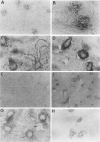
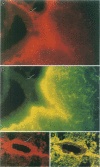
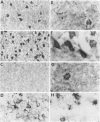
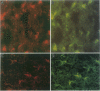
Abstract
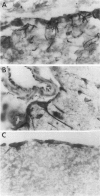
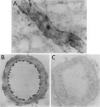
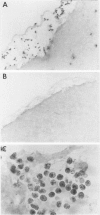
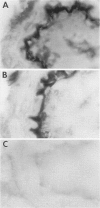
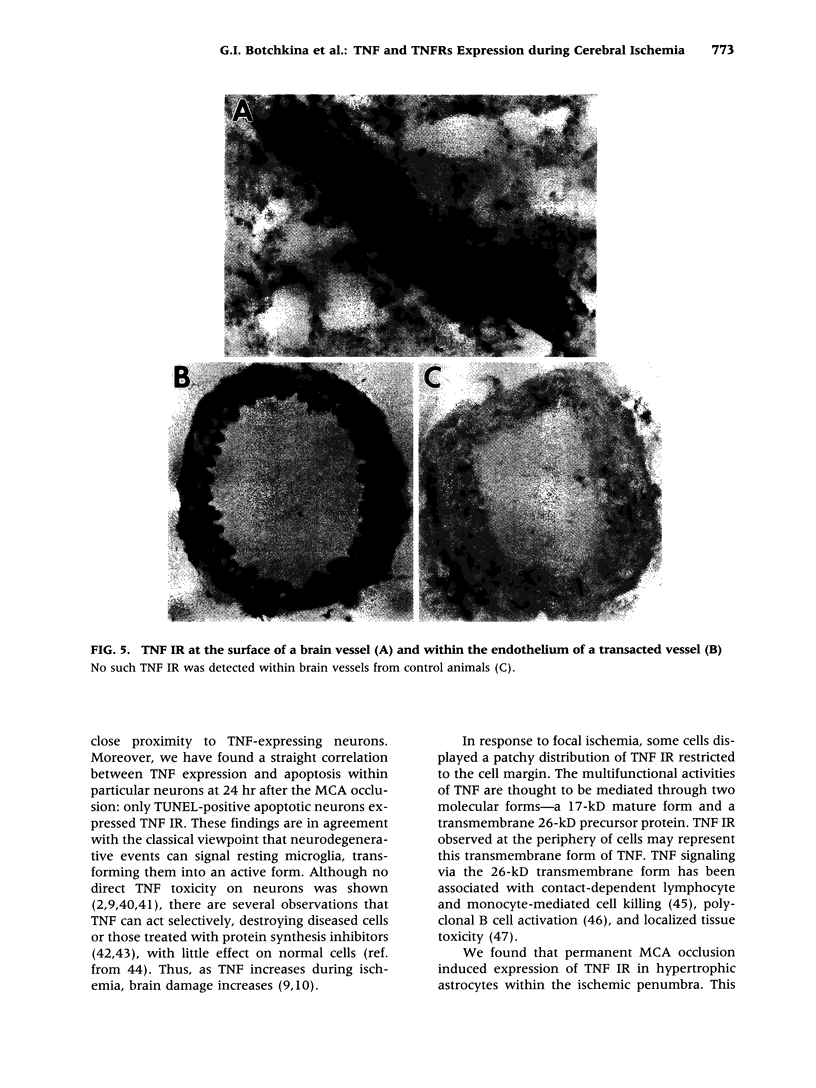
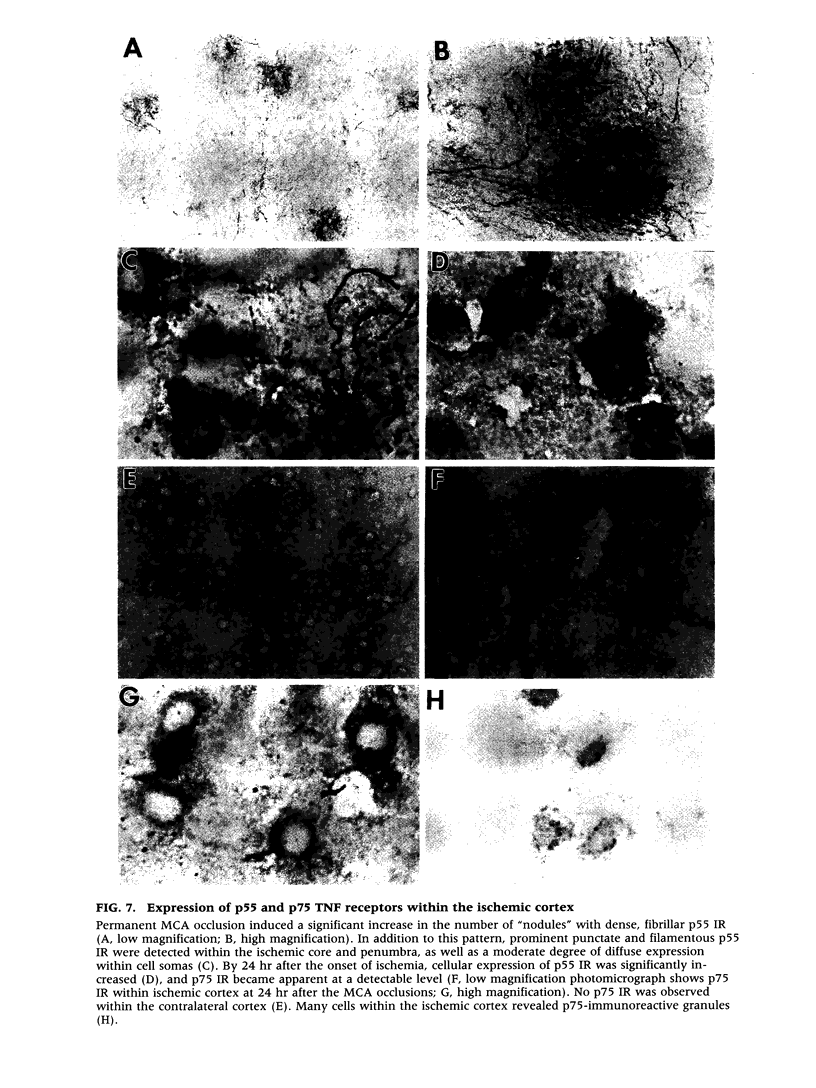
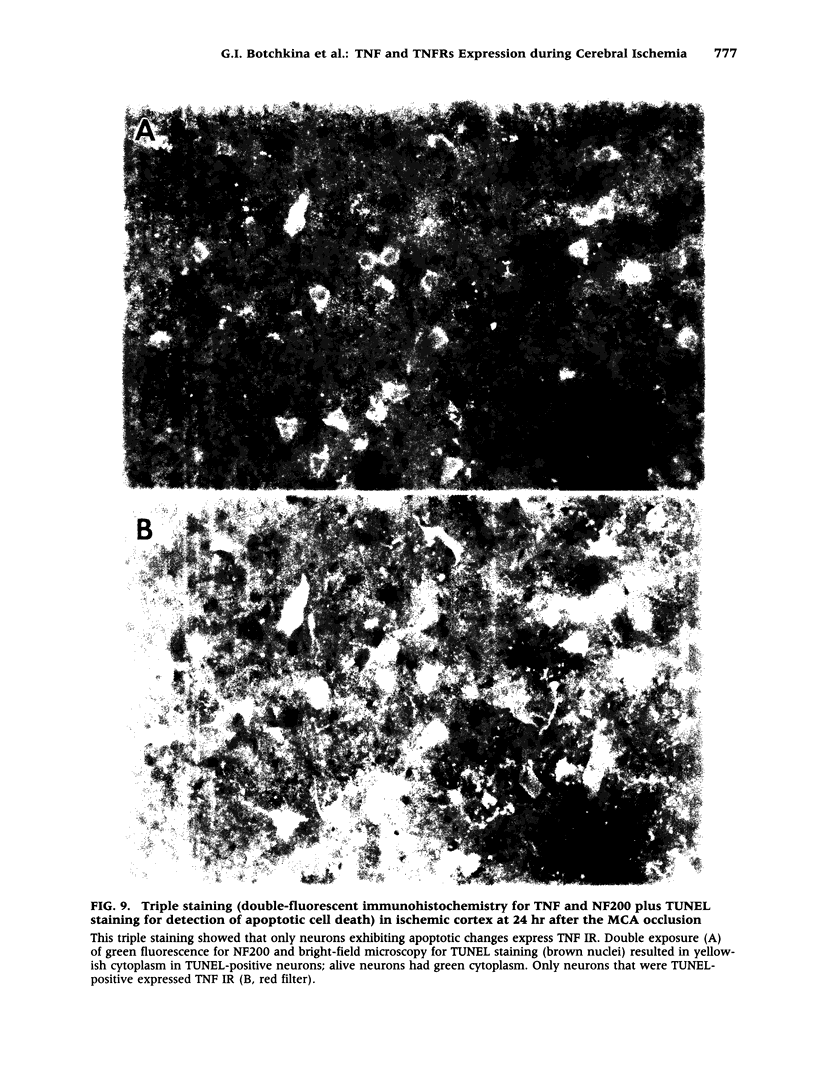
Cerebral ischemia induces a rapid and dramatic up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) protein and mRNA, but the cellular sources of TNF in the ischemic brain have not been defined. The diverse activities of TNF are mediated via ligand interaction with two distinct receptors, p55 and p75, which activate separate intracellular signal transduction pathways, leading to distinct biological effects. Since the effects of cerebral ischemia on TNF receptor (TNFR) expression are unknown, we examined the cellular localization and protein expression of TNF and its two receptors in the rat cerebral cortex in response to permanent middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. The results indicate that focal. cerebral ischemia up-regulates expression of TNF and both TNFRs within the ischemic cortex. The most abundant type of TNF immunoreactivity (IR) was a punctate and filamentous pattern of transected cellular processes; however, cell bodies of neurons, astrocytes, and microglia, as well as infiltrating polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes also showed TNF IR. Brain vasculature displayed TNF IR not only within endothelial cells but also in the perivascular space. MCA occlusion induced significant up-regulation of TNF receptors, with p55 IR appearing within 6 hr, significantly before the appearance of p75 IR at 24 hr after the onset of ischemia. Since p55 has been implicated in transducing cytotoxic signalling of TNF, these results support the proposed injurious role of excessive TNF produced during the acute response to cerebral ischemia.
Full text
PDF


