The crystal structure of l-lactate oxidase (LOX) from A. viridans at 2.1 Å resolution.
Keywords: l-lactate oxidase, FMN-dependent enzymes
Abstract
The crystal structure of l-lactate oxidase (LOX) from Aerococcus viridans has been determined at 2.1 Å resolution. LOX catalyzes the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) dependent oxidation of lactate to pyruvate and hydrogen peroxide. LOX belongs to the α-hydroxy-acid oxidase flavoenzyme family; members of which bind similar substrates and to some extent have conserved catalytic properties and structural motifs. LOX crystallized as two tightly packed tetramers in the asymmetric unit, each having fourfold symmetry. The present structure shows a conserved FMN coordination, but also reveals novel residues involved in substrate binding compared with other family members.
1. Introduction
Lactate oxidase is one of a group of FMN-dependent enzymes which catalyse the conversion of α-hydroxy acids to α-keto acids via a two-electron reduction of the FMN cofactor. Although the details of the mechanism are still under debate, it ultimately results in the transfer of two electrons and two protons from the reduced cofactor to molecular oxygen to generate hydrogen peroxide and the α-keto acid and ultimately to regenerate the oxidized cofactor. The reaction proceeds via a ping-pong mechanism with sequential reductive and oxidative steps (Macheroux et al., 1992 ▶). In the most widely accepted model, the first step involves the abstraction of a proton from the substrate α-carbon by an adjacent base to generate a carbanion, followed by the transfer of two electrons to the cofactor. An alternative model involves the direct transfer of a hydride ion from the substrate α-carbon to the N5 atom of the cofactor. Both mechanisms have been investigated extensively (Ghisla & Massey, 1989 ▶). Crystallographic support for the alternative models rests on contacts between the substrate and cofactor and surrounding residues which are proposed to modify the acid/base properties of the Cα- or α-OH hydrogen or to stabilize the reaction intermediate. Evidence for the formation of a possible covalent substrate–cofactor intermediate in glycolate oxidase has been reported by Stenberg et al. (1995 ▶).
In crystal structures of FMN enzymes the isoalloxazine system in the cofactor is almost invariably found in the bent and thus reduced form, but in structures of thioredoxin it is found in both oxidized and reduced forms (Lennon et al., 1999 ▶). The reduced cofactor is regenerated via a peroxo adduct at C4 in the isoalloxazine-ring system (Bolognesi et al., 1978 ▶; Vervoort et al., 1986 ▶). In the mechanistically related (Molla, Motteran, Job et al., 2003 ▶; Molla, Motteran, Piubelli et al., 2003 ▶) but structurally unrelated (Umhau et al., 2000 ▶) FMN-dependent d-amino-acid oxidases, the reaction is currently believed to proceed via hydride transfer to generate an α-imine and hydrogen peroxide. The imine product is then spontaneously hydrolysed to yield an α-hydroxy acid and NH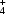 (Walsh et al., 1971 ▶).
(Walsh et al., 1971 ▶).
The structures of the four related enzymes glycolate oxidase (GLO; PDB code 1gox; Lindqvist & Branden, 1989 ▶), a soluble chimeric form of mandelate oxidase (MDH; PDB code 1p4c; Sukumar et al., 2004 ▶), long-chain hydroxy-acid oxidase (HAO; PDB code 1tb3; Cunane et al., 2005 ▶) and flavocytochrome b 2 (B2; PDB code 1fcb; also known as lactate dehydrogenase; Xia et al., 1987 ▶) have been determined by X-ray crystallography. In each of these structures, the monomer contains a classic eight-stranded α/β-barrel with binding sites for the FMN cofactor and substrate at the C-terminal end of the β-barrel. In GLO and HAO the biologically active unit consists of two tetramers, stacked with a slight rotation. The active unit in MDH contains a single tetramer, but in B2 it is a heterodimer containing two α/β-barrel units complete with FMN-binding and substrate-binding sites. B2 has been the subject of studies to elucidate the reaction mechanism, but it is somewhat different from the others in that one of the chains also contains a haem unit which is involved in electron transfer, so that cofactor regeneration proceeds by a different pathway.
