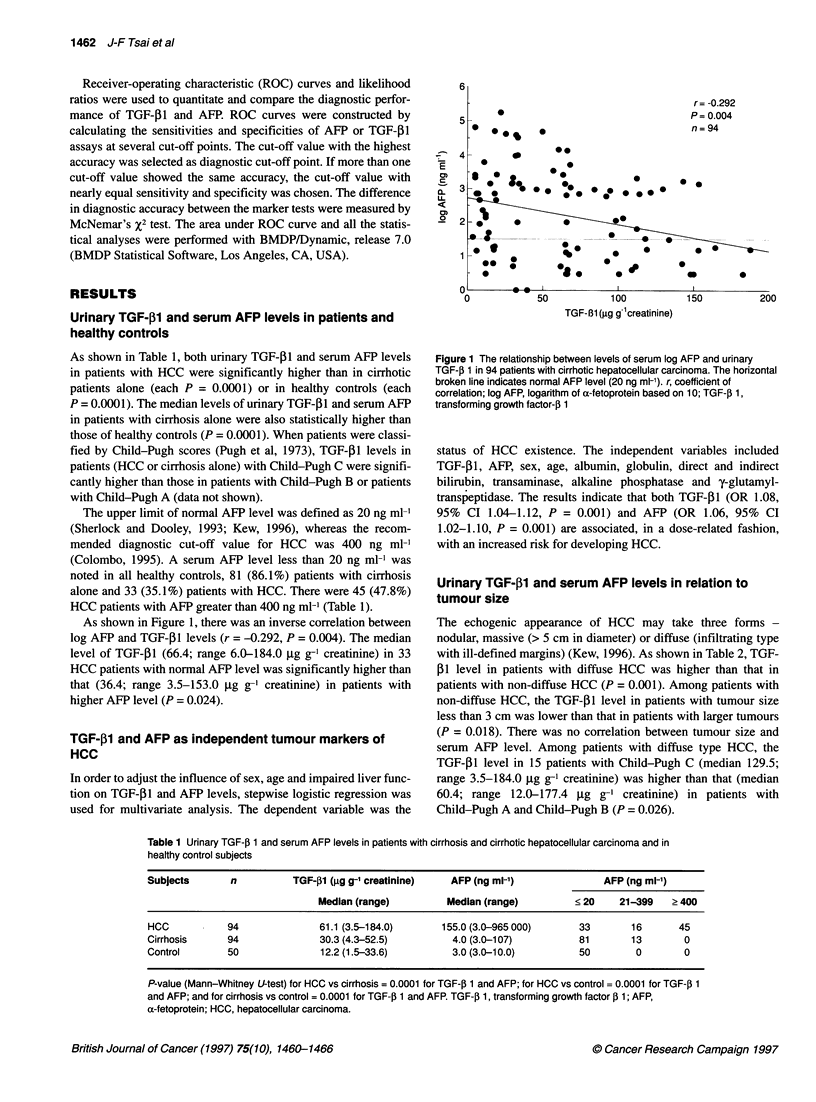
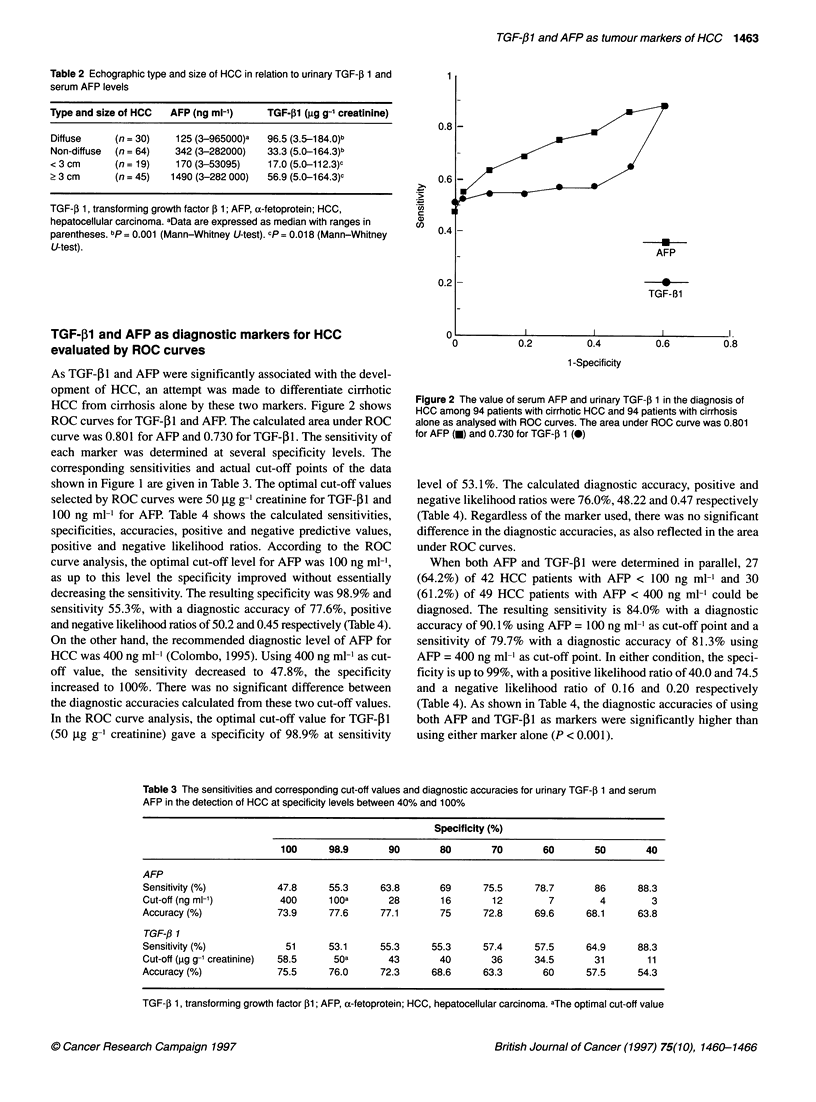
Abstract
To evaluate the diagnostic application of urinary transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) and serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), TGF-beta1 and AFP were determined in 94 patients with cirrhotic HCC and in 94 sex- and age-matched patients with cirrhosis alone. TGF-beta1 and AFP levels in HCC were higher than in cirrhosis alone (P = 0.0001). There is an inverse correlation between TGF-beta1 and log AFP (r = -0.292, P = 0.004). Multivariate analysis indicated that TGF-beta1 and AFP were closely associated, in a dose-related fashion, with the development of HCC. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the optimal cut-off values of TGF-beta1 (50 microg g(-1) creatinine) and AFP (100 ng ml(-1)). Both TGF-beta1 and AFP showed a high specificity (99%) and positive likelihood ratio. The sensitivity was 53.1% for TGF-beta1 and 55.3% for AFP. The determination of both markers in parallel significantly increased the diagnostic accuracy (90.1%) and sensitivity (84%), with a high specificity (98%) and positive likelihood ratio (40.0). In conclusion, TGF-beta1 and AFP are independent tumour markers of HCC and may be used as complementary tumour markers to discriminate HCC from cirrhosis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin G. S., Zhang Q. X. Measurement of gastrin and transforming growth factor alpha messenger RNA levels in colonic carcinoma cell lines by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2261–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedossa P., Peltier E., Terris B., Franco D., Poynard T. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and TGF-beta 1 receptors in normal, cirrhotic, and neoplastic human livers. Hepatology. 1995 Mar;21(3):760–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilla A., Prieto J., Fausto N. Transforming growth factors beta 1 and alpha in chronic liver disease. Effects of interferon alfa therapy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):933–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. Y., Hung W. C., Yang M. L., Chang C. C., Tsai J. F. Urinary epidermal growth factor receptor-binding growth factors in patients with cancers of the digestive tract. Clin Biochem. 1994 Dec;27(6):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(94)00053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. Y., Tsai J. H., Yeh Y. C., Chang C. C., Yeh H. W., Guh J. Y., Tsai J. F. Epidermal growth factor-related transforming growth factors in the urine of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1991 Jun;13(6):1112–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupes B. M., Newstead C. G., Short C. D., Brenchley P. E. Transforming growth factor beta 1 in renal allograft recipients. Transplantation. 1994 Jun 27;57(12):1727–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama S., Izuno K., Yamasaki K., Sato T., Taketa K. Determination of optimum cutoff levels of plasma des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and serum alpha-fetoprotein for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using receiver operating characteristic curves. Tumour Biol. 1992;13(5-6):316–323. doi: 10.1159/000217781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Kawata S., Tamura S., Takaishi K., Shirai Y., Kiso S., Yabuuchi I., Matsuda Y., Nishioka M., Tarui S. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor beta messenger RNA and its polypeptide in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4080–4083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Kawata S., Tamura S., Takaishi K., Yabuuchi I., Matsuda Y., Nishioka M., Tarui S. