Abstract
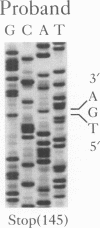
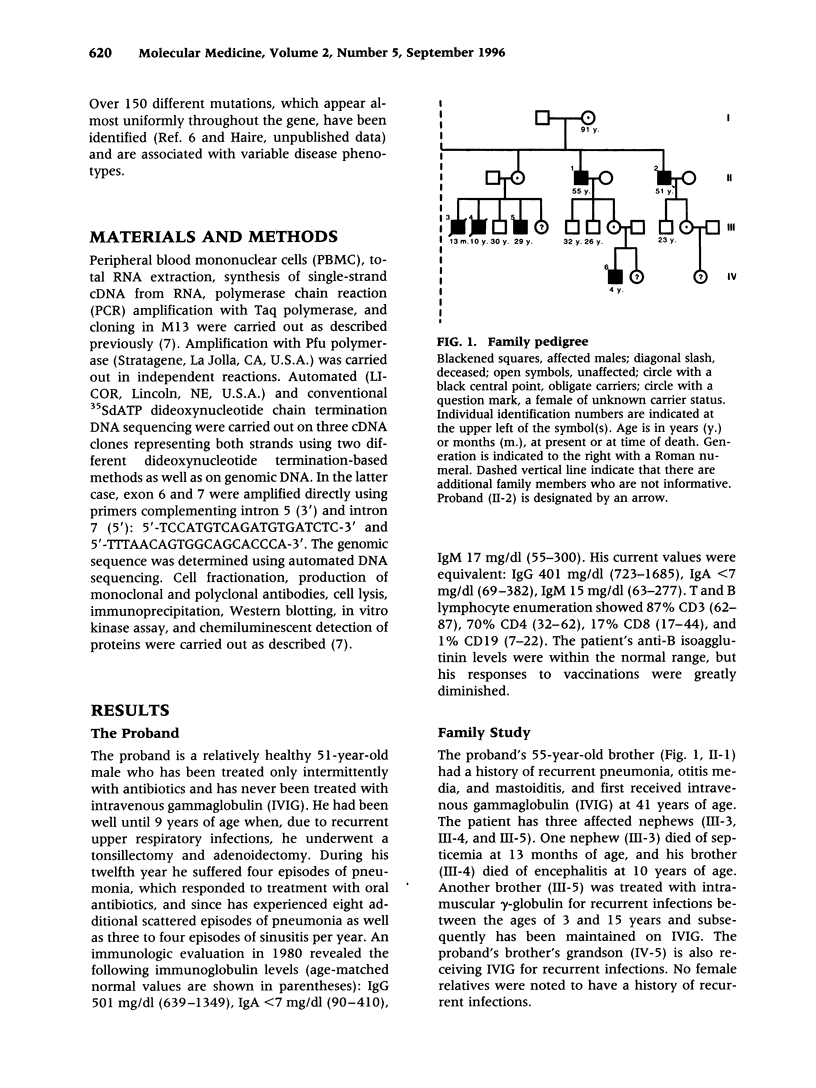
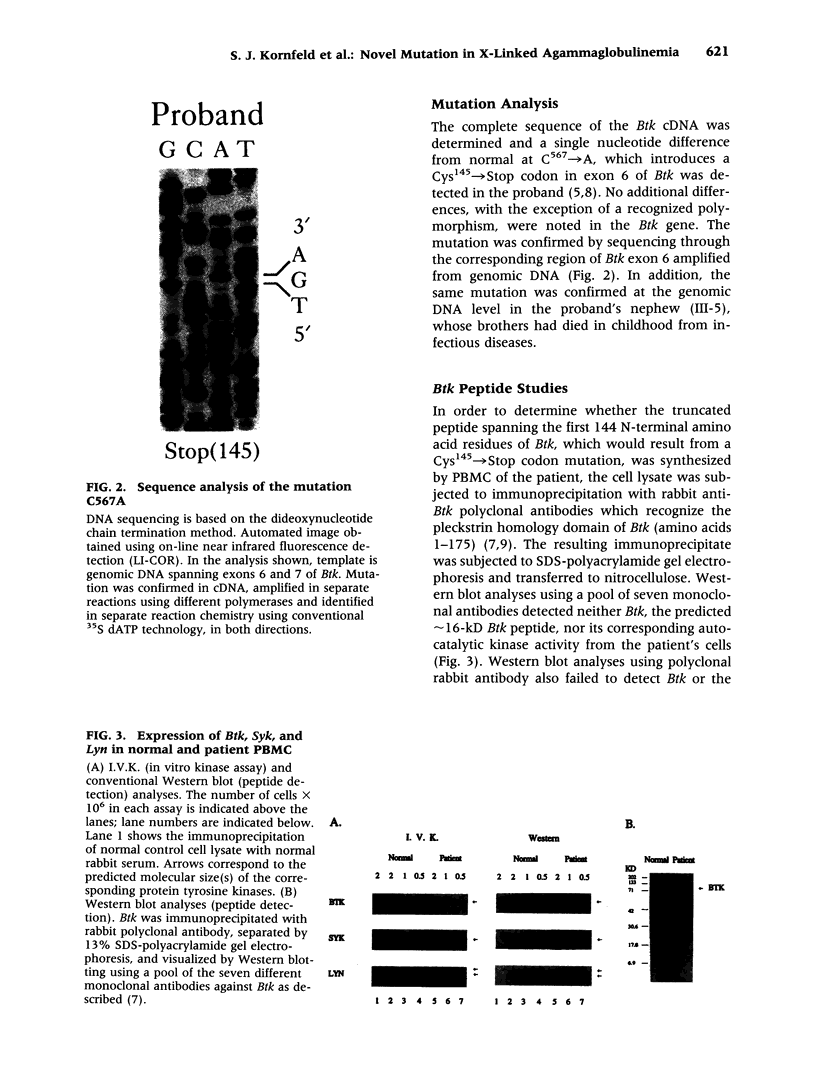
BACKGROUND: X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a severe, life-threatening disease characterized by failure of B cell differentiation and antibody production and is associated with mutations in Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk). The proband in this study is a 51-year-old male presenting with chronic nasal congestion, recurrent sinusitis, sporadic pneumonia, and pronounced B cell deficiency. A family history suggestive of an X-linked immunodeficiency disease was noted. MATERIALS AND METHODS: cDNA was synthesized from mRNA prepared from peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes. Btk cDNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was subjected to both manual and automated DNA sequencing. A DNA sequence corresponding to exons 6 and 7 of Btk was amplified from genomic DNA. Western blot analysis employed both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to Btk and reaction patterns were obtained both by chemiluminescence and an in vitro kinase assay. RESULTS: A mutation (Cys145-->Stop) was identified in Btk cDNA and was confirmed in amplified exon 6 of genomic DNA from both the proband and an affected nephew. Neither Btk nor a truncated peptide was detected in Western blot analyses of peripheral blood mononuclear cell lysates. CONCLUSIONS: The C145A mutation reported here is novel. This family study is extraordinary in that affected male members who did not undergo aggressive medical management either succumbed to complications in early life or survived into later life. The proband is the oldest de novo diagnosed patient with XLA reported to date.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bykowsky M. J., Haire R. N., Ohta Y., Tang H., Sung S. S., Veksler E. S., Greene J. M., Fu S. M., Litman G. W., Sullivan K. E. Discordant phenotype in siblings with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;58(3):477–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Kratz J., Haire R. N., Litman G. W., Good R. A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia presenting as transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Apr;95(4):915–917. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman H. M., Winkelstein J. A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: an analysis of 96 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 May;64(3):145–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leickley F. E., Buckley R. Variability in B cell maturation and differentiation in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):90–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Haire R. N., Litman R. T., Fu S. M., Nelson R. P., Kratz J., Kornfeld S. J., de la Morena M., Good R. A., Litman G. W. Genomic organization and structure of Bruton agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase: localization of mutations associated with varied clinical presentations and course in X chromosome-linked agammaglobulinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9062–9066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Cooper M. D., Wedgwood R. J. The primary immunodeficiencies (1). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 26;311(4):235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407263110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffran D. C., Parolini O., Fitch-Hilgenberg M. E., Rawlings D. J., Afar D. E., Witte O. N., Conley M. E. Brief report: a point mutation in the SH2 domain of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 26;330(21):1488–1491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405263302104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Smith C. I. Molecular and cellular aspects of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:135–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60631-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Saffran D. C., Rawlings D. J., Parolini O., Allen R. C., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Kubagawa H., Mohandas T., Quan S. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihinen M., Iwata T., Kinnon C., Kwan S. P., Ochs H. D., Vorechovský I., Smith C. I. BTKbase, mutation database for X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jan 1;24(1):160–165. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]