The FAD-dependent glucose and cholesterol oxidases are also used in biosensors (Sarath Babu et al., 2004 ▶; Svobodova et al., 2002 ▶; Pan et al., 2003 ▶). The current l-lactate oxidase (LOX) from Aerococcus viridans is used as the receptor in biosensor applications developed to determine blood lactate levels (Gavalas & Chaniotakis, 2001 ▶; Ito et al., 1996 ▶; Poscia et al., 2005 ▶). At present, the reaction occurs in solution, with potentiometric detection of the product hydrogen peroxide. The literature characterizes LOX as unstable (Lillis et al., 2000 ▶) and long-term stability is often the problem when using LOX in biosensors. The detailed three-dimensional structure will aid in assessing how the enzyme may be stabilized and the reaction rate increased and in the development of novel methods for immobilizing LOX onto sensors or other surfaces.
Crystallization of LOX was first reported in 1998 (Morimoto et al., 1998 ▶) and subsequently in 2005 (Umena et al., 2005 ▶); an unreleased structure was submitted to the PDB during preparation of this manuscript.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Crystallization and data collection
Freeze-dried protein purchased from Genzyme Diagnostics was dissolved in water. 7 µl 18 mg ml−1 LOX in 0.1 M sodium l-lactate was mixed with 3 µl 20% PEG 4000, 10%(v/v) 2-propanol buffered with 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.5 (reservoir solution) and equilibrated against 500 µl reservoir solution through vapour diffusion at room temperature using sitting drops. The reservoir solution was based on Crystal Screen I solution No. 41 (Hampton Research). Small three-dimensional crystals with dimensions of about 0.01 × 0.02 × 0.2 mm appeared in 6 d. The crystals were yellow, as expected with the FMN cofactor, and were cryoprotected by a stepwise increase in the concentration of glycerol (2–10%) prior to flash-cooling in liquid nitrogen. A data set extending to 2.1 Å resolution was collected at 100 K using a wavelength of 0.934 Å on the macromolecular crystallography beamline ID14-1 at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF). The data were indexed, integrated and scaled using XDS (Kabsch, 1993 ▶). The intensities were reduced using the CCP4 program TRUNCATE (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4, 1994 ▶). Crystals were orthorhombic, with unit-cell parameters a = 117.34, b = 134.74, c = 185.56 Å, α = β = γ = 90°. Systematic absences uniquely identified the space group as P212121. The solvent content was estimated to be 44.6%, with a Matthews coefficient of 2.2 Å3 Da−1, assuming the presence of eight molecules in the asymmetric unit, where each molecule has a molecular weight of about 41 kDa. The data-collection and processing statistics are presented in Table 1 ▶.
Table 1. Data-collection and refinement summary.
Values in parentheses are for the resolution shell 2.15–2.10 Å.
| Data collection | |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50–2.1 (2.15–2.10) |
| No. of unique reflections | 171468 |
| Redundancy | 4.2 (4.2) |
| Rmerge† (%) | 18.9 (51.7) |
| Completeness (%) | 100.0 (100.0) |
| Mean I/σ(I) | 6.6 (2.4) |
| Refinement statistics | |
| R value (%) | 19.97 (26.2) |
| Free R value (%) | 25.68 (32.6) |
| Deviations from ideal geometry | |
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.011 |
| Bond angles (°) | 1.317 |
| ESU‡ (Å) | 0.162 |
| Average B values (Å2) | |
| Main-chain atoms | 12.80 |
| Side-chain atoms | 13.58 |
| FMN (8) | 8.24 |
| Zn2+ (1) | 26.60 |
| Water molecules (1330) | 16.24 |
| All atoms | 13.35 |
| Ramachandran plot (%) | |
| Most favoured | 89.8 |
| Additionally allowed | 9.2 |
| Generously allowed | 0.6 |
R
merge = 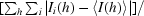
 , where Ii(h) is the ith measurement of reflection h and 〈I(h)〉 is the weighted mean of all measurements of h.