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Dec;81(12):1202–1205. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng J. E., Tsai J. F. Hepatitis C virus antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. J Med Virol. 1991 May;34(1):74–77. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890340113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. H., Merlino G., Fausto N. Development of liver tumors in transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5162–5170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maussier M. L., Valenza V., Schinco G., Galli G. AFP, CEA, CA 19-9 and TPA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Markers. 1990 Jul-Sep;5(3):121–126. doi: 10.1177/172460089000500304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy P., Schaff Z., Lapis K. Immunohistochemical detection of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in fibrotic liver diseases. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Nakata K., Mitsuoka S., Ohtsuru A., Ido A., Hatano M., Sato Y., Nakayama T., Shima M., Kusumoto Y. Transforming growth factor beta 1 differentially regulates alpha-fetoprotein and albumin in HuH-7 human hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1294–1299. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Okumura H., Noda K., Yasumitsu H., Umeda M. High level of beta-type transforming growth factor activity in human urine obtained from cancer patients. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;77(6):560–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M., Stjernswärd J., Muir C. S. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of twelve major cancers. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(2):163–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan G., Lyons R., Jiang N. S., Moses H. Transforming growth factor type beta in normal human urine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1503–1512. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Thompson N. L., Heine U., Flanders C., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta: possible roles in carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jun;57(6):594–600. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Viruses and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 1994 Jun;35(6):828–832. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Twardzik D. R., Bohn W. H., Cockley K. D., Todaro G. J. High-molecular-weight transforming growth factor activity in the urine of patients with disseminated cancer. Cancer Res. 1983 Jan;43(1):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai Y., Kawata S., Ito N., Tamura S., Takaishi K., Kiso S., Tsushima H., Matsuzawa Y. Elevated levels of plasma transforming growth factor-beta in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):676–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai Y., Kawata S., Tamura S., Ito N., Tsushima H., Takaishi K., Kiso S., Matsuzawa Y. Plasma transforming growth factor-beta 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Comparison with chronic liver diseases. Cancer. 1994 May 1;73(9):2275–2279. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940501)73:9<2275::aid-cncr2820730907>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonetti R. G., Cammà C., Fiorello F., Politi F., D'Amico G., Pagliaro L. Hepatocellular carcinoma. A worldwide problem and the major risk factors. