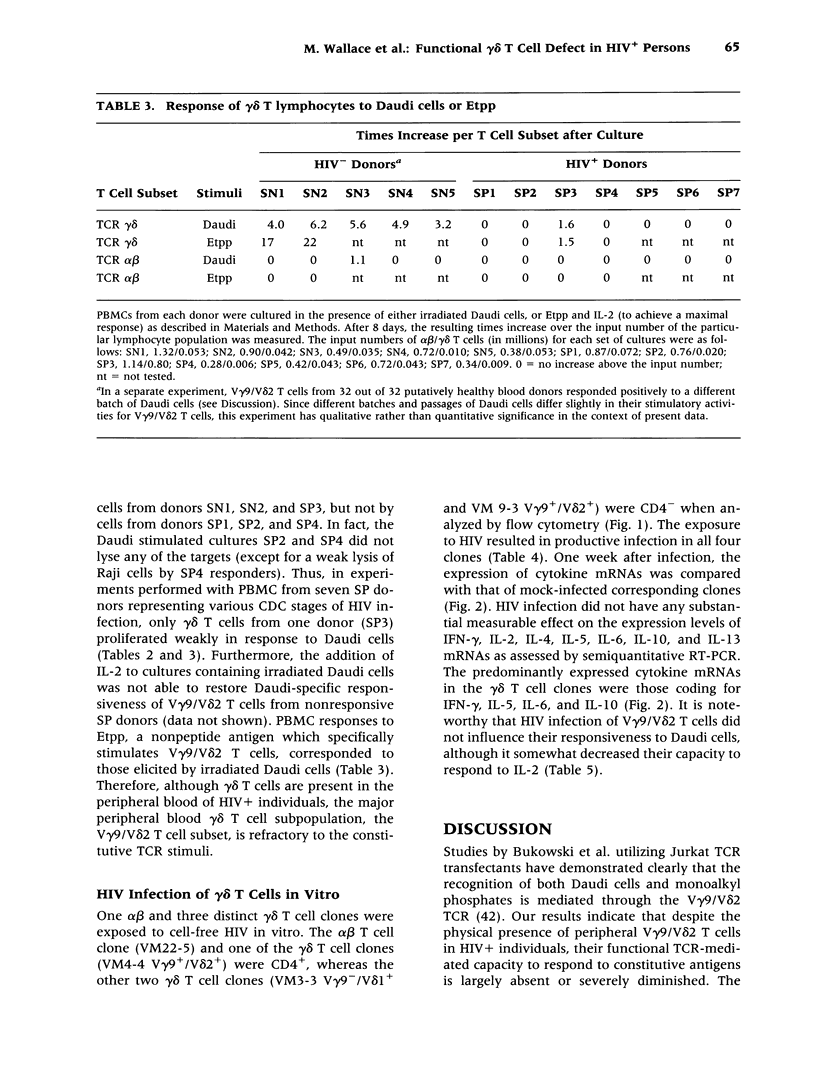
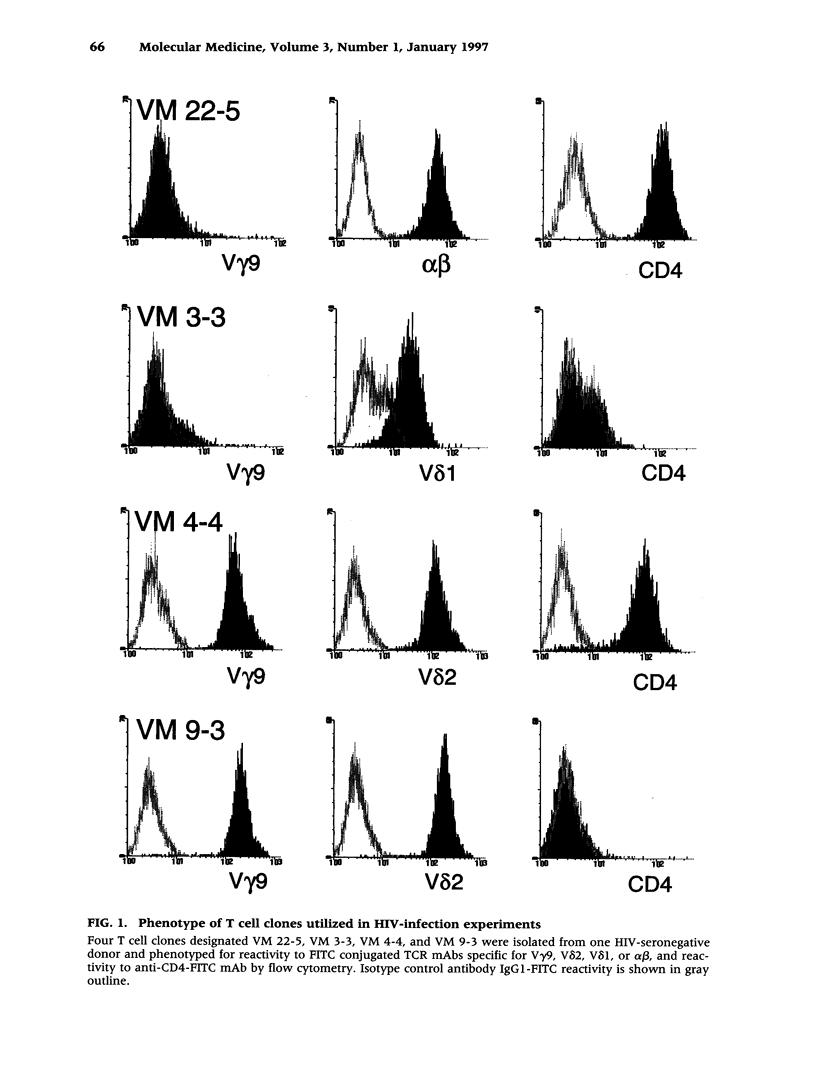
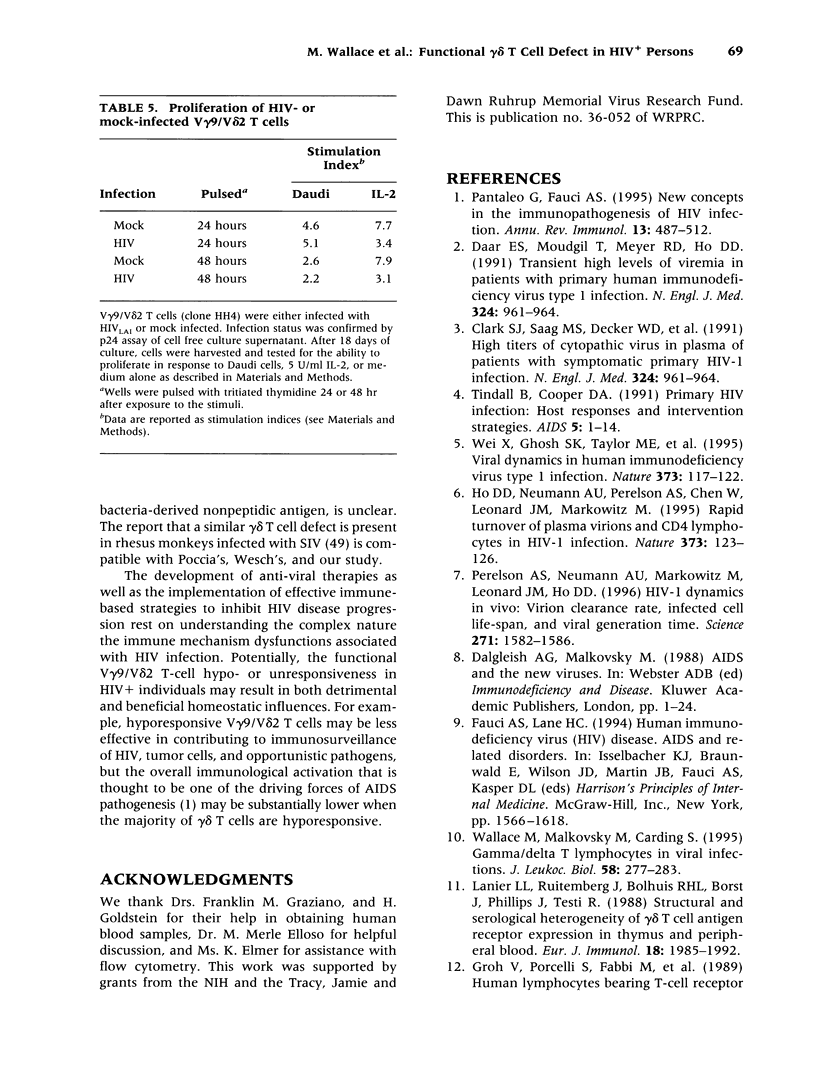
Abstract
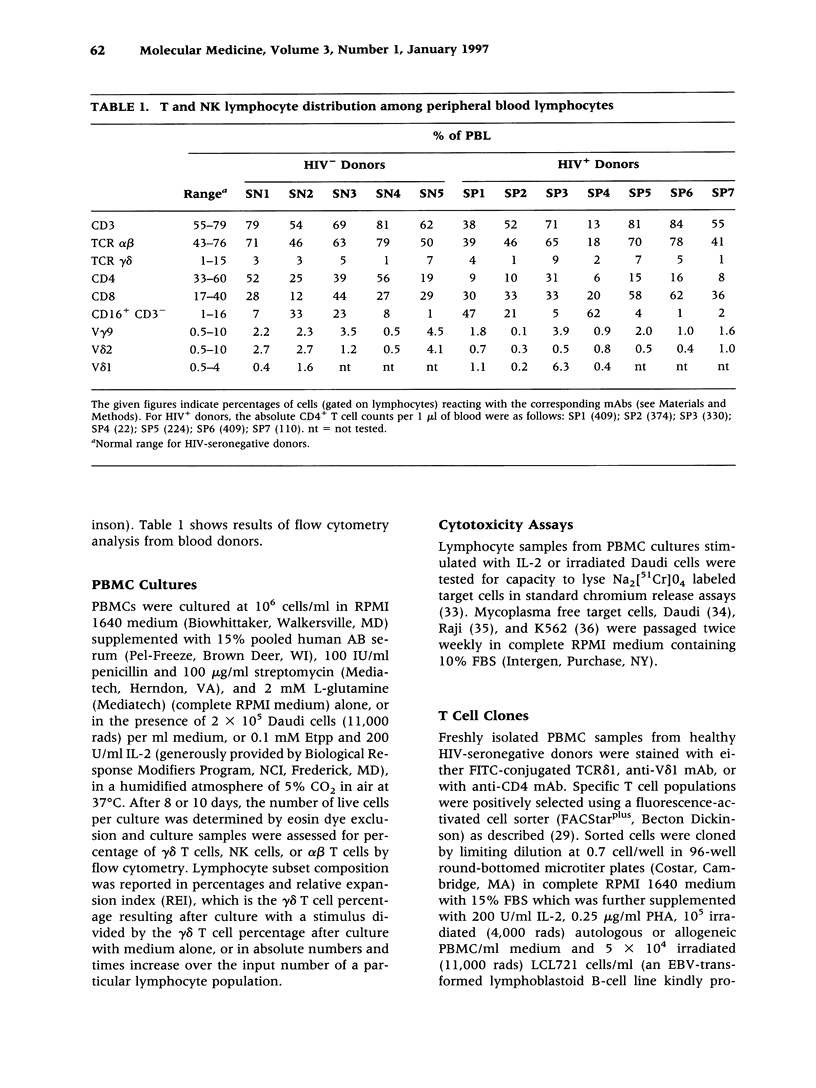
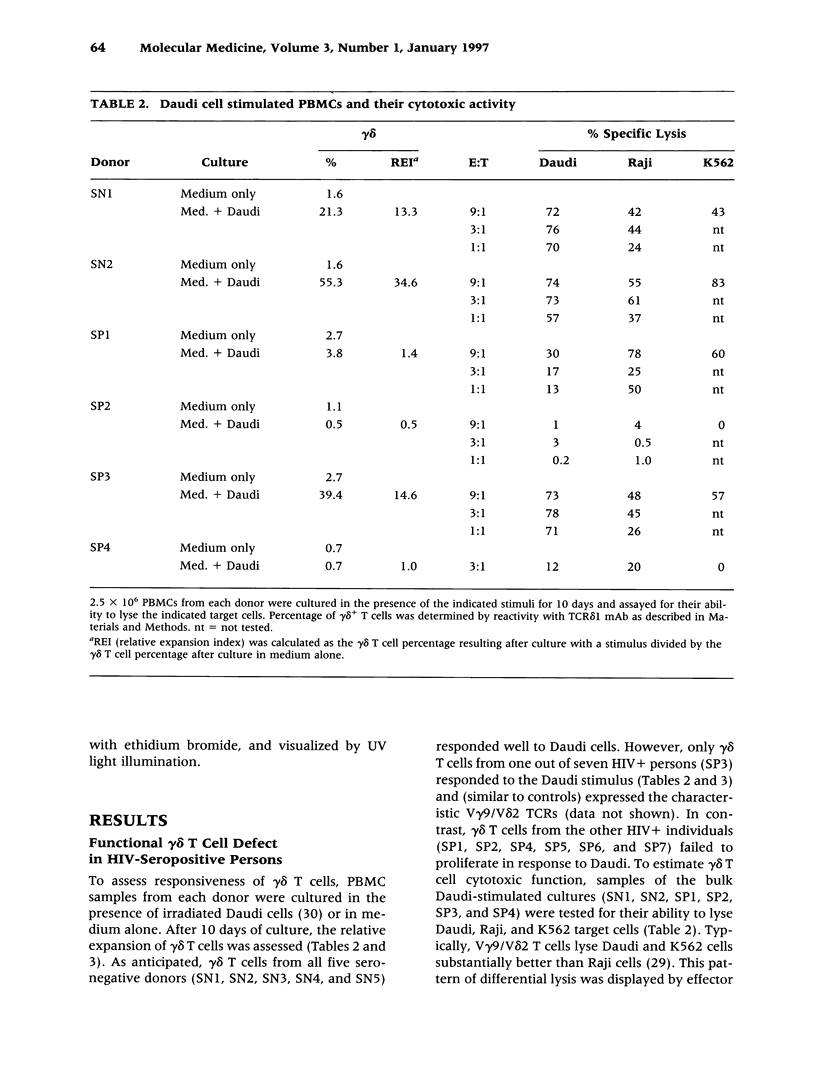
BACKGROUND: Antiviral cellular immune responses may influence immunological homeostasis in HIV-infected persons. Recent data indicate that V gamma 9/V delta 2 T lymphocytes display potent cytotoxic activities against human cells infected with certain viruses including HIV. Understanding the role of gamma delta T cells in the course of HIV infection may be helpful for designing novel treatment strategies for HIV-associated disorders. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The constitutive recognition of Daudi cells and monoethyl pyrophosphate (Etpp) by peripheral blood V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cells was assessed using a proliferation assay. The cytotoxicity of Daudi-stimulated lymphocyte populations was measured by chromium release assays. The HIV infectivity for gamma delta T cell clones was determined by measuring the levels of HIV p24 in cell supernatants. The effect of in vitro HIV-infection on cytokine mRNA production by gamma delta T cell clones was assessed by PCR. RESULTS: The constitutive proliferative responses of peripheral blood V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cells and the lytic functions of Daudi-expanded lymphoid cells from HIV+ persons were substantially diminished in comparison with those of HIV-seronegative persons. These alterations were present in asymptomatic HIV+ persons prior to substantial alpha beta CD4+ T cell loss. Productive HIV infection of gamma delta T cells in vitro had no measurable effect either on their proliferative response to Daudi stimuli or on the expression of cytokine mRNAs for IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13. CONCLUSIONS: The constitutive responsiveness of V gamma 9/V delta 2 T lymphocytes to Daudi and Etpp is severely altered in HIV+ persons. HIV infection of gamma delta T cells in vitro does not substantially change their cytokine expression or antigenic response.