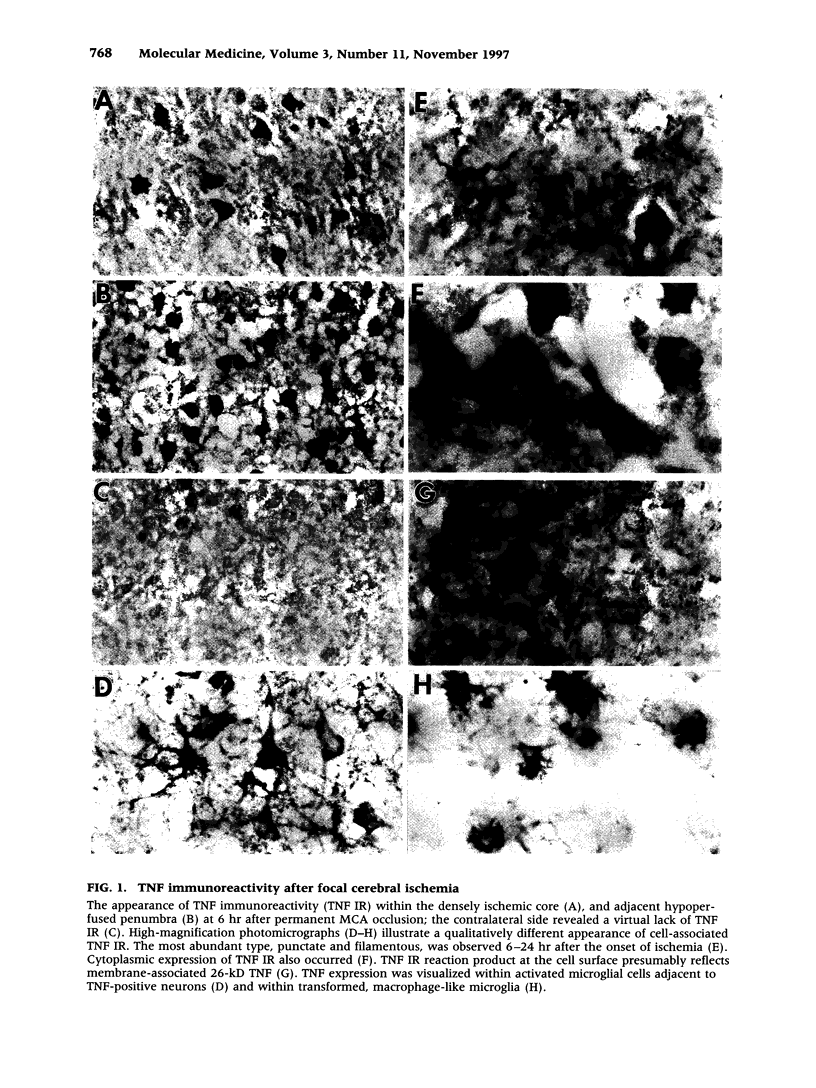
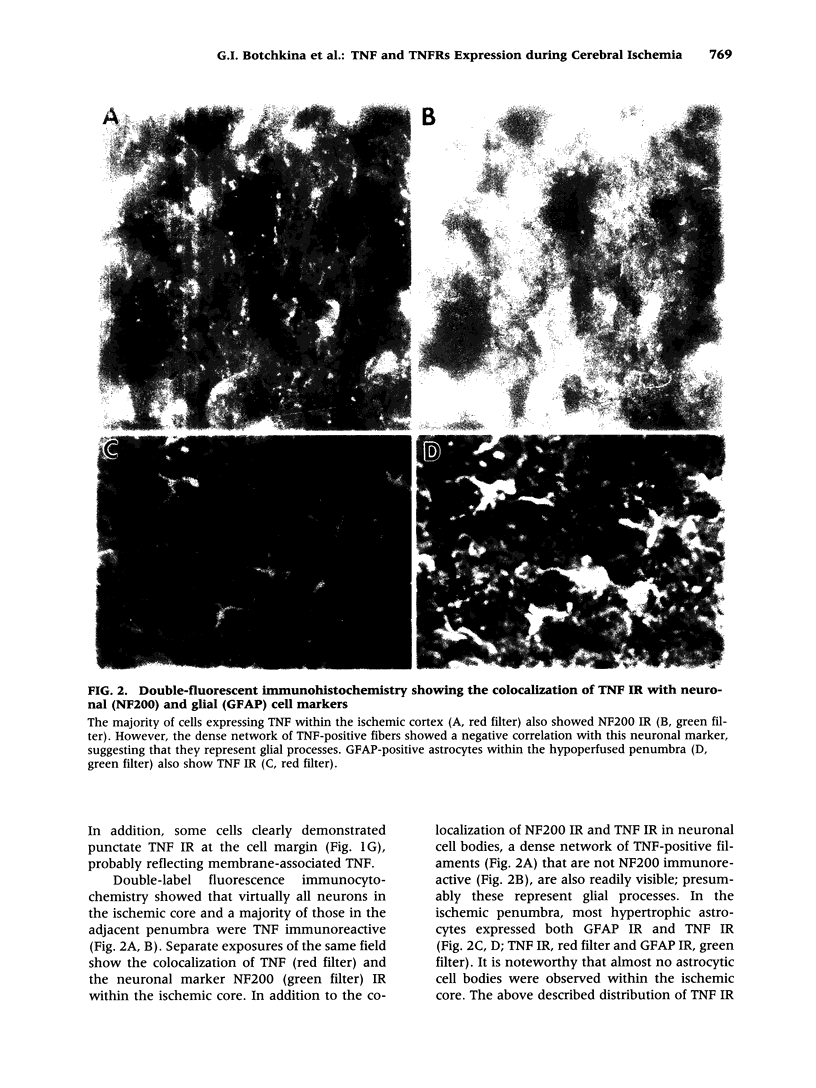

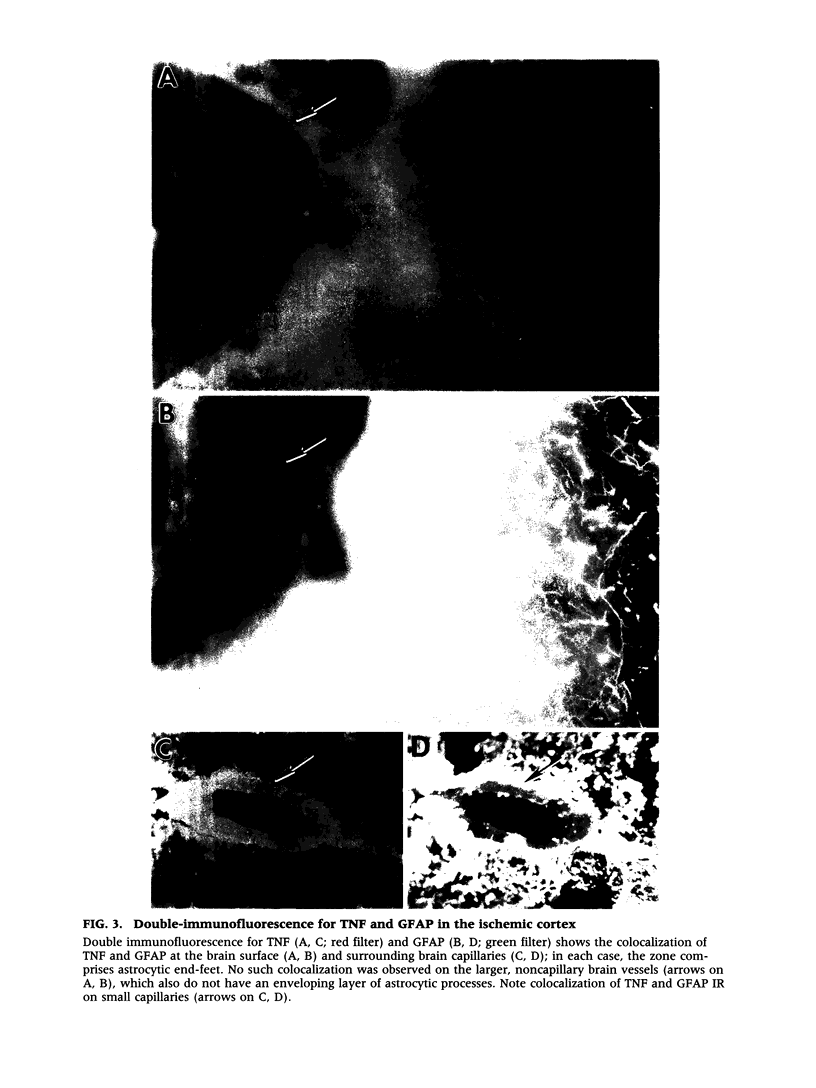







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B. Comparative analysis of the structure and function of TNF-alpha and TNF-beta. Immunol Ser. 1992;56:61–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvin B., Neville L. F., Barone F. C., Feuerstein G. Z. Brain injury and inflammation. A putative role of TNF alpha. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 15;765:62–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb16561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., D'Arcy A., Janes W., Gentz R., Schoenfeld H. J., Broger C., Loetscher H., Lesslauer W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):431–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90132-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone F. C., Arvin B., White R. F., Miller A., Webb C. L., Willette R. N., Lysko P. G., Feuerstein G. Z. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 1997 Jun;28(6):1233–1244. doi: 10.1161/01.str.28.6.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes M. P., Zivin J. A., Rothlein R. Monoclonal antibody to the ICAM-1 adhesion site reduces neurological damage in a rabbit cerebral embolism stroke model. Exp Neurol. 1993 Feb;119(2):215–219. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Tsujimoto M., Terano Y., Scott D. W., Saper C. B. Distribution and characterization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-like immunoreactivity in the murine central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Nov 22;337(4):543–567. doi: 10.1002/cne.903370403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. J., Boling W., Kindy M. S., Peschon J., Kraemer P. J., Carpenter M. K., Holtsberg F. W., Mattson M. P. Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med. 1996 Jul;2(7):788–794. doi: 10.1038/nm0796-788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttini M., Appel K., Sauter A., Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Boddeke H. W. Expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha after focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Neuroscience. 