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jul;36(7):962–972. doi: 10.1007/BF01297149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swets J. A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1285–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3287615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Chang W. Y., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Effects of hepatitis C and B viruses infection on the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol. 1994 Sep;44(1):92–95. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890440117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Chang W. Y., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Frequency of raised alpha-fetoprotein level among Chinese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma related to hepatitis B and C. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jun;69(6):1157–1159. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Chang W. Y., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Hepatitis B and C virus infection as risk factors for liver cirrhosis and cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study. Liver. 1994 Apr;14(2):98–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1994.tb00055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Chang W. Y., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Wang L. Y., Hsieh M. Y., Chen S. C., Chuang W. L., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Hepatitis C virus infection as a risk factor for non-alcoholic liver cirrhosis in Taiwan. J Med Virol. 1993 Dec;41(4):296–300. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890410407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Chang W. Y., Hsieh M. Y., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Additive effect modification of hepatitis B surface antigen and e antigen on the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1996 Jun;73(12):1498–1502. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Chang W. Y., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Clinical evaluation of serum alpha-fetoprotein and circulating immune complexes as tumour markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1995 Aug;72(2):442–446. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Chang W. Y., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Hepatitis B and C virus infection as risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese: a case-control study. Int J Cancer. 1994 Mar 1;56(5):619–621. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Jeng J. E., Ho M. S., Chang W. Y., Lin Z. Y., Tsai J. H. Independent and additive effect modification of hepatitis C and B viruses infection on the development of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1996 Mar;24(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Tsai J. H., Chang W. Y. Relationship of serum alpha-fetoprotein to circulating immune complexes and complements in patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1990 Jun;25(3):388–393. doi: 10.1007/BF02779456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. F., Tsai J. H., Chang W. Y., Ton T. C. Elevation of circulating immune complexes and its relationship to alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 1991;9(2):137–143. doi: 10.3109/07357909109044224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y. C., Tsai J. F., Chuang L. Y., Yeh H. W., Tsai J. H., Florine D. L., Tam J. P. Elevation of transforming growth factor alpha and its relationship to the epidermal growth factor and alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):896–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