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autran B., Triebel F., Katlama C., Rozenbaum W., Hercend T., Debre P. T cell receptor gamma/delta+ lymphocyte subsets during HIV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Feb;75(2):206–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartz S. R., Hohenwalter E., Hu M. K., Rich D. H., Malkovsky M. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by nonimmunosuppressive analogs of cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5381–5385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartz S. R., Pauza C. D., Ivanyi J., Jindal S., Welch W. J., Malkovsky M. An Hsp60 related protein is associated with purified HIV and SIV. J Med Primatol. 1994 Feb-May;23(2-3):151–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.1994.tb00116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullier S., Cochet M., Poccia F., Gougeon M. L. CDR3-independent gamma delta V delta 1+ T cell expansion in the peripheral blood of HIV-infected persons. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):1418–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Morita C. T., Brenner M. B. Recognition and destruction of virus-infected cells by human gamma delta CTL. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 1;153(11):5133–5140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Morita C. T., Tanaka Y., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B., Band H. V gamma 2V delta 2 TCR-dependent recognition of non-peptide antigens and Daudi cells analyzed by TCR gene transfer. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):998–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Moudgil T., Meyer R. D., Ho D. D. Transient high levels of viremia in patients with primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):961–964. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria A., Ferrazin A., Ferrini S., Ciccone E., Terragna A., Moretta L. Selective increase of a subset of T cell receptor gamma delta T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):917–919. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Basaglia G., Crovatto M., Battistin S., Santini G. A subset of gamma delta lymphocytes is increased during HIV-1 infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusch K., Lüling F., Reich K., Classen M., Wagner H., Pfeffer K. A major fraction of human intraepithelial lymphocytes simultaneously expresses the gamma/delta T cell receptor, the CD8 accessory molecule and preferentially uses the V delta 1 gene segment. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch P., Malkovsky M., Braakman E., Sturm E., Bolhuis R. L., Prieve A., Sosman J. A., Lam V. A., Sondel P. M. Gamma/delta T cell clones and natural killer cell clones mediate distinct patterns of non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1567–1579. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch P., Malkovsky M., Kovats S., Sturm E., Braakman E., Klein B. S., Voss S. D., Morrissey L. W., DeMars R., Welch W. J. Recognition by human V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cells of a GroEL homolog on Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1269–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.1978758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihashi K., Yamamoto M., Hiroi T., Bamberg T. V., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H. Selected Th1 and Th2 cytokine mRNA expression by CD4(+) T cells isolated from inflamed human gingival tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Mar;103(3):422–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1996.tb08297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihashi K., Yamamoto M., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H. alpha beta T cell receptor-positive intraepithelial lymphocytes with CD4+, CD8- and CD4+, CD8+ phenotypes from orally immunized mice provide Th2-like function for B cell responses. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6681–6691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan Y. H., Pauza C. D., Malkovsky M. Gamma delta T cells in rhesus monkeys and their response to simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Nov;102(2):251–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinz T., Wesch D., Friese K., Reckziegel A., Arden B., Kabelitz D. T cell receptor gamma delta repertoire in HIV-1-infected individuals. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3044–3049. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen O., Wesselborg S., Heckl-Ostreicher B., Pechhold K., Bender A., Schondelmaier S., Moldenhauer G., Kabelitz D. T cell receptor/CD3-signaling induces death by apoptosis in human T cell receptor gamma delta + T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Pechhold K., Bender A., Wesselborg S., Wesch D., Friese K., Janssen O. Activation and activation-driven death of human gamma/delta T cells. Immunol Rev. 1991 Apr;120:71–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Ruitenberg J., Bolhuis R. L., Borst J., Phillips J. H., Testi R. Structural and serological heterogeneity of gamma/delta T cell antigen receptor expression in thymus and peripheral blood. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):1985–1992. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusso P., Garzino-Demo A., Crowley R. W., Malnati M. S. Infection of gamma/delta T lymphocytes by human herpesvirus 6: transcriptional induction of CD4 and susceptibility to HIV infection. J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1303–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccario R., Revello M. G., Comoli P., Montagna D., Locatelli F., Gerna G. HLA-unrestricted killing of HSV-1-infected mononuclear cells. Involvement of either gamma/delta+ or alpha/beta+ human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovsky M., Asherson G. L., Stockinger B., Watkins M. C. Nonspecific inhibitor released by T acceptor cells reduces the production of interleukin-2. