Abstract
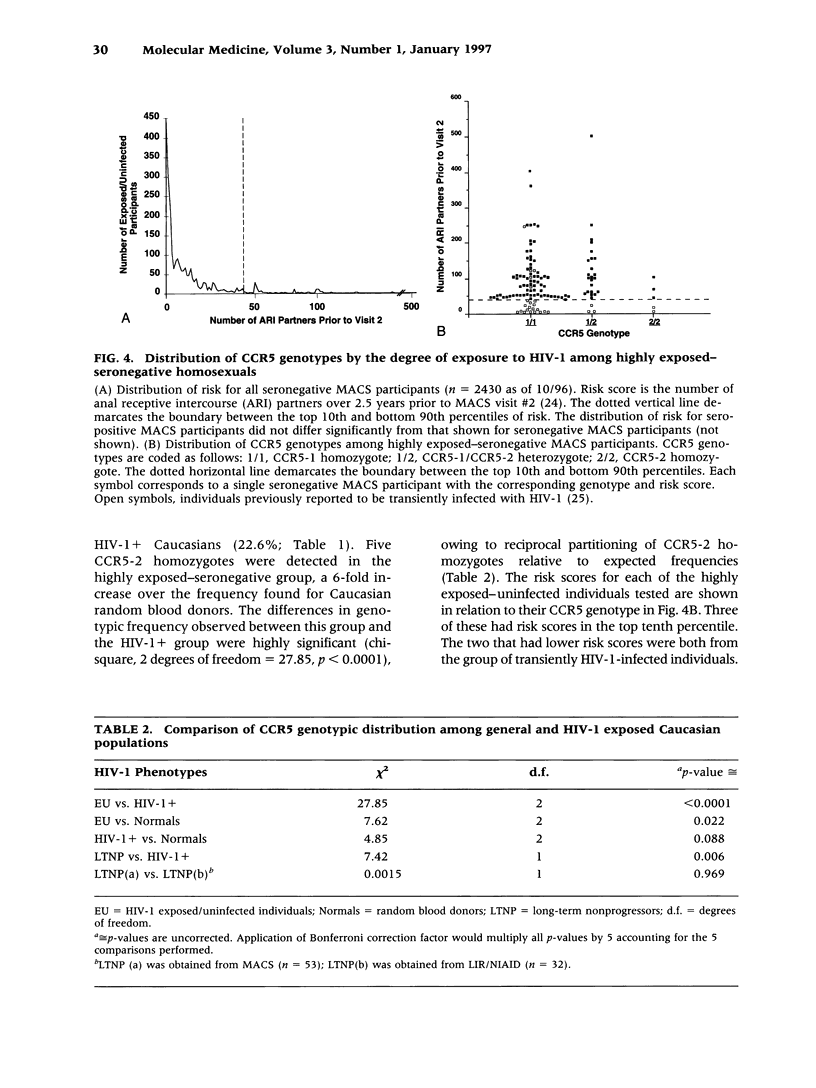
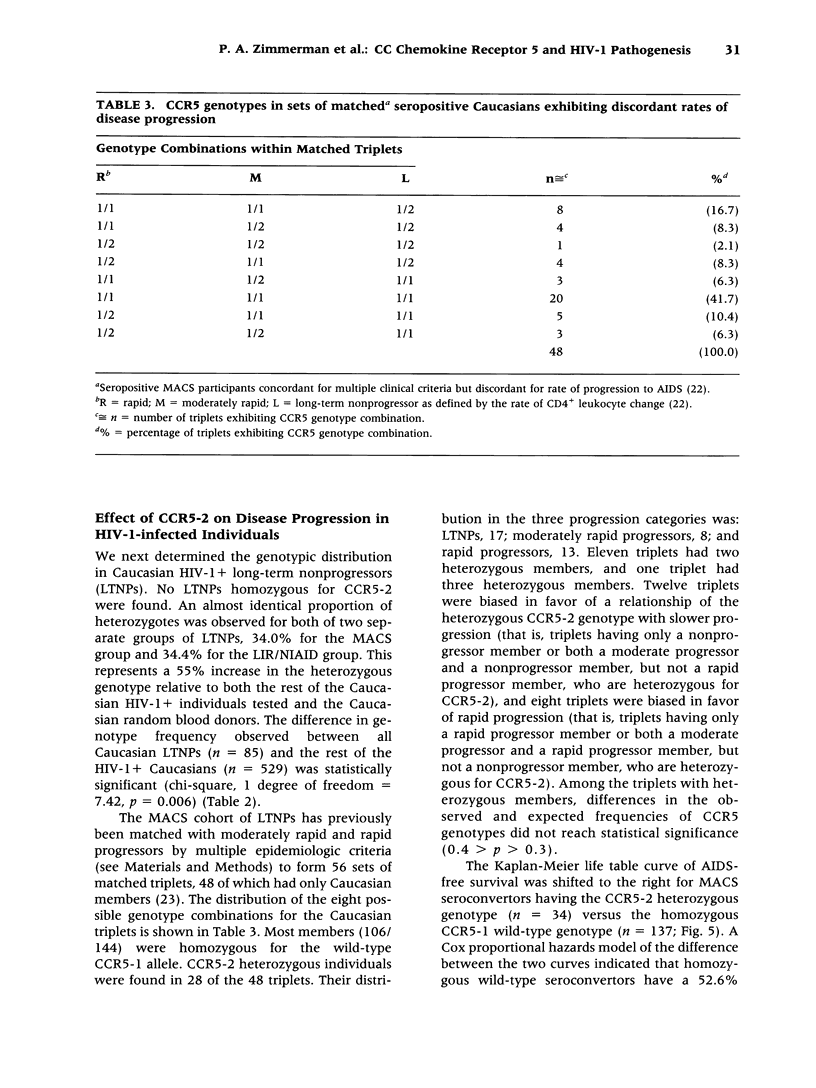
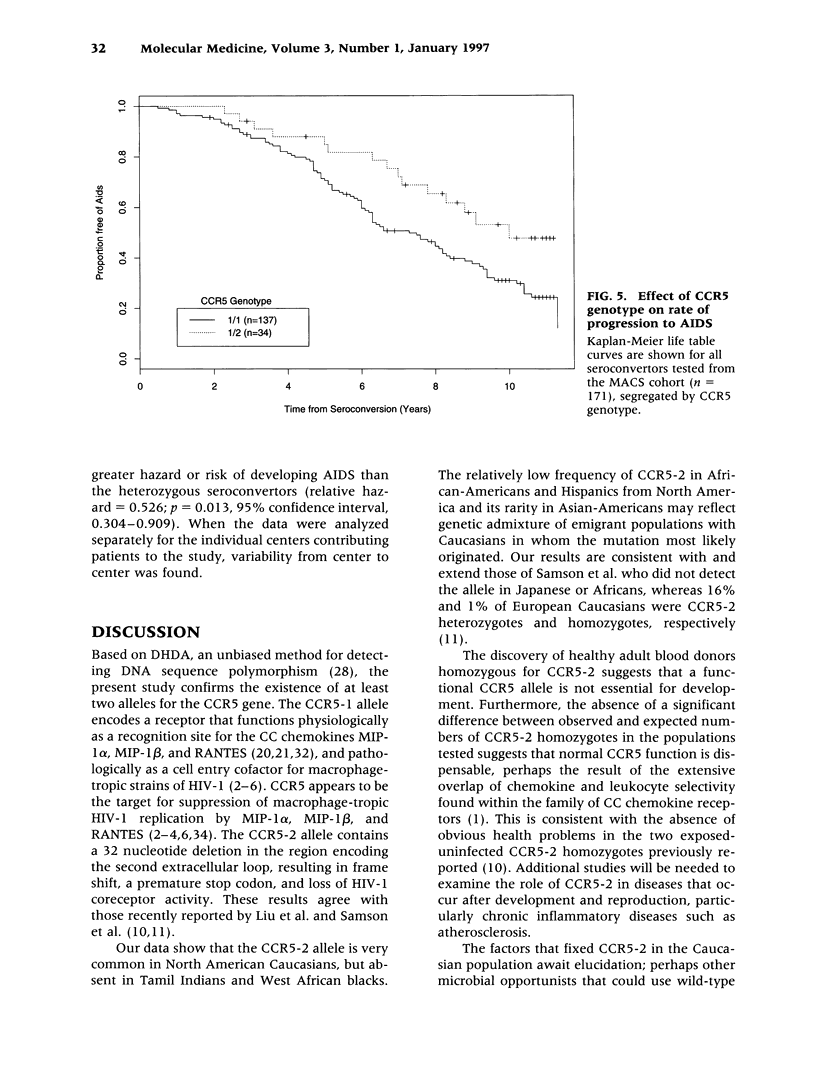
BACKGROUND: CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) is a cell entry cofactor for macrophage-tropic isolates of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1). Recently, an inactive CCR5 allele (designated here as CCR5-2) was identified that confers resistance to HIV-1 infection in homozygotes and slows the rate of progression to AIDS in heterozygotes. The reports conflict on the effect of heterozygous CCR5-2 on HIV-1 susceptibility, and race and risk levels have not yet been fully analyzed. Here we report our independent identification of CCR5-2 and test its effects on HIV-1 pathogenesis in individuals with contrasting clinical outcomes, defined race, and quantified risk. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Mutant CCR5 alleles were sought by directed heteroduplex analysis of genomic DNA from random blood donors. Genotypic frequencies were then determined in (1) random blood donors from North America, Asia, and Africa; (2) HIV-1+ individuals; and (3) highly exposed-seronegative homosexuals with quantified risk. RESULTS: CCR5-2 was the only mutant allele found. It was common in Caucasians, less common in other North American racial groups, and not detected in West Africans or Tamil Indians. Homozygous CCR5-2 frequencies differed reciprocally in highly exposed-seronegative (4.5%, n = 111) and HIV-1-seropositive (0%, n = 614) Caucasians relative to Caucasian random blood donors (0.8%, n = 387). This difference was highly significant (p < 0.0001). By contrast, heterozygous CCR5-2 frequencies did not differ significantly in the same three groups (21.6, 22.6, and 21.7%, respectively). A 55% increase in the frequency of heterozygous CCR5-2 was observed in both of two cohorts of Caucasian homosexual male, long-term nonprogressors compared with other HIV-1+ Caucasian homosexuals (p = 0.006) and compared with Caucasian random blood donors. Moreover, Kaplan-Meier estimates indicated that CCR5-2 heterozygous seroconvertors had a 52.6% lower risk of developing AIDS than homozygous wild-type seroconvertors. CONCLUSIONS: The data suggest that homozygous CCR5-2 is an HIV-1 resistance factor in Caucasians with complete penetrance, and that heterozygous CCR5-2 slows the rate of disease progression in infected Caucasian homosexuals. Since the majority (approximately 96%) of highly exposed-seronegative individuals tested are not homozygous for CCR5-2, other resistance factors must exist. Since CCR5-2 homozygotes have no obvious clinical problems, CCR5 may be a good target for the development of novel antiretroviral therapy.