, where Ii(h) is the ith measurement of reflection h and 〈I(h)〉 is the weighted mean of all measurements of h.
Estimated overall coordinate error from REFMAC5 based on maximum likelihood.
2.2. Structure determination and refinement
The crystal structure was determined by molecular replacement with MOLREP (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4, 1994 ▶) using the crystal structure of GLO (PDB code 1gox; Lindqvist, 1989 ▶), with a sequence identity of 32.3%, as the search model. Inspection of the Patterson map showed a pseudo-translational vector with fractional length (0.500, 0.500, 0.033) and a height roughly 1/4 that of the origin peak. This strongly suggested that the contents of the asymmetric unit are organized into two tetramers, as is the case for members of the α-hydroxy-acid oxidase flavoenzyme family. LOX is believed to be active as a tetramer (Duncan et al., 1989 ▶) and the biological units of several members of the α-hydroxy-acid oxidase flavoenzyme family are also tetramers. For this reason, the biologically relevant tetramer of GLO was reconstructed by crystallographic symmetry (GLO crystallizes in space group I422) using SwissPDBViewer (Guex & Peitsch, 1997 ▶) and used as a search model in MOLREP (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4, 1994 ▶). Data to a high-resolution cutoff at 4.0 Å were included and as the statistics were slightly better when searching for individual tetramers (not using the strict pseudo-translational symmetry), giving a lower R factor and a higher correlation coefficient, the two tetramers were treated individually in the following. The best solution from MOLREP had an R factor and a correlation coefficient of 0.572 and 0.347, respectively, whereas the values for the second highest solution were 0.592 and 0.098. Rigid-body fitting in REFMAC5 (Murshudov et al., 1999 ▶), treating the eight molecules as individual entities, caused an immediate drop in R for both the working and free sets of reflections (R work and R free fell to 0.480 and 0.483, respectively, using all reflections to 2.1 Å resolution). After a round of positional refinement with REFMAC5, followed by the removal of flexible regions using O (Jones et al., 1991 ▶), the eight molecules could be autobuilt using ARP/wARP (Perrakis et al., 1999 ▶), resulting in the correct docking of 2550 of the possible 2992 residues. Although the eight molecules in the asymmetric unit are similar, they are not identical and all were refined and built individually. The final refinement statistics are presented in Table 1 ▶.
Figures were prepared with PyMOL (DeLano Scientific LLC) and edited in Adobe Photoshop. The structure-based sequence alignment was produced by superpositioning the structures using SwissPDBViewer (Guex & Peitsch, 1997 ▶). The subsequent alignment was then run through ESPript (Gouet et al., 1999 ▶) to create Fig. 2. No crystal structure exists for lactate monooxygenase (LMO), but its sequence was aligned with the others using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw) and thereafter manually adjusted where applicable. l-Lactate was manually positioned in the substrate-binding site using Coot (Emsley & Cowtan, 2004 ▶), guided by mutation studies and inhibitor binding.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Overall structure
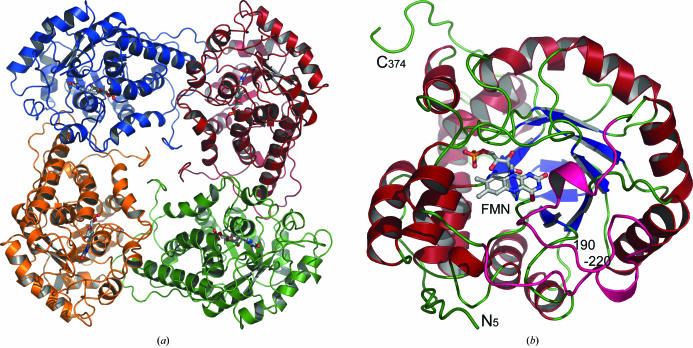
The asymmetric unit of lactate oxidase (LOX) contains two tightly packed tetramers. Each tetramer forms a biologically active unit and has internal 422 symmetry similar to that of the related glycolate oxidase (GLO; Lindqvist & Branden, 1989 ▶). The overall dimensions of each LOX tetramer are approximately 50 × 100 × 100 Å, with the C-terminus folding to fill the central pore (Fig. 1 ▶ a). The individual LOX monomers superimpose well onto each other with root-mean-square (r.m.s.) deviations in the range 0.19–0.69 Å, with the most similar being C and F and the most different being C and E. For simplicity, the following discussion is based on monomer A of LOX. The LOX tetramer superimposes onto the crystallographically generated tetramer of GLO with an r.m.s. deviation of 1.24 Å for 1268 Cα atoms. Similarly, superimposing monomers of LOX (374 residues) and GLO (359 residues) yields an r.m.s. deviation of 1.11 Å for 317 Cα atoms, where, except for a few residues at both termini and a flexible loop region in the middle of the structure, the structures superimpose well onto each other.
