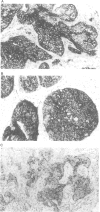
Abstract
The prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein overexpression detected in tumours by immunocytochemical assays (ICAs) was investigated in 148 breast carcinomas. ICAs were performed under optimal technical conditions with frozen tissue sections and included automated immunoperoxidase technique and computer-assisted analysis (densitometry) of digitized coloured microscopic images. Results of quantitative ICAs (expressed in percentages of c-erbB-2-positive surfaces and mean optical densities) were correlated with the patients' follow-up in axillary lymph node-positive (N+) and node-negative (N-) subgroups of patients. Patients' follow-up ranged from 9 months (for the first death) to 101 months (for the 121 alive patients) with a 62.5 months mean overall follow-up. It was shown that marked c-erbB-2 immunocytochemical expression in tumours (cut-off point 35%) significantly correlated with the patients' poor overall survival in N+ and in N- patients (Kaplan-Meier, log-rank test, P = 0.045 and P = 0.015). Also, marked c-erbB-2 immunohistochemical expression correlates with short disease-free (P = 0.005), recurrence-free (P = 0.048) and metastasis-free survival (P = 0.05) (Kaplan-Meier, log-rank test) in N+, but not in N- subgroups. It is concluded that in optimal conditions (automated and quantitative ICAs on frozen sections) c-erbB immunohistochemical expression is a significant prognostic indicator in terms of overall and disease-free survival. The c-erbB-2 protein prognostic significance is independent of node status in terms of overall survival, but not of disease-free survival.
Full text
PDF
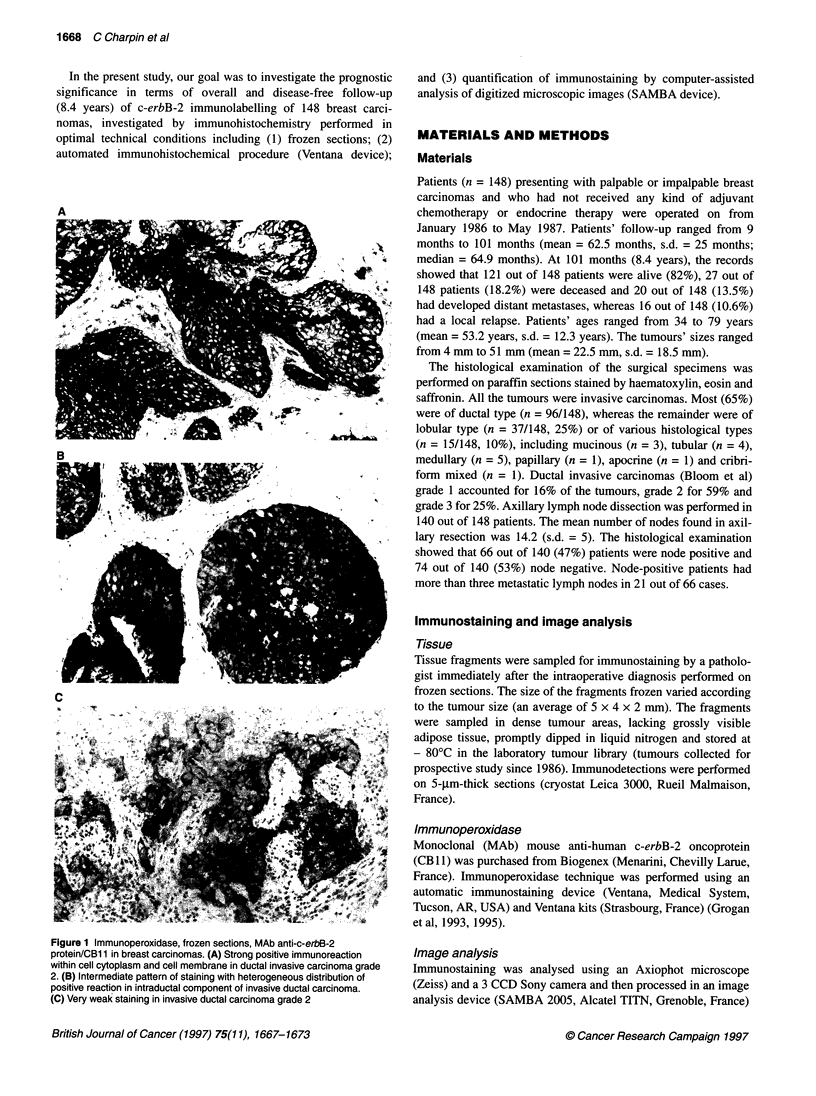
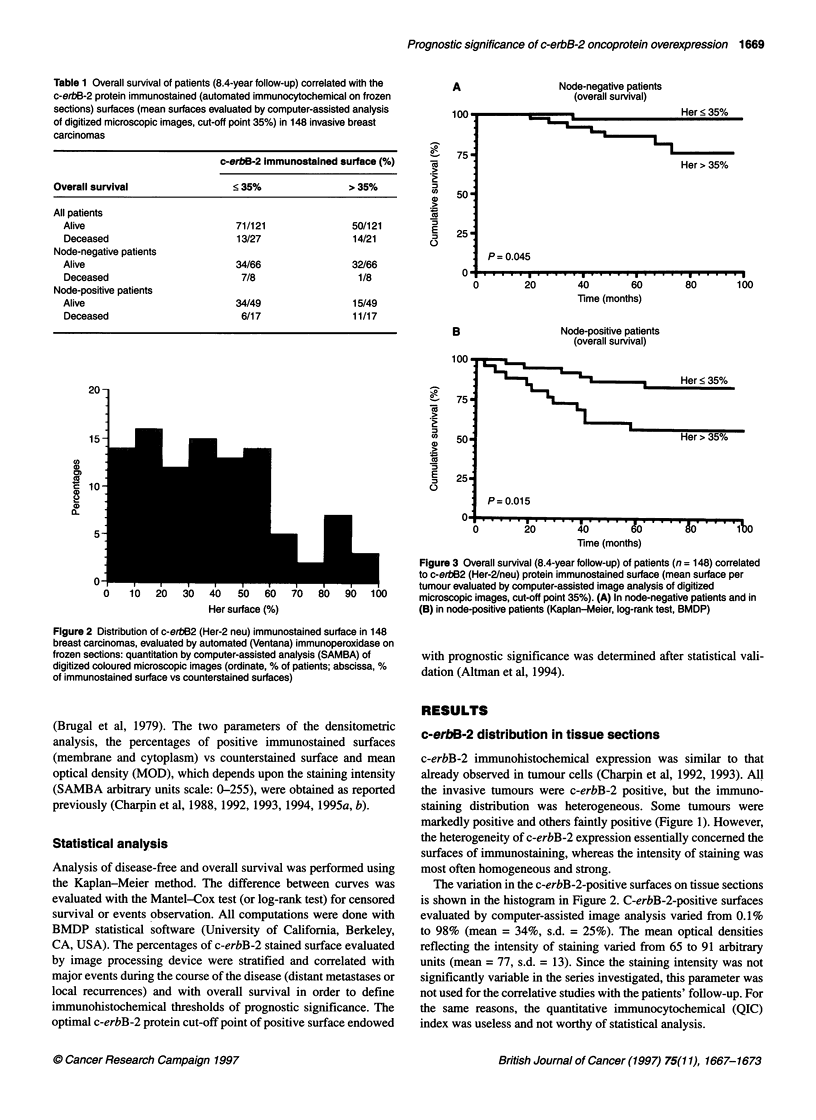
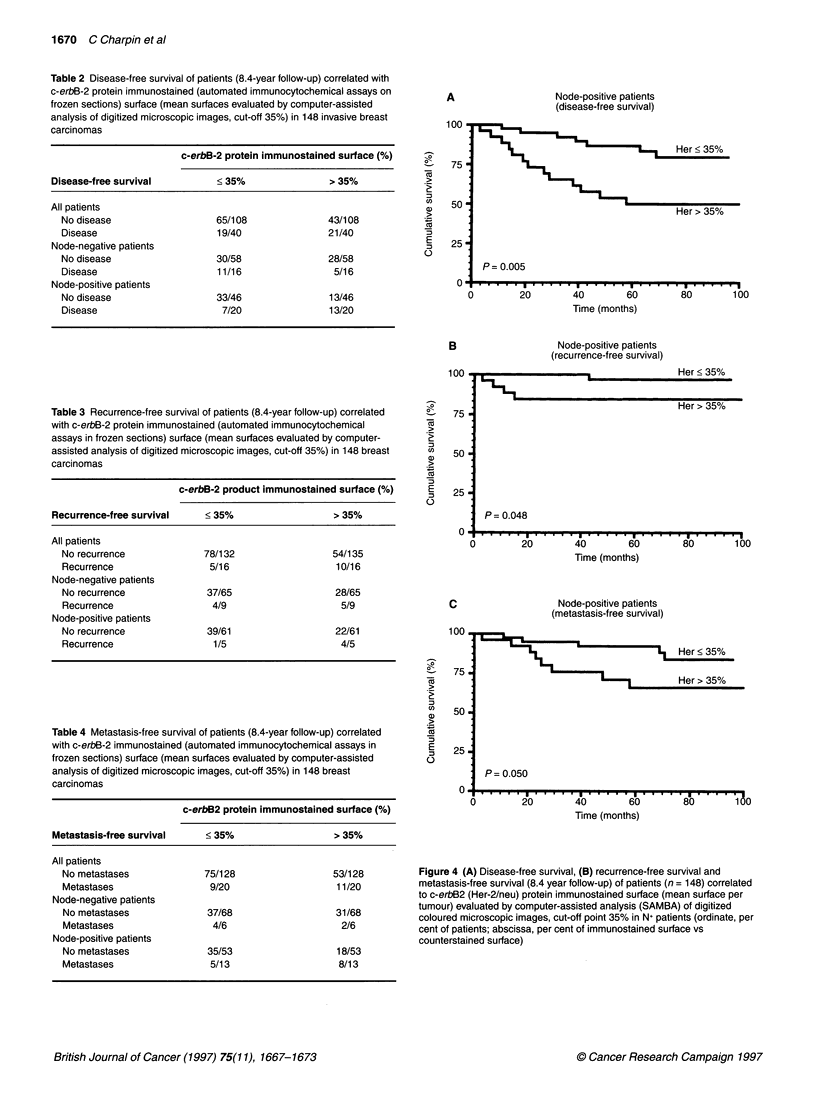



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman D. G., Lausen B., Sauerbrei W., Schumacher M. Dangers of using "optimal" cutpoints in the evaluation of prognostic factors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Jun 1;86(11):829–835. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.11.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baak J. P., Chin D., van Diest P. J., Ortiz R., Matze-Cok P., Bacus S. S. Comparative long-term prognostic value of quantitative HER-2/neu protein expression, DNA ploidy, and morphometric and clinical features in paraffin-embedded invasive breast cancer. Lab Invest. 1991 Feb;64(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Bacus J. W., Slamon D. J., Press M. F. HER-2/neu oncogene expression and DNA ploidy analysis in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Feb;114(2):164–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Ruby S. G., Weinberg D. S., Chin D., Ortiz R., Bacus J. W. HER-2/neu oncogene expression and proliferation in breast cancers. