Abstract
Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix (SCC) is preceded by a premalignant condition known as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). The majority of cases of CIN regress spontaneously; however, methods are needed to identify those lesions likely to progress. Increased blood vessel density, signifying angiogenesis, is an independent prognostic indicator in a number of cancers, although little is known about its significance in premalignant lesions. The aim of the present study was to determine the relationship between vessel density, expression of the potent angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and CIN grade. Using immunohistochemistry, mean vessel density (MVD) and VEGF expression were assessed in samples from 54 patients who had undergone cone biopsy for CIN or hysterectomy for SCC and from 16 patients with no cervical pathology. There were significant increases in MVD and VEGF expression from normal cervix through CIN I to CIN III to invasive SCC, but no difference in mean vessel diameter between groups. There was a strong correlation between mean vessel density and VEGF expression, and both were associated with histological grade of CIN. The original MVDs for a small group of patients later presenting with recurrent disease were found to be equal to or greater than the mean for their histological grade. We conclude that the onset of angiogenesis is an early event in premalignant changes of the cervix due, in part, to enhanced expression of VEGF by the abnormal epithelium.
Full text
PDF

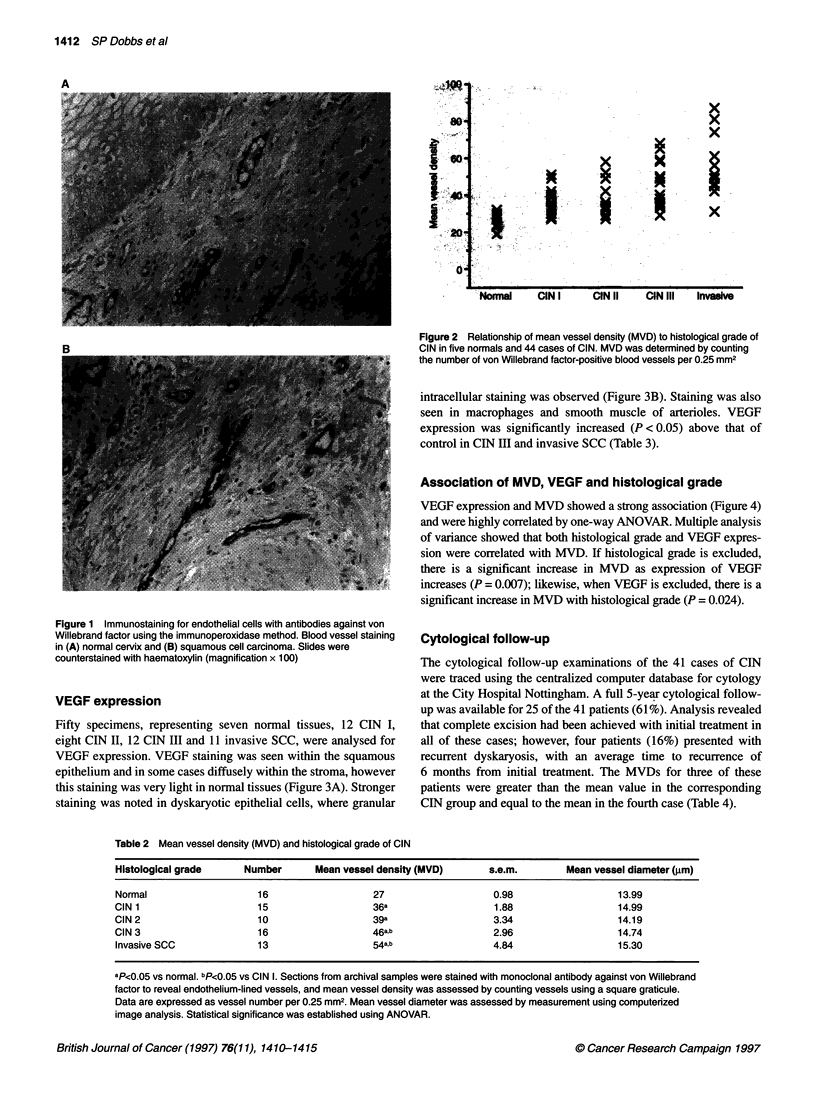
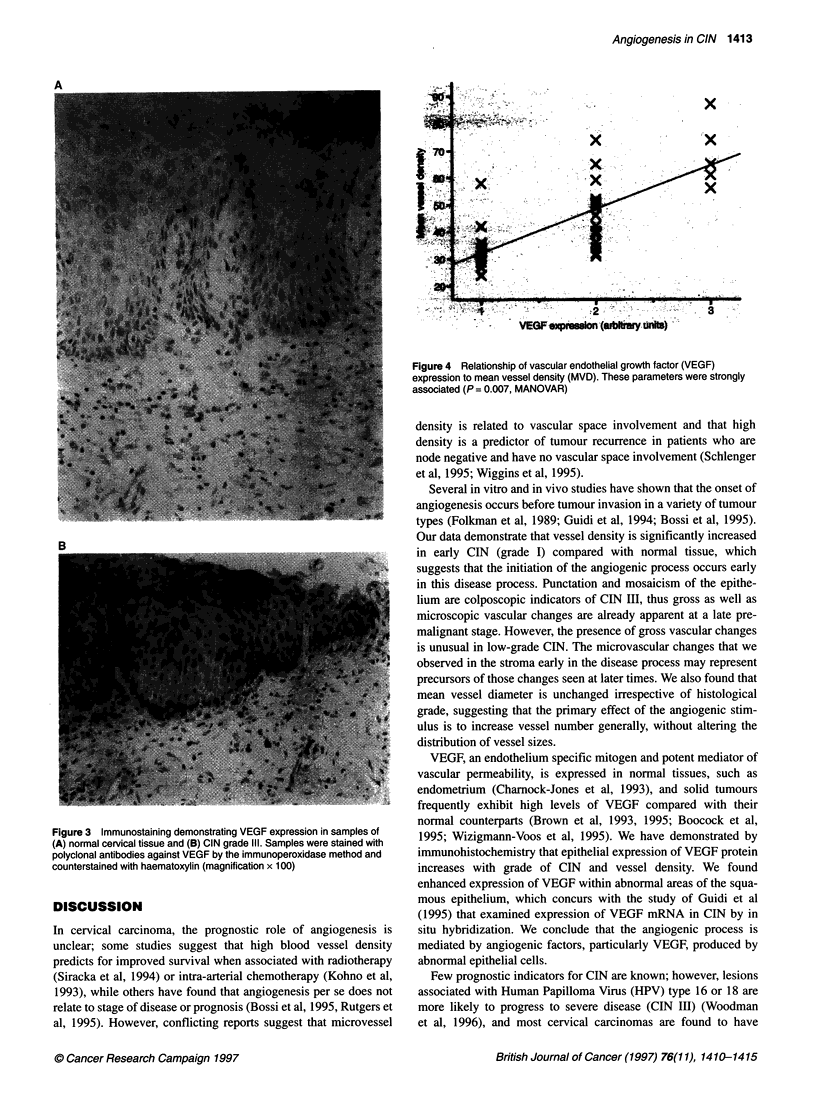
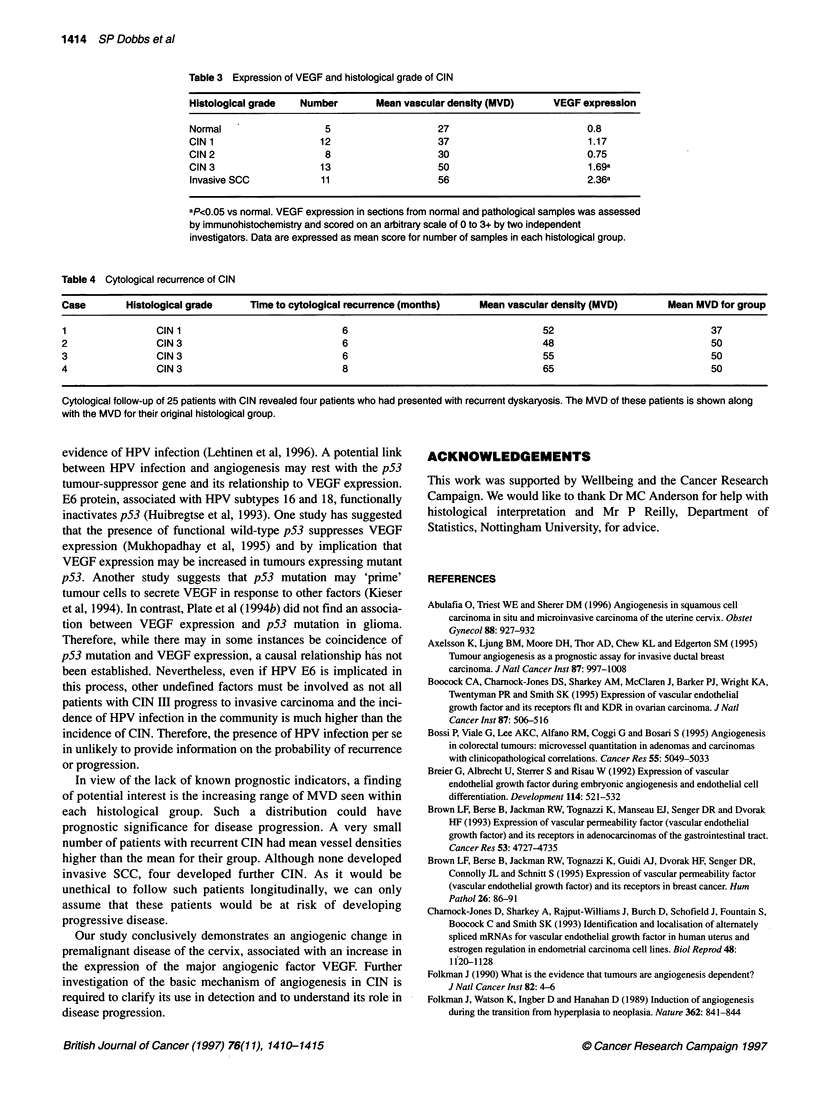

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abulafia O., Triest W. E., Sherer D. M. Angiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma in situ and microinvasive carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Dec;88(6):927–932. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(96)00334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson K., Ljung B. M., Moore D. H., 2nd, Thor A. D., Chew K. L., Edgerton S. M., Smith H. S., Mayall B. H. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic assay for invasive ductal breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Jul 5;87(13):997–1008. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.13.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boocock C. A., Charnock-Jones D. S., Sharkey A. M., McLaren J., Barker P. J., Wright K. A., Twentyman P. R., Smith S. K. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors flt and KDR in ovarian carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Apr 5;87(7):506–516. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.7.