Figure 1.
Overall structure of the A. viridans l-lactate oxidase. (a) The l-lactate oxidase tetramer, describing half of the asymmetric unit. The C-terminus of the monomer folds to fill the central channel within the biologically relevant tetramer. (b) The monomer structure viewed from the C-terminal side of the β-barrel and into the active site where the FMN cofactor is located. The active site is located on the tip of the β-barrel and residues 190–220 (in pink) form a lid over the active site.
The 374 amino acids in each LOX subunit are folded into an α/β-barrel with two short β-strands located at the bottom of the barrel. One monomer contains 15 α-helices of various sizes, all but one of which are found in the structure of GLO. The FMN-binding site and the active site are formed on the C-terminal side of the β-barrel (Fig. 1 ▶ b), where LOX residues 190–220 form a lid-like structure for the active site (shown in pink in Fig. 1 ▶ b). This region is poorly conserved in the aligned sequences (Fig. 2 ▶) and is disordered in the GLO, HAO and B2 structures. In order to obtain diffraction-quality crystals of MDH, this region had to be replaced by the GOX sequence (Sukumar et al., 2004 ▶), despite the fact that this region is flexible in GLO. The loop area is also not fully visible in our current LOX structure; of the eight chains, D, F and H are missing 15, 9 and 19 residues in this area, respectively, in agreement with increased mobility of the loop region.
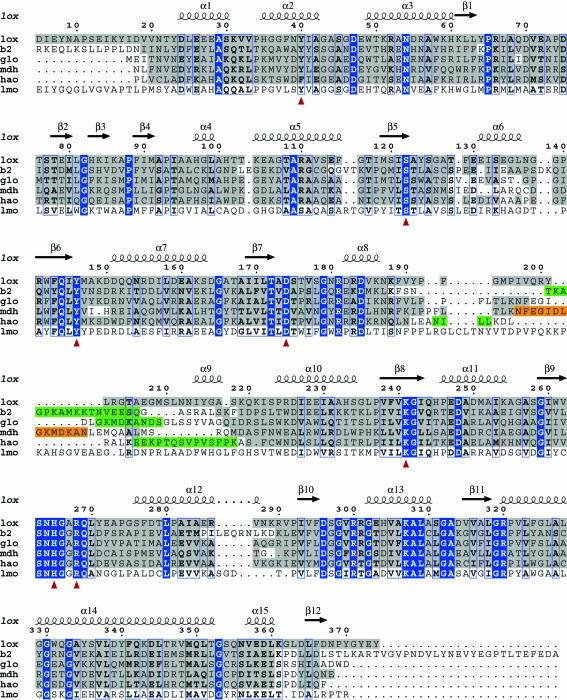
Figure 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of selected FMN-dependent enzymes. lox; lactate oxidase from A. viridans, b2; flavocytochrome b 2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (PDB code 1fcb), glo; glycolate oxidase from Spinacia oleracea (PDB code 1gox), mdh; mandelate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida (PDB code 1p4c), hao; long-chain hydroxy-acid oxidase from Rattus norvegicus (PDB code 1tb3), lmo; lactate monooxygenase from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Residues showing structural conservation to the lox crystal structure are boxed in grey, while identical residues are boxed in blue and similar residues are indicated in bold. Green boxes indicate flexible regions not defined in the deposited crystal structures, while the orange box indicates the region in mandelate dehydrogenase (mdh) which was substituted by glycolate oxidase (glo) residues in order to obtain crystals. Red arrows indicate the highly conserved residues important for FMN binding in this class of enzymes. The secondary-structure elements of lox are indicated above the alignment. No crystal structure exists for lactate monooxygenase (lmo), but its sequence was aligned with the others using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw) and thereafter manually adjusted where applicable.