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):652–655. doi: 10.1038/300652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovsky M., Bartz S. R., MacKenzie D., Radtke B. E., Wallace M., Manning J., Pauza C. D., Fisch P. Are gamma delta T cells important for the elimination of virus-infected cells? J Med Primatol. 1992 Feb-May;21(2-3):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Philpott K., Dalgleish A. G., Mellor A. L., Patterson S., Webster A. D., Edwards A. J., Maddon P. J. Infection of B lymphocytes by the human immunodeficiency virus and their susceptibility to cytotoxic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Sep;18(9):1315–1321. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita C. T., Beckman E. M., Bukowski J. F., Tanaka Y., Band H., Bloom B. R., Golan D. E., Brenner M. B. Direct presentation of nonpeptide prenyl pyrophosphate antigens to human gamma delta T cells. Immunity. 1995 Oct;3(4):495–507. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. CYTOLOGY OF BURKITT'S TUMOUR (AFRICAN LYMPHOMA). Lancet. 1964 Feb 1;1(7327):238–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Fauci A. S. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:487–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. M., Groh V., Band H., Porcelli S. A., Morita C., Fabbi M., Glass D., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Evidence for extrathymic changes in the T cell receptor gamma/delta repertoire. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1597–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Neumann A. U., Markowitz M., Leonard J. M., Ho D. D. HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1582–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poccia F., Boullier S., Lecoeur H., Cochet M., Poquet Y., Colizzi V., Fournie J. J., Gougeon M. L. Peripheral V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cell deletion and anergy to nonpeptidic mycobacterial antigens in asymptomatic HIV-1-infected persons. