Abstract
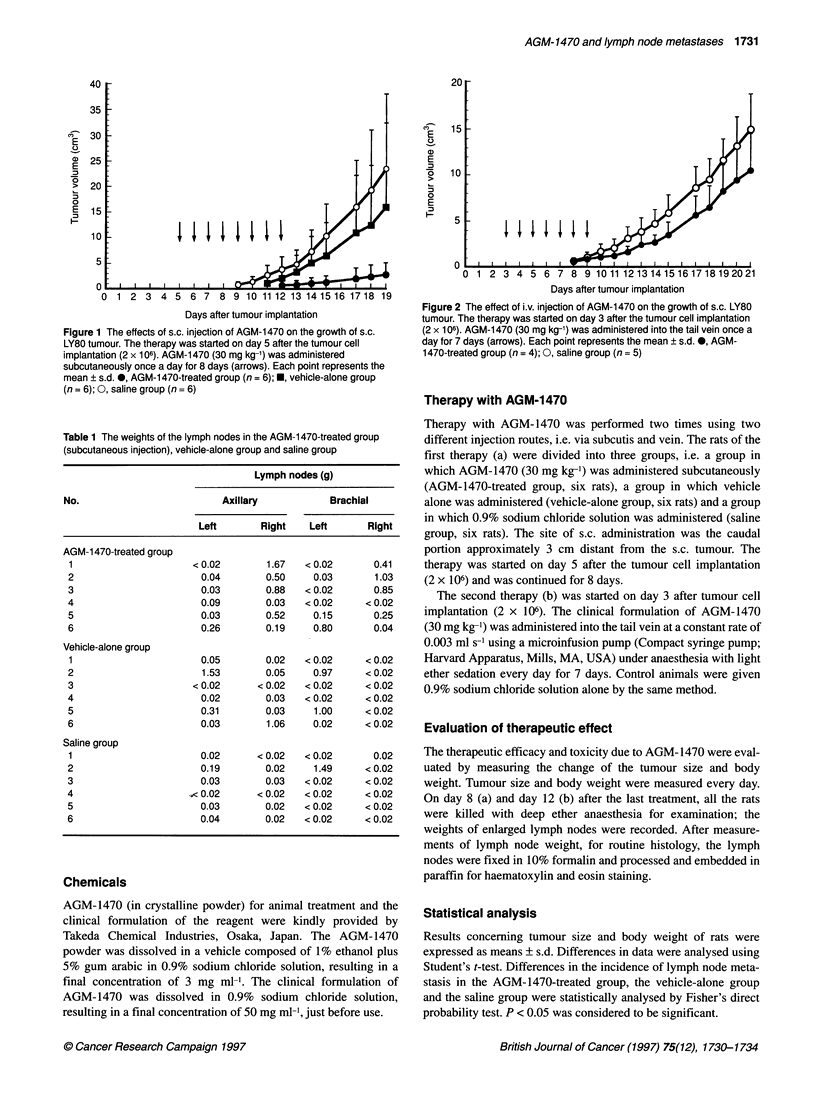
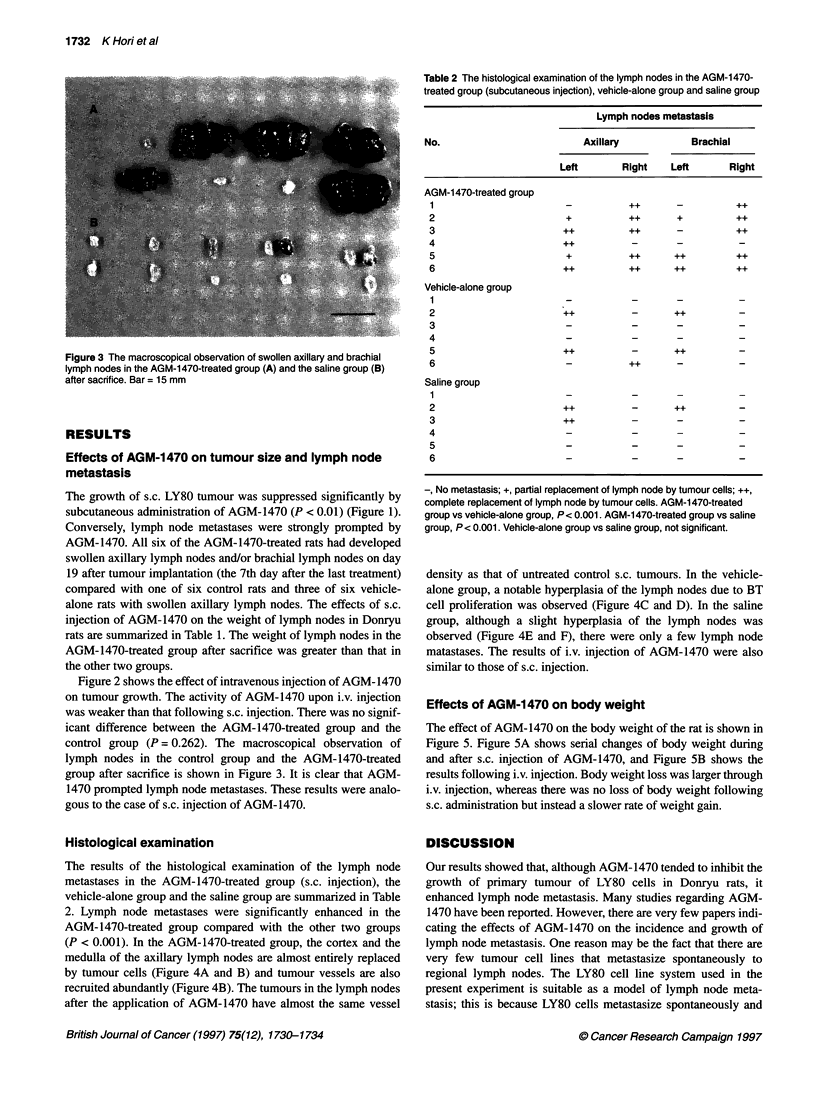
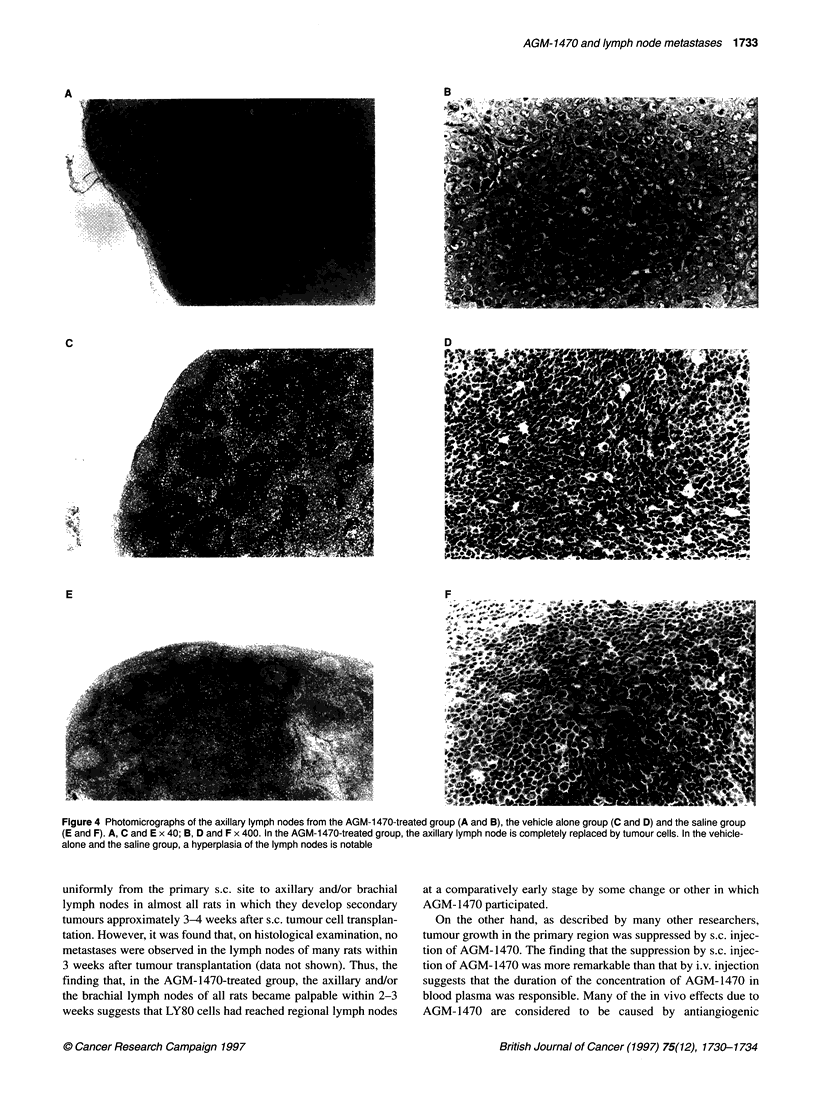
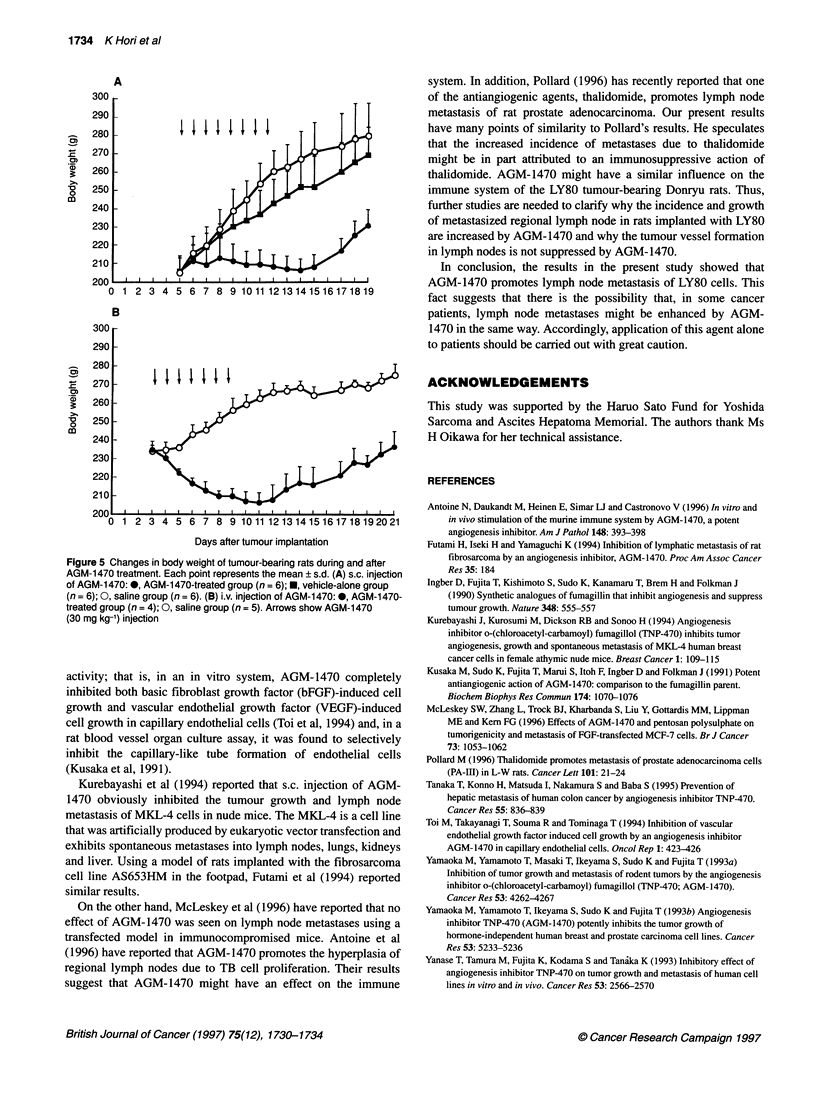
Using the rat tumour cell line LY80, a subline of Yoshida sarcoma, the effects of AGM-1470 on the growth of primary tumour and the incidence of regional lymph node metastasis were evaluated. AGM-1470 (30 mg kg(-1)) was administered subcutaneously or intravenously. Subcutaneous (s.c.) and intravenous (i.v.) injections were repeated for 8 days and 7 days respectively. Tumour growth of a primary region tended to be suppressed by AGM-1470. The s.c. tumours after sacrifice were much smaller in the AGM-1470-treated group (s.c. injection) than in the control groups. However, the growth of metastatic foci in the lymph nodes was prompted markedly by AGM-1470. All six of the AGM-1470-treated rats had developed swollen axillary lymph nodes and/or brachial lymph nodes on day 19 after tumour implantation (the 7th day after the last treatment) compared with one of six saline-injected rats and three of six vehicle-alone treated rats with swollen axillary lymph nodes. The weight of lymph nodes after sacrifice in the AGM-1470-treated rats was much heavier than that of the other