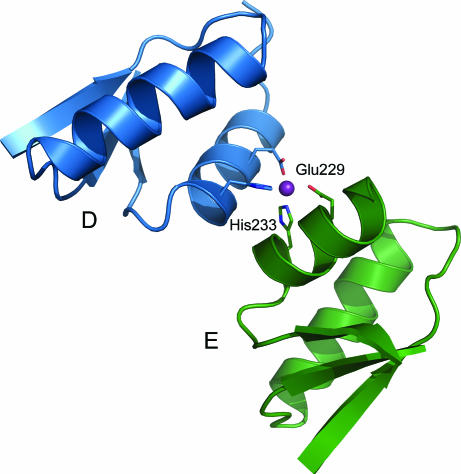
The crystal contacts have furthermore created a metal-binding site between two of the tetramers (Fig. 3 ▶). The residues Glu229 (O∊1/O∊2) and His233 (N∊2) from the D and E subunits coordinate a metal ion which we have assigned as Zn2+ based on its coordination, which is typical for Zn2+ (Harding, 2001 ▶). Although Zn2+ was not added during crystallization, traces of Zn2+ are present in all but the most highly purified reagents and, if the binding site has a high affinity, would readily be scavenged during expression or purification.
Figure 3.
A zinc-binding site located at the crystal contact site between two tetramers. The metal ion is coordinated by Glu229 and His233 of subunits D and E.
3.2. The FMN-binding site
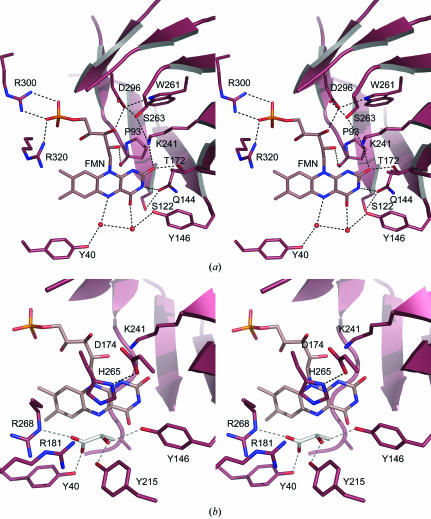
The oxidative cofactor of the active site, flavin mononucleotide (FMN), is positioned in the same place as in GLO (Lindqvist & Branden, 1989 ▶), deep down in the funnel-shaped substrate-binding site, behind (or underneath) the substrate when it is bound (Fig. 4 ▶ a). In all eight LOX monomers the FMN cofactor is bent by about 15° around the central atoms, giving the flavin group a slight U shape. The LOX FMN-binding residues Tyr40, Pro93, Gln144, Tyr146, Thr172, Lys241, Asp296, Arg300 and Arg320 are all conserved between LOX and GLO (Fig. 2 ▶). Five of these residues are involved in stabilization of the reactive isoalloxazine ring: Thr172 Oγ1 and Lys241 Nζ form a hydrogen bond to FMN O2 and Gln144 O∊1 to FMN N3, Tyr146 Oη coordinates a water molecule together with FMN O4 and, finally, Tyr40 Oη coordinates a second water molecule with FMN N5 (Fig. 4 ▶ a). The 5-phosphoribosyl chain is stabilized by the backbone of Pro93 hydrogen bonding to the FMN O2* and by three additional residues; Asp296 Oδ2 hydrogen bonds to FMN O3* and Arg300 Nη1/Nη2 and Arg320 Nη1 stabilize the terminal phosphate group. The binding site is further stabilized by hydrogen bonding: the position of Asp296 via an interaction from Trp261 and the well conserved residue Ser263 and the side chain of Gln144 by Thr172 Oγ and Ser122 Oγ (Fig. 4 ▶).
