Abstract
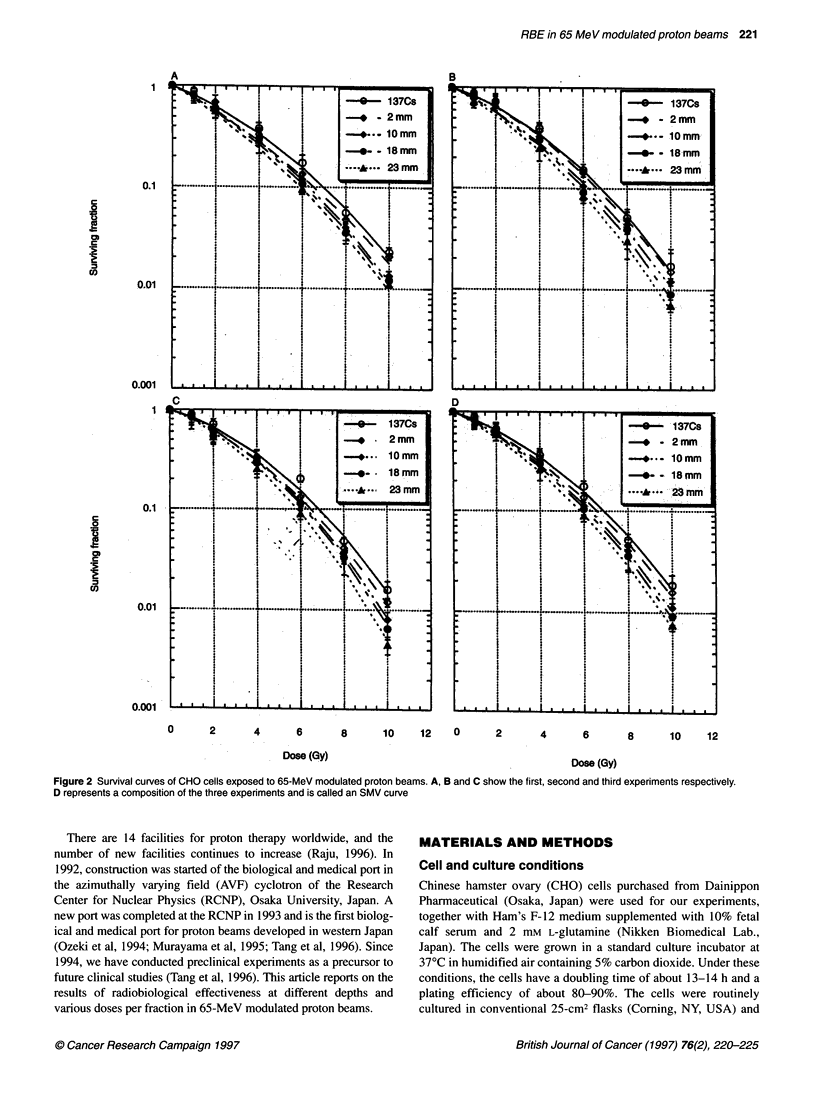
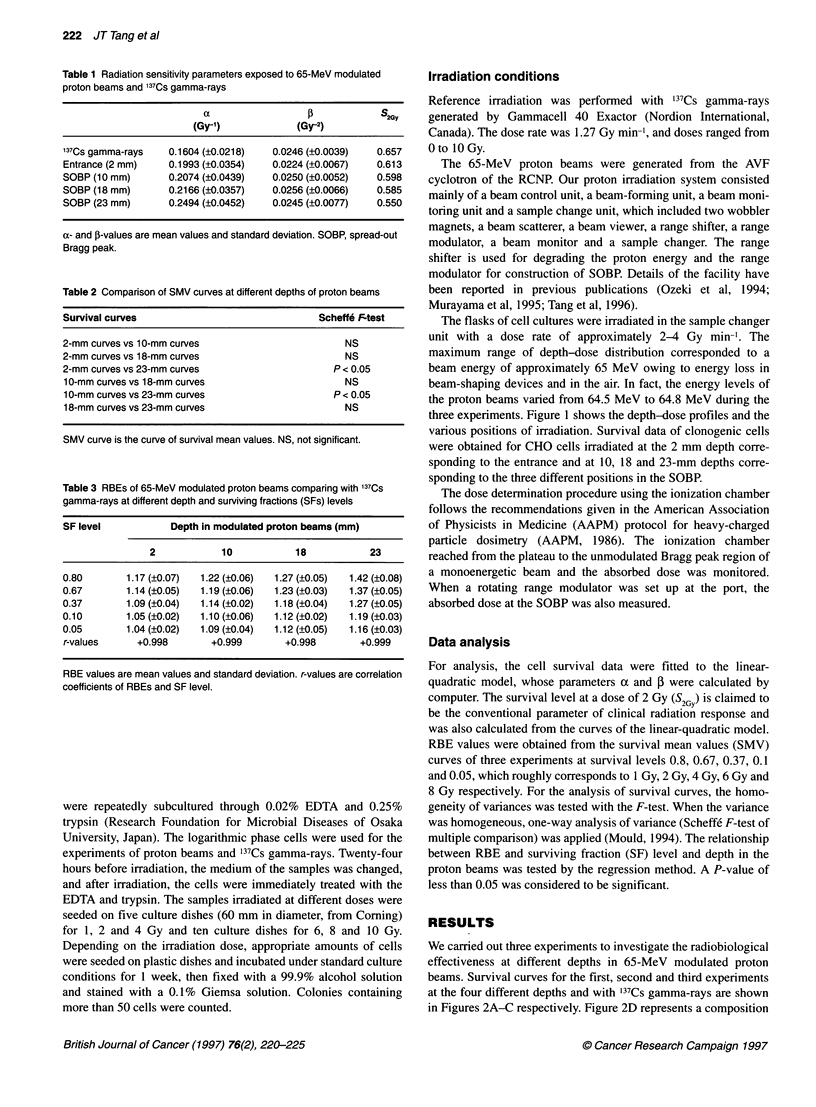
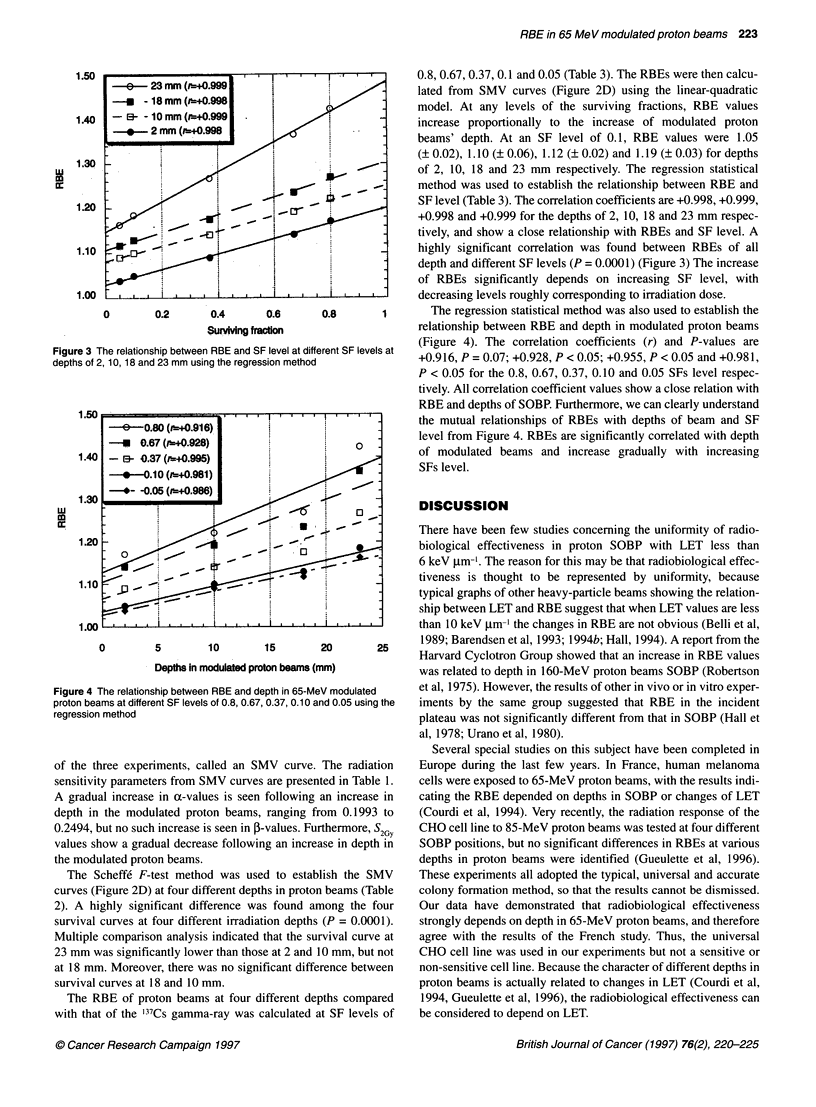
To assess the achievement of uniformity of radiobiological effectiveness at different depths in the proton spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP), Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were exposed to 65-MeV modulated proton beams at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. We selected four different irradiation positions: 2 mm depth, corresponding to the entrance, and 10, 18 and 23 mm depths, corresponding to different positions in the SOBP. Cell survival curves were generated with the in vitro colony formation method and fitted to the linear-quadratic model. With 137Cs gamma-rays as the reference irradiation, the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for a surviving fraction (SF) level of 0.1 are 1.05, 1.10, 1.12 and 1.19 for depths of 2, 10, 18 and 23 mm respectively. A significant difference was found between the survival curves at 10 and 23 mm (P < 0.05), but not between 18 and 10 mm or between 18 and 23 mm. There was a significant dependence of RBE on depths in modulated proton beams at the 0.1 surviving fraction level (P < 0.05). Moreover, the rise of RBEs significantly depended on increasing SF level or decreased approximately in correspondence with irradiation dose (P = 0.0001). To maintain uniformity of radiobiological effectiveness for the target volume, careful attention should be paid to the influence of depth of beam and irradiation dose.