1996 Mar;71(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Hu S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha potentiates glutamate neurotoxicity in human fetal brain cell cultures. Dev Neurosci. 1994;16(3-4):172–179. doi: 10.1159/000112104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng B., Christakos S., Mattson M. P. Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung I. Y., Benveniste E. N. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by astrocytes. Induction by lipopolysaccharide, IFN-gamma, and IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2999–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. M., Madden K. P., Rothlein R., Zivin J. A. Reduction of central nervous system ischemic injury by monoclonal antibody to intercellular adhesion molecule. J Neurosurg. 1991 Oct;75(4):623–627. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.4.0623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockroft K. M., Meistrell M., 3rd, Zimmerman G. A., Risucci D., Bloom O., Cerami A., Tracey K. J. Cerebroprotective effects of aminoguanidine in a rodent model of stroke. Stroke. 1996 Aug;27(8):1393–1398. doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.8.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. A., Martin D., Hallenbeck J. M. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Oct 25;218(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(96)13116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubravec D. B., Spriggs D. R., Mannick J. A., Rodrick M. L. Circulating human peripheral blood granulocytes synthesize and secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6758–6761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan L., Young P. R., Barone F. C., Feuerstein G. Z., Smith D. H., McIntosh T. K. Experimental brain injury induces differential expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in the CNS. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996 Mar;36(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00274-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Siepl C., Groscurth P., Bodmer S., Schwerdel C., Fontana A. Antigen presentation and tumor cytotoxicity by interferon-gamma-treated microglial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1271–1278. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. E., Jr, Nonner D., Ross D., Barrett J. N. Neurotoxic components in normal serum. Exp Neurol. 1992 Dec;118(3):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(92)90188-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell M., Scheurich P., Meager A., Pfizenmaier K. TR60 and TR80 tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-receptors can independently mediate cytolysis. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993 Jun;12(3):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T., Toker L., Budilovsky S., Aderka D., Eshhar Z., Wallach D. Use of monoclonal antibodies to a human cytotoxin for its isolation and for examining the self-induction of resistance to this protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3814–3818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Kogure K., Araki T., Itoyama Y. Astroglial and microglial reactions in the gerbil hippocampus with induced ischemic tolerance. Brain Res. 1994 Nov 21;664(1-2):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91955-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keel M., Bonaccio M., Steckholzer U., Ungethüm U., Gallati H., Trentz O., Ertel W. Erhöhte Plasmaspiegel der löslichen TNF-Rezeptoren (sTNFRs) Typ I (p55) und Typ II (p75) nach Trauma. Swiss Surg. 1995;(5):241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korematsu K., Goto S., Nagahiro S., Ushio Y. Microglial response to transient focal cerebral ischemia: an immunocytochemical study on the rat cerebral cortex using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Sep;14(5):825–830. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T., Clark R. K., McDonnell P. C., Young P. R., White R. F., Barone F. C., Feuerstein G. Z. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke. 1994 Jul;25(7):1481–1488. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.7.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia D., Almerigogna F., Parronchi P., Ravina A., Maggi E., Romagnani S. Membrane tumour necrosis factor-alpha is involved in the polyclonal B-cell activation induced by HIV-infected human T cells. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):464–466. doi: 10.1038/363464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawashiro H., Martin D., Hallenbeck J. M. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor and amelioration of brain infarction in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997 Feb;17(2):229–232. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199702000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino H., Czurkó A., Fukuda A., Hashitani T., Hida H., Karadi Z., Lénárd L. Pathophysiological process after transient ischemia of the middle cerebral artery in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1994;35(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nophar Y., Holtmann H., Ber R., Wallach D. Dominance of resistance to the cytocidal effect of tumor necrosis factor in heterokaryons formed by fusion of resistant and sensitive cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3456–3460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck R., Brockhaus M., Frey J. R. Cell surface tumor necrosis factor (TNF) accounts for monocyte- and lymphocyte-mediated killing of TNF-resistant target cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Aug;122(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard J. K., Sheehan K. C., Arthur C. D., Schreiber R. D. Constitutive shedding of both p55 and p75 murine TNF receptors in vivo. J Immunol. 1997 Apr 15;158(8):3869–3873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. S., Shirazi Y., Drysdale B. E., Lieberman A., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of cytotoxic factor for oligodendrocytes by stimulated astrocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe J., Gehr G., Loetscher H., Lesslauer W. Tumor necrosis factor receptors--structure and function. Immunol Res. 1992;11(2):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02918612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Kondo N., Suzumura A., Marunouchi T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y., Li R., Shiosaki K. Inhibition of p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor by antisense oligonucleotides increases hypoxic injury and beta-amyloid toxicity in human neuronal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 7;272(6):3550–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga Y., Onodera H., Kogure K., Yamasaki Y., Yashima Y., Syozuhara H., Sendo F. Neutrophil as a mediator of ischemic edema formation in the brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Apr 29;125(2):110–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90003-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shohami E., Bass R., Wallach D., Yamin A., Gallily R. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) activity in rat brain is associated with cerebroprotection after closed head injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996 May;16(3):378–384. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199605000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippy B. D., Hofman F. M., Wallach D., Hinton D. R. Increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors in the brains of patients with AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Dec 15;10(5):511–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Farrah T., Goodwin R. G. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation, and death. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):959–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szaflarski J., Burtrum D., Silverstein F. S. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia stimulates cytokine gene expression in perinatal rats. Stroke. 1995 Jun;26(6):1093–1100. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Diserens A. C., Desbaillets I., de Tribolet N. Analysis of cytokine receptor messenger RNA expression in human glioblastoma cells and normal astrocytes by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. J Neurosurg. 1994 Jun;80(6):1063–1073. doi: 10.3171/jns.1994.80.6.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlow M. J., Jenkins R., Comis S. D., Osborne M. P., Stephens S., Stanley P., Crocker J. Ependymal cells of the choroid plexus express tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;19(4):324–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V., Reynolds C., Figari I. S., Weber R. F., Fendly B. M., Palladino M. A., Jr Stimulation of human T-cell proliferation by specific activation of the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4637–4641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V. Two TNF receptors. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90116-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Weber R. F., Figari I. S., Reynolds C., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9292–9296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taupin V., Toulmond S., Serrano A., Benavides J., Zavala F. Increase in IL-6, IL-1 and TNF levels in rat brain following traumatic lesion. Influence of pre- and post-traumatic treatment with Ro5 4864, a peripheral-type (p site) benzodiazepine ligand. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Feb;42(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90008-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchelingerian J. L., Quinonero J., Booss J., Jacque C. Localization of TNF alpha and IL-1 alpha immunoreactivities in striatal neurons after surgical injury to the hippocampus. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90312-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Vlassara H., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumour necrosis factor. Lancet. 1989 May 20;1(8647):1122–1126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turetskaya R. L., Fashena S. J., Paul N. L