Figure 4.
The LOX active site. (a) The coordination of FMN involves conserved residues and two water molecules. O atoms are coloured red and N atoms blue; hydrogen bonding is indicated by dashed lines. (b) A modelled l-lactate (in white) fits well into the active site, suggesting the involvement of Tyr215 and Arg181 in addition to Tyr40, Tyr146, His265 and Arg268. The hypothetical hydrogen bonding to the lactate not present in crystal structure is displayed in grey; otherwise colouring is as in (a).
3.3. The substrate-binding site
The substrate-binding region in LOX is well conserved in all of the related GLO, MDH, HAO and B2 structures. As expected for enzymes with similar substrate specificities, the residues described for glycolate coordination in GLO (Lindqvist & Branden, 1989 ▶; Maeda-Yorita et al., 1995 ▶) are structurally identical to those in LOX: Tyr40, Arg268, His265, Tyr146 and Asp174. Also, all six mechanistically important residues suggested in Maeda-Yorita et al. (1995 ▶) have similar conformations in all the structures and superimpose with main-chain r.m.s. deviations ranging from 0.39 Å for GLO/B2 to 0.57 Å for LOX/HAO.
In addition, a conserved arginine residue, Arg181, and a non-conserved Tyr215 (Fig. 2 ▶) from the lid area fold towards the active site. Unfortunately, no substrate is present in the LOX structure, even though l-lactate was present in the crystallization. However, the substrate-binding site snugly accommodates a manually docked l-lactate molecule (Fig. 4 ▶ b), replacing two of the active-site water molecules in Fig. 4 ▶(a). Residues Tyr40, Tyr146, Lys241, Arg268, His265 and Asp174 (Maeda-Yorita et al., 1995 ▶) cluster around the binding site. In addition, it seems likely that Arg181 and Tyr215 also play a role in stabilization of the reaction. As Tyr215 is not conserved in the sequences of the other enzymes, it is possibly also involved in defining the unique properties of LOX compared with the other enzymes in this family.
Mutation of Ala95 to Gly has been shown to broaden the substrate specificity of LOX (Yorita et al., 1997 ▶). The side chain of this residue hinders the docking of larger side chains on the α-carbon of the substrate and this is removed by the mutation. Another difference in the active sites between LOX and GLO is Tyr124, which is Trp108 in GLO. This residue was proposed to interfere with GLO substrate binding (Stenberg et al., 1995 ▶), but Tyr124 Oη in LOX points away from the active site and thus most likely does not perform a similar function in LOX.
Supplementary Material
PDB reference: l-lactate oxidase, 2j6x, r2j6xsf
Acknowledgments
Crystallization screening was carried out using the robotic crystallization facility at the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki. The Norwegian Structural Biology Centre (NorStruct) is supported by the National Program in Functional Genomics (FUGE) and the Research Council of Norway, grant NFR 154197/432, and this project was also directly supported by FUGE-Nord and NordForsk. Provision of synchrotron beamtime at the ESRF is gratefully acknowledged.
References
- Bolognesi, M., Ghisla, S. & Incoccia, L. (1978). Acta Cryst. B34, 821–828. [Google Scholar]
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Cunane, L. M., Barton, J. D., Chen, Z. W., Le, K. H., Amar, D., Lederer, F. & Mathews, F. S. (2005). Biochemistry, 44, 1521–1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, J. D., Wallis, J. O. & Azari, M. R. (1989). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.164, 919–926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2126–2132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalas, V. G. & Chaniotakis, N. A. (2001). Mikrochim. Acta, 136, 211–215.