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja S. K., Lee J. C., Murphy P. M. CXC chemokines bind to unique sets of selectivity determinants that can function independently and are broadly distributed on multiple domains of human interleukin-8 receptor B. Determinants of high affinity binding and receptor activation are distinct. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 5;271(1):225–232. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Combadiere C., Broder C. C., Feng Y., Kennedy P. E., Murphy P. M., Berger E. A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996 Jun 28;272(5270):1955–1958. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5270.1955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleul C. C., Farzan M., Choe H., Parolin C., Clark-Lewis I., Sodroski J., Springer T. A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996 Aug 29;382(6594):829–833. doi: 10.1038/382829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe H., Farzan M., Sun Y., Sullivan N., Rollins B., Ponath P. D., Wu L., Mackay C. R., LaRosa G., Newman W. The beta-chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR5 facilitate infection by primary HIV-1 isolates. Cell. 1996 Jun 28;85(7):1135–1148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi F., DeVico A. L., Garzino-Demo A., Arya S. K., Gallo R. C., Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1995 Dec 15;270(5243):1811–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5243.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combadiere C., Ahuja S. K., Murphy P. M. Cloning and functional expression of a human eosinophil CC chemokine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16491–16494. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combadiere C., Ahuja S. K., Tiffany H. L., Murphy P. M. Cloning and functional expression of CC CKR5, a human monocyte CC chemokine receptor selective for MIP-1(alpha), MIP-1(beta), and RANTES. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Jul;60(1):147–152. doi: 10.1002/jlb.60.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor R. I., Ho D. D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants with increased replicative capacity develop during the asymptomatic stage before disease progression. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4400–4408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4400-4408.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty B. L., Siciliano S. J., DeMartino J. A., Malkowitz L., Sirotina A., Springer M. S. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human eosinophil eotaxin receptor. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2349–2354. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
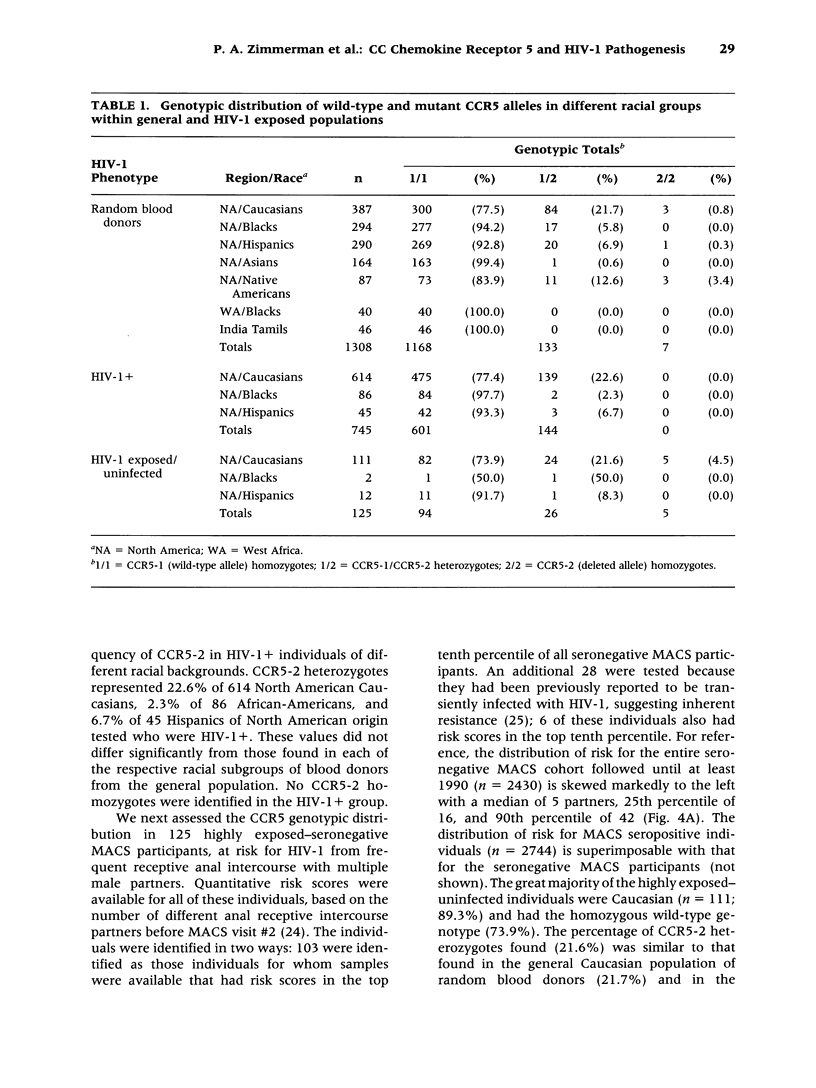