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):103–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg A., Tandon A. K., Sigurdsson H., Clark G. M., Fernö M., Fuqua S. A., Killander D., McGuire W. L. HER-2/neu amplification predicts poor survival in node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4332–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugal G., Garbay C., Giroud F., Adelh D. A double scanning microphotometer for image analysis: hardware, software and biomedical applications. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Jan;27(1):144–152. doi: 10.1177/27.1.374569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpin C., Bonnier P., Devictor B., Andrac L., Lavaut M. N., Allasia C., Piana L. Immunodetection of HER-2/neu protein in frozen sections evaluated by image analysis: correlation with overall and disease-free survival in breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1993 May-Jun;13(3):603–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpin C., DeVictor B., Andrac L., Amabile J., Bergeret D., LaVaut M. N., Allasia C., Piana L. p53 quantitative immunocytochemical analysis in breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 1995 Feb;26(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpin C., Devictor B., Bergeret D., Andrac L., Boulat J., Horschowski N., Lavaut M. N., Piana L. CD31 quantitative immunocytochemical assays in breast carcinomas. Correlation with current prognostic factors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Apr;103(4):443–448. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.4.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpin C., Martin P. M., De Victor B., Lavaut M. N., Habib M. C., Andrac L., Toga M. Multiparametric study (SAMBA 200) of estrogen receptor immunocytochemical assay in 400 human breast carcinomas: analysis of estrogen receptor distribution heterogeneity in tissues and correlations with dextran coated charcoal assays and morphological data. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1578–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpin C., Vielh P., Duffaud F., Devictor B., Andrac L., Lavaut M. N., Allasia C., Horschowski N., Piana L. Quantitative immunocytochemical assays of P-glycoprotein in breast carcinomas: correlation to messenger RNA expression and to immunohistochemical prognostic indicators. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Oct 19;86(20):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.20.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. Follow-up study of HER-2/neu amplification in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusterson B. A., Machin L. G., Gullick W. J., Gibbs N. M., Powles T. J., Elliott C., Ashley S., Monaghan P., Harrison S. c-erbB-2 expression in benign and malignant breast disease. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):453–457. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley M., Maxwell P., Whiteside C., Toner P. G. C-erbB-2 oncogene product expression depends on tumour type and is related to oestrogen receptor and lymph node status in human breast carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 1993 Apr;189(3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80508-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Leslie K. O., Rogers L. A., Howard P. L. Amplification of the c-erb B-2 oncogene and prognosis of breast adenocarcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Feb;114(2):160–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kury F., Sliutz G., Schemper M., Reiner G., Reiner A., Jakesz R., Wrba F., Zeillinger R., Knogler W., Huber J. HER-2 oncogene amplification and overall survival of breast carcinoma patients. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(9):946–949. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90616-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipponen H. J., Aaltomaa S., Syrjänen S., Syrjänen K. c-erbB-2 oncogene related to p53 expression, cell proliferation and prognosis in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 1993 Jul-Aug;13(4):1147–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann A. H., Dervan P. A., O'Regan M., Codd M. B., Gullick W. J., Tobin B. M., Carney D. N. Prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 and estrogen receptor status in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 15;51(12):3296–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Clark G. M. Prognostic factors and treatment decisions in axillary-node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 25;326(26):1756–1761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206253262607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Dietrich K. D., Danyluk J., Paterson A. H., Lees A. W., Jamil N., Hanson J., Jenkins H., Krause B. E., McBlain W. A. Correlation between c-erbB-2 amplification and risk of recurrent disease in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):556–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauletti G., Godolphin W., Press M. F., Slamon D. J. Detection and quantitation of HER-2/neu gene amplification in human breast cancer archival material using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Oncogene. 1996 Jul 4;13(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffanelli A., Dittadi R., Catozzi L., Gion M., Capitanio G., Gelli M. C., Brazzale A., Malagutti R., Pelizzola D., Menegon A. Determination of ErbB2 protein in breast cancer tissues by different methods. Relationships with other biological parameters. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;37(3):267–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01806508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Pike M. C., Chazin V. R., Hung G., Udove J. A., Markowicz M., Danyluk J., Godolphin W., Sliwkowski M., Akita R. Her-2/neu expression in node-negative breast cancer: direct tissue quantitation by computerized image analysis and association of overexpression with increased risk of recurrent disease. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4960–4970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quénel N., Wafflart J., Bonichon F., de Mascarel I., Trojani M., Durand M., Avril A., Coindre J. M. The prognostic value of c-erbB2 in primary breast carcinomas: a study on 942 cases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995 Sep;35(3):283–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00665980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin P. M., Chamness G. C. The c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene as a prognostic and predictive marker in breast cancer: a paradigm for the development of other macromolecular markers--a review. Gene. 1995 Jun 14;159(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00866-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stål O., Sullivan S., Wingren S., Skoog L., Rutqvist L. E., Carstensen J. M., Nordenskjöld B. c-erbB-2 expression and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1995 Dec;31A(13-14):2185–2190. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Chamness G. C., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Aug;7(8):1120–1128. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.8.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Gullick W. J., Varley J. M. An evaluation of immunoreactivity for c-erbB-2 protein as a marker of poor short-term prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1989 Sep;60(3):426–429. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley J., Cooke T., Murray G. D., Platt-Higgins A., George W. D., Holt S., Myskov M., Spedding A., Barraclough B. R., Rudland P. S. The long term prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):447–450. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C., Angus B., Nicholson S., Sainsbury J. R., Cairns J., Gullick W. J., Kelly P., Harris A. L., Horne C. H. Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein: a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 15;49(8):2087–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. J., Ahuja H., Cline M. J. Proto-oncogene abnormalities in human breast cancer: c-ERBB-2 amplification does not correlate with recurrence of disease. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):105–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Peterse J. L., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Lomans J., Dalesio O., Nusse R. Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 10;319(19):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811103191902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]