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):449–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharko A. M., Graziano F. M., Malkovsky M., Pauza C. D., Wallace M. Persistent non-B cell lymphocytosis in HIV-infected individuals. Immunol Lett. 1995 Dec;48(2):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(95)02450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Morita C. T., Tanaka Y., Nieves E., Brenner M. B., Bloom B. R. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):155–158. doi: 10.1038/375155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Sano S., Nieves E., De Libero G., Rosa D., Modlin R. L., Brenner M. B., Bloom B. R., Morita C. T. Nonpeptide ligands for human gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8175–8179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall B., Cooper D. A. Primary HIV infection: host responses and intervention strategies. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M., Bartz S. R., Chang W. L., Mackenzie D. A., Pauza C. D., Malkovsky M. Gamma delta T lymphocyte responses to HIV. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Feb;103(2):177–184. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.d01-625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M., Malkovsky M., Carding S. R. Gamma/delta T lymphocytes in viral infections. J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Sep;58(3):277–283. doi: 10.1002/jlb.58.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesch D., Kabelitz D., Friese K., Pechhold K. Mycobacteria-reactive gamma delta T cells in HIV-infected individuals: lack of V gamma 9 cell responsiveness is due to deficiency of antigen-specific CD4 T helper type 1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Mar;26(3):557–562. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]