- Dean M., Carrington M., Winkler C., Huttley G. A., Smith M. W., Allikmets R., Goedert J. J., Buchbinder S. P., Vittinghoff E., Gomperts E. Genetic restriction of HIV-1 infection and progression to AIDS by a deletion allele of the CKR5 structural gene. Hemophilia Growth and Development Study, Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study, San Francisco City Cohort, ALIVE Study. Science. 1996 Sep 27;273(5283):1856–1862. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5283.1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H., Liu R., Ellmeier W., Choe S., Unutmaz D., Burkhart M., Di Marzio P., Marmon S., Sutton R. E., Hill C. M. Identification of a major co-receptor for primary isolates of HIV-1. Nature. 1996 Jun 20;381(6584):661–666. doi: 10.1038/381661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detels R., Liu Z., Hennessey K., Kan J., Visscher B. R., Taylor J. M., Hoover D. R., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Phair J. P., Saah A. J. Resistance to HIV-1 infection. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1994 Dec;7(12):1263–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doranz B. J., Rucker J., Yi Y., Smyth R. J., Samson M., Peiper S. C., Parmentier M., Collman R. G., Doms R. W. A dual-tropic primary HIV-1 isolate that uses fusin and the beta-chemokine receptors CKR-5, CKR-3, and CKR-2b as fusion cofactors. Cell. 1996 Jun 28;85(7):1149–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragic T., Litwin V., Allaway G. P., Martin S. R., Huang Y., Nagashima K. A., Cayanan C., Maddon P. J., Koup R. A., Moore J. P. HIV-1 entry into CD4+ cells is mediated by the chemokine receptor CC-CKR-5. Nature. 1996 Jun 20;381(6584):667–673. doi: 10.1038/381667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y., Broder C. C., Kennedy P. E., Berger E. A. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1996 May 10;272(5263):872–877. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5263.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Chitnis C. E., Darbonne W. C., Colby T. J., Rybicki A., Hadley T. J., Miller L. H. A receptor for the malarial parasite Plasmodium vivax: the erythrocyte chemokine receptor. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1182–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.7689250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Wang Z. X., Peiper S. C., Hesselgesser J. Identification and characterization of a promiscuous chemokine-binding protein in a human erythroleukemic cell line. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17730–17733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa D. T., Lee M. H., Wolinsky S. M., Sano K., Morales F., Kwok S., Sninsky J. J., Nishanian P. G., Giorgi J., Fahey J. L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in homosexual men who remain seronegative for prolonged periods. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1458–1462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaura M., Nakajima T., Imai T., Harada S., Combadiere C., Tiffany H. L., Murphy P. M., Yoshie O. Molecular cloning of human eotaxin, an eosinophil-selective CC chemokine, and identification of a specific eosinophil eotaxin receptor, CC chemokine receptor 3. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 29;271(13):7725–7730. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.13.7725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu R., Paxton W. A., Choe S., Ceradini D., Martin S. R., Horuk R., MacDonald M. E., Stuhlmann H., Koup R. A., Landau N. R. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996 Aug 9;86(3):367–377. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher M., Geiser T., O'Reilly T., Zwahlen R., Baggiolini M., Moser B. Cloning of a human seven-transmembrane domain receptor, LESTR, that is highly expressed in leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H., Rothman I. K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1145213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Kirby A. J., He Y. D., Margolick J. B., Visscher B. R., Rinaldo C. R., Kaslow R. A., Phair J. P. Long-term survivors with HIV-1 infection: incubation period and longitudinal patterns of CD4+ lymphocytes. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Apr 15;8(5):496–505. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199504120-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng J., Hurley C. K., Baxter-Lowe L. A., Chopek M., Coppo P. A., Hegland J., KuKuruga D., Monos D., Rosner G., Schmeckpeper B. Large-scale oligonucleotide typing for HLA-DRB1/3/4 and HLA-DQB1 is highly accurate, specific, and reliable. Tissue Antigens. 1993 Nov;42(5):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1993.tb02191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum O., Broder C. C., Berger E. A. Fusogenic mechanisms of enveloped-virus glycoproteins analyzed by a novel recombinant vaccinia virus-based assay quantitating cell fusion-dependent reporter gene activation. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5411–5422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5411-5422.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutman T. B., Zimmerman P. A., Kubofcik J., Kostyu D. D. A universally applicable diagnostic approach to filarial and other infections. Parasitol Today. 1994 Jun;10(6):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlin E., Amara A., Bachelerie F., Bessia C., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Schwartz O., Heard J. M., Clark-Lewis I., Legler D. F. The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature. 