two groups. Histological examination showed that in the AGM-1470-treated group, the cortex and the medulla of the axillary lymph nodes were almost entirely replaced by tumour cells while, in the vehicle alone group, a notable hyperplasia of the lymph nodes due to BT cell proliferation tended to be induced. In the saline group, although a slight hyperplasia of lymph nodes was observed, there were only a few lymph node metastases. In the case of i.v. injection of AGM-1470, similar results were obtained. It is thought that LY80 cells spread to regional lymph nodes at a comparatively early stage by some change or other in which AGM-1470 participated. From the present experiment, it is concluded that application of AGM-1470 alone to patients should be carried out with great caution.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoine N., Daukandt M., Heinen E., Simar L. J., Castronovo V. In vitro and in vivo stimulation of the murine immune system by AGM-1470, a potent angiogenesis inhibitor. Am J Pathol. 1996 Feb;148(2):393–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D., Fujita T., Kishimoto S., Sudo K., Kanamaru T., Brem H., Folkman J. Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):555–557. doi: 10.1038/348555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurebayashi J, Kurosumi M, Dickson RB, Sonoo H. Angiogenesis Inhibitor O-(Chloroacetyl-carbamoyl) fumagillol (TNP-470) Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis, Growth and Spontaneous Metastasis of MKL-4 Human Breast Cancer Cells in Female Athymic Nude Mice. Breast Cancer. 1994 Dec 30;1(2):109–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02967040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusaka M., Sudo K., Fujita T., Marui S., Itoh F., Ingber D., Folkman J. Potent anti-angiogenic action of AGM-1470: comparison to the fumagillin parent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1070–1076. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91529-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeskey S. W., Zhang L., Trock B. J., Kharbanda S., Liu Y., Gottardis M. M., Lippman M. E., Kern F. G. Effects of AGM-1470 and pentosan polysulphate on tumorigenicity and metastasis of FGF-transfected MCF-7 cells. Br J Cancer. 1996 May;73(9):1053–1062. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard M. Thalidomide promotes metastasis of prostate adenocarcinoma cells (PA-III) in L-W rats. Cancer Lett. 1996 Mar 19;101(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)04105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Konno H., Matsuda I., Nakamura S., Baba S. Prevention of hepatic metastasis of human colon cancer by angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 15;55(4):836–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka M., Yamamoto T., Ikeyama S., Sudo K., Fujita T. Angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 (AGM-1470) potently inhibits the tumor growth of hormone-independent human breast and prostate carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5233–5236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka M., Yamamoto T., Masaki T., Ikeyama S., Sudo K., Fujita T. Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis of rodent tumors by the angiogenesis inhibitor O-(chloroacetyl-carbamoyl)fumagillol (TNP-470; AGM-1470). Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4262–4267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase T., Tamura M., Fujita K., Kodama S., Tanaka K. Inhibitory effect of angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 on tumor growth and metastasis of human cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2566–2570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]