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi P., Viale G., Lee A. K., Alfano R., Coggi G., Bosari S. Angiogenesis in colorectal tumors: microvessel quantitation in adenomas and carcinomas with clinicopathological correlations. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 1;55(21):5049–5053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):521–532. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Tognazzi K., Guidi A. J., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R., Connolly J. L., Schnitt S. J. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1995 Jan;26(1):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Tognazzi K., Manseau E. J., Senger D. R., Dvorak H. F. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 1;53(19):4727–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Hübner G., Breier G., Longaker M. T., Greenhalgh D. G., Werner S. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12607–12613. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi A. J., Abu-Jawdeh G., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Tognazzi K., Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) expression and angiogenesis in cervical neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Aug 16;87(16):1237–1245. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.16.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi A. J., Fischer L., Harris J. R., Schnitt S. J. Microvessel density and distribution in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Apr 20;86(8):614–619. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.8.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. R., Leek R., Klenk N., LeJeune S., Smith K., Stuart N., Greenall M., Stepniewska K., Harris A. L. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1120–1124. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Scheffner M., Howley P. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for E6-AP, a protein that mediates the interaction of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein with p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):775–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser A., Weich H. A., Brandner G., Marmé D., Kolch W. Mutant p53 potentiates protein kinase C induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):963–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Winer J., Armanini M., Gillett N., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):841–844. doi: 10.1038/362841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Iwanari O., Kitao M. Prognostic importance of histologic vascular density in cervical cancer treated with hypertensive intraarterial chemotherapy. Cancer. 1993 Oct 15;72(8):2394–2400. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931015)72:8<2394::aid-cncr2820720817>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen M., Dillner J., Knekt P., Luostarinen T., Aromaa A., Kirnbauer R., Koskela P., Paavonen J., Peto R., Schiller J. T. Serologically diagnosed infection with human papillomavirus type 16 and risk for subsequent development of cervical carcinoma: nested case-control study. BMJ. 1996 Mar 2;312(7030):537–539. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7030.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIndoe W. A., McLean M. R., Jones R. W., Mullins P. R. The invasive potential of carcinoma in situ of the cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Oct;64(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millauer B., Shawver L. K., Plate K. H., Risau W., Ullrich A. Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):576–579. doi: 10.1038/367576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay D., Tsiokas L., Sukhatme V. P. Wild-type p53 and v-Src exert opposing influences on human vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression. Cancer Res. 1995 Dec 15;55(24):6161–6165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen T., Alitalo K. Endothelial receptor tyrosine kinases involved in angiogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(4):895–898. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivarez D., Ulbright T., DeRiese W., Foster R., Reister T., Einhorn L., Sledge G. Neovascularization in clinical stage A testicular germ cell tumor: prediction of metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2800–2802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Risau W. Molecular mechanisms of developmental and tumor angiogenesis. Brain Pathol. 1994 Jul;4(3):207–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1994.tb00835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Mennel H. D., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor and glioma angiogenesis: coordinate induction of VEGF receptors, distribution of VEGF protein and possible in vivo regulatory mechanisms. Int J Cancer. 1994 Nov 15;59(4):520–529. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910590415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. H., Woodend B. E., Crozier E. H., Hutchinson J. Risk of cervical cancer associated with mild dyskaryosis. BMJ. 1988 Jul 2;297(6640):18–21. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6640.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers J. L., Mattox T. F., Vargas M. P. Angiogenesis in uterine cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1995 Apr;14(2):114–118. doi: 10.1097/00004347-199504000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenger K., Höckel M., Mitze M., Schäffer U., Weikel W., Knapstein P. G., Lambert A. Tumor vascularity--a novel prognostic factor in advanced cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1995 Oct;59(1):57–66. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1995.