Full text
PDF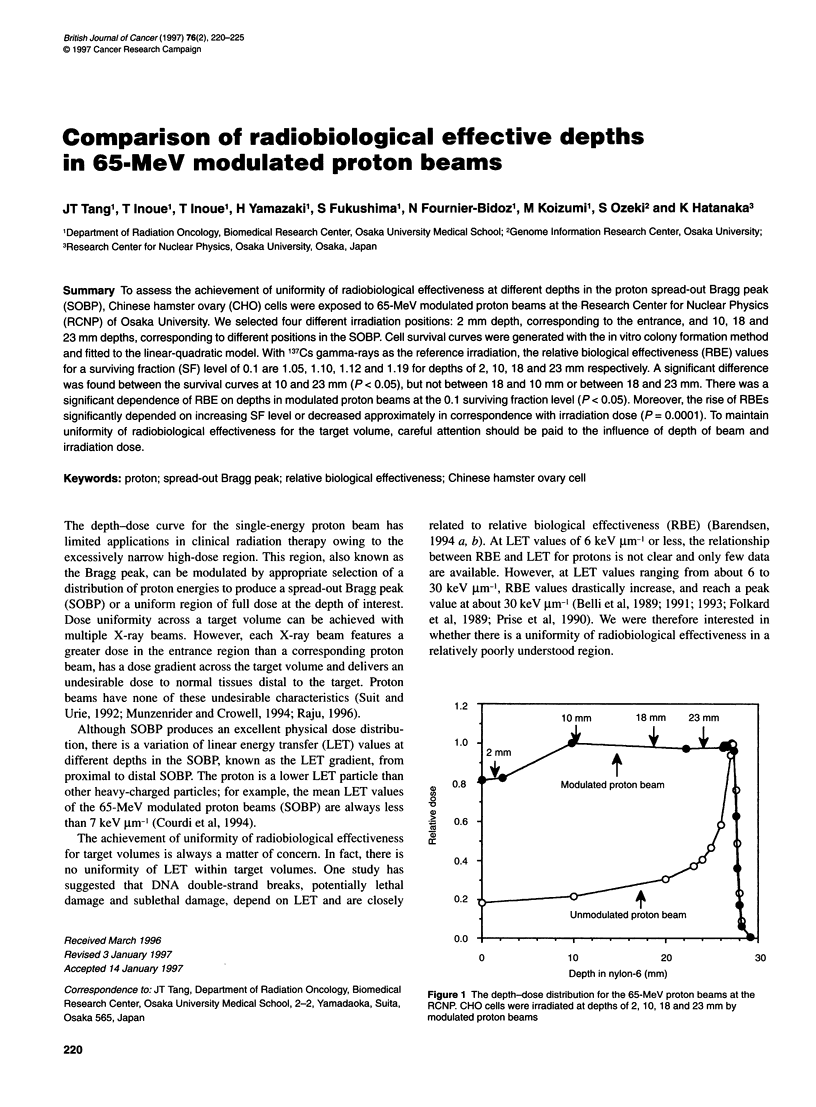


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barendsen G. W. RBE-LET relationships for different types of lethal radiation damage in mammalian cells: comparison with DNA dsb and an interpretation of differences in radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Nov;66(5):433–436. doi: 10.1080/09553009414551411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barendsen G. W. Sublethal damage and DNA double strand breaks have similar RBE-LET relationships: evidence and implications. Int J Radiat Biol. 1993 Mar;63(3):325–330. doi: 10.1080/09553009314550431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barendsen G. W. The relationships between RBE and LET for different types of lethal damage in mammalian cells: biophysical and molecular mechanisms. Radiat Res. 1994 Sep;139(3):257–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli M., Cera F., Cherubini R., Haque A. M., Ianzini F., Moschini G., Sapora O., Simone G., Tabocchini M. A., Tiveron P. Inactivation and mutation induction in V79 cells by low energy protons: re-evaluation of the results at the LNL facility. Int J Radiat Biol. 1993 Mar;63(3):331–337. doi: 10.1080/09553009314550441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli M., Cera F., Cherubini R., Ianzini F., Moschini G., Sapora O., Simone G., Tabocchini M. A., Tiveron P. Mutation induction and RBE-LET relationship of low-energy protons in V79 cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Feb;59(2):459–465. doi: 10.1080/09553009114550411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli M., Cherubini R., Finotto S., Moschini G., Sapora O., Simone G., Tabocchini M. A. RBE-LET relationship for the survival of V79 cells irradiated with low energy protons. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Jan;55(1):93–104. doi: 10.1080/09553008914550101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist E., Russell K. R., Stenerlöw B., Montelius A., Grusell E., Carlsson J. Relative biological effectiveness of intermediate energy protons. Comparisons with 60Co gamma-radiation using two cell lines. Radiother Oncol. 1993 Jul;28(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(93)90184-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courdi A., Brassart N., Hérault J., Chauvel P. The depth-dependent radiation response of human melanoma cells exposed to 65 MeV protons. Br J Radiol. 1994 Aug;67(800):800–804. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-67-800-800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cucinotta F. A., Katz R., Wilson J. W., Townsend L. W., Shinn J., Hajnal F. Biological effectiveness of high-energy protons: target fragmentation. Radiat Res. 1991 Aug;127(2):130–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkard M., Prise K. M., Vojnovic B., Davies S., Roper M. J., Michael B. D. The irradiation of V79 mammalian cells by protons with energies below 2 MeV. Part I: Experimental arrangement and measurements of cell survival. Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Sep;56(3):221–237. doi: 10.1080/09553008914551401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gueulette J., Grégoire V., Octave-Prignot M., Wambersie A. Measurements of radiobiological effectiveness in the 85 MeV proton beam produced at the cyclotron CYCLONE of Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium. Radiat Res. 1996 Jan;145(1):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J., Kellerer A. M., Rossi H. H., Lam Y. M. The relative biological effectiveness of 160 MeV protons--II. Biological data and their interpretation in terms of microdosimetry. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978 Nov-Dec;4(11-12):1009–1013. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(78)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mijnheer B. J., Battermann J. J., Wambersie A. What degree of accuracy is required and can be achieved in photon and neutron therapy? Radiother Oncol. 1987 Mar;8(3):237–252. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(87)80247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prise K. M., Folkard M., Davies S., Michael B. D. The irradiation of V79 mammalian cells by protons with energies below 2 MeV. Part II. Measurement of oxygen enhancement ratios and DNA damage. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990 Aug;58(2):261–277. doi: 10.1080/09553009014551611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju M. R. Particle radiotherapy: historical developments and current status. Radiat Res. 1996 Apr;145(4):391–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. B., Williams J. R., Schmidt R. A., Little J. B., Flynn D. F., Suit H. D. Radiobiological studies of a high-energy modulated proton beam utilizing cultured mammalian cells. Cancer. 1975 Jun;35(6):1664–1677. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197506)35:6<1664::aid-cncr2820350628>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suit H., Urie M. Proton beams in radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Feb 5;84(3):155–164. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.3.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano M., Goitein M., Verhey L., Mendiondo O., Suit H. D., Koehler A. Relative biological effectiveness of a high energy modulated proton beam using a spontaneous murine tumor in vivo. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980 Sep;6(9):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(80)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashkin P. N., Silin D. I., Zolotov V. A., Kostjuchenko V. I., Nichiporov D. F., Feoktistova T. P., Martirosov K. S., Minakova Y. I., Khoroshkov V. S., Polonski P. B. Relative biological effectiveness of proton medical beam at Moscow synchrotron determined by the Chinese hamster cells assay. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995 Feb 1;31(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)00381-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