1996 Aug 29;382(6594):833–835. doi: 10.1038/382833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton W. A., Martin S. R., Tse D., O'Brien T. R., Skurnick J., VanDevanter N. L., Padian N., Braun J. F., Kotler D. P., Wolinsky S. M. Relative resistance to HIV-1 infection of CD4 lymphocytes from persons who remain uninfected despite multiple high-risk sexual exposure. Nat Med. 1996 Apr;2(4):412–417. doi: 10.1038/nm0496-412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponath P. D., Qin S., Post T. W., Wang J., Wu L., Gerard N. P., Newman W., Gerard C., Mackay C. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human eotaxin receptor expressed selectively on eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2437–2448. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raport C. J., Gosling J., Schweickart V. L., Gray P. W., Charo I. F. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel human CC chemokine receptor (CCR5) for RANTES, MIP-1beta, and MIP-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 19;271(29):17161–17166. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.29.17161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M., Labbe O., Mollereau C., Vassart G., Parmentier M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a new human CC-chemokine receptor gene. Biochemistry. 1996 Mar 19;35(11):3362–3367. doi: 10.1021/bi952950g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M., Libert F., Doranz B. J., Rucker J., Liesnard C., Farber C. M., Saragosti S., Lapoumeroulie C., Cognaux J., Forceille C. Resistance to HIV-1 infection in caucasian individuals bearing mutant alleles of the CCR-5 chemokine receptor gene. Nature. 1996 Aug 22;382(6593):722–725. doi: 10.1038/382722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuitemaker H., Koot M., Kootstra N. A., Dercksen M. W., de Goede R. E., van Steenwijk R. P., Lange J. M., Schattenkerk J. K., Miedema F., Tersmette M. Biological phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clones at different stages of infection: progression of disease is associated with a shift from monocytotropic to T-cell-tropic virus population. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1354-1360.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman P. A., Carrington M. N., Nutman T. B. Exploiting structural differences among heteroduplex molecules to simplify genotyping the DQA1 and DQB1 alleles in human lymphocyte typing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4541–4547. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman P. A., Steiner L. L., Titanji V. P., Nde P. N., Bradley J. E., Pogonka T., Begovich A. B. Three new DPB1 alleles identified in a Bantu-speaking population from central Cameroon. Tissue Antigens. 1996 Apr;47(4):293–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1996.tb02556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]