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafi M. I. Management of women with mild dyskaryosis. Cytological surveillance avoids overtreatment. BMJ. 1994 Sep 3;309(6954):590–591. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6954.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillman F., Boyce J., Fruchter R. The significance of atypical vessels and neovascularization in cervical neoplasia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Jan 15;139(2):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(81)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracká E., Siracký J., Pappová N., Révész L. Vascularization and radiocurability in cancer of the uterine cervix. A retrospective study. Neoplasma. 1982;29(2):183–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-McCune K. K., Weidner N. Demonstration and characterization of the angiogenic properties of cervical dysplasia. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):800–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Laidler P., Davies R. P., Horgan K., Hughes L. E. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76-4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):419–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafl A., Mattingly R. F. Angiogenesis of cervical neoplasia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar 15;121(6):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A. Vascular endothelial growth factor, a potent and selective angiogenic agent. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):603–606. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Kashitani J., Tominaga T. Tumor angiogenesis is an independent prognostic indicator in primary breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993 Sep 30;55(3):371–374. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Carroll P. R., Flax J., Blumenfeld W., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Folkman J., Pozza F., Bevilacqua P., Allred E. N., Moore D. H., Meli S., Gasparini G. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Dec 16;84(24):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.24.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins D. L., Granai C. O., Steinhoff M. M., Calabresi P. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic factor in cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1995 Mar;56(3):353–356. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1995.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wizigmann-Voos S., Breier G., Risau W., Plate K. H. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated and sporadic hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman C. B., Rollason T., Ellis J., Tierney R., Wilson S., Young L. Human papillomavirus infection and risk of progression of epithelial abnormalities of the cervix. Br J Cancer. 1996 Feb;73(4):553–556. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]