- Ghisla, S. & Massey, V. (1989). Eur. J. Biochem.181, 1–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouet, P., Courcelle, E., Stuart, D. I. & Metoz, F. (1999). Bioinformatics, 15, 305–308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guex, N. & Peitsch, M. C. (1997). Electrophoresis, 18, 2714–2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding, M. M. (2001). Acta Cryst. D57, 401–411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito, N., Miyamoto, S., Kimura, J. & Karube, I. (1996). Biosens. Bioelectron.11, 119–126.
- Jones, T. A., Zou, J.-Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. (1991). Acta Cryst. A47, 110–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch, W. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst.26, 795–800. [Google Scholar]
- Lennon, B. W., Williams, C. H. Jr & Ludwig, M. L. (1999). Protein Sci.8, 2366–2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillis, B., Grogan, C., Berney, H. & Lane, W. A. (2000). Sens. Actuators B Chem.68, 109–114.
- Lindqvist, Y. (1989). J. Mol. Biol.209, 151–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, Y. & Branden, C. I. (1989). J. Biol. Chem.264, 3624–3628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macheroux, P., Mulrooney, S. B., Williams, C. H. Jr & Massey, V. (1992). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1132, 11–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda-Yorita, K., Aki, K., Sagai, H., Misaki, H. & Massey, V. (1995). Biochimie, 77, 631–642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla, G., Motteran, L., Job, V., Pilone, M. S. & Pollegioni, L. (2003). Eur. J. Biochem.270, 1474–1482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla, G., Motteran, L., Piubelli, L., Pilone, M. S. & Pollegioni, L. (2003). Yeast, 20, 1061–1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, Y., Yorita, K., Aki, K., Misaki, H. & Massey, V. (1998). Biochimie, 80, 309–312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A., Lebedev, A., Wilson, K. S. & Dodson, E. J. (1999). Acta Cryst. D55, 247–255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M., Guo, X. S., Cai, Q., Li, G. & Chen, Y. Q. (2003). Sens. Actuators A Phys.108, 258–262.
- Perrakis, A., Morris, R. & Lamzin, V. S. (1999). Nature Struct. Biol.6, 458–463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poscia, A., Messeri, D., Moscone, D., Ricci, F. & Valgimigli, F. (2005). Biosens. Bioelectron.20, 2244–2250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarath Babu, V. R., Kumar, M. A., Karanth, N. G. & Thakur, M. S. (2004). Biosens. Bioelectron.19, 1337–1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg, K., Clausen, T., Lindqvist, Y. & Macheroux, P. (1995). Eur. J. Biochem.228, 408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar, N., Dewanti, A. R., Mitra, B. & Mathews, F. S. (2004). J. Biol. Chem.279, 3749–3757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svobodova, L., Snejdarkova, M. & Hianik, T. (2002). Anal. Bioanal. Chem.373, 735–741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umena, Y., Yorita, K., Matsuoka, T., Abe, M., Kita, A., Fukui, K., Tsukihara, T. & Morimoto, Y. (2005). Acta Cryst. F61, 439–441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Umhau, S., Pollegioni, L., Molla, G., Diederichs, K., Welte, W., Pilone, M. S. & Ghisla, S. (2000). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 12463–12468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervoort, J., Muller, F., Mayhew, S. G., van den Berg, W. A., Moonen, C. T. & Bacher, A. (1986). Biochemistry, 25, 6789–6799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C. T., Schonbrunn, A. & Abeles, R. H. (1971). J. Biol. Chem.246, 6855–6866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.-X., Shamala, N., Bethge, P. H., Lim, L. W., Bellamy, H. D., Xuong, N.-H., Lederer, F. & Mathews, F. S. (1987). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 84, 2629–2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorita, K., Janko, K., Aki, K., Ghisla, S., Palfey, B. A. & Massey, V. (1997). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 9590–9595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
PDB reference: l-lactate oxidase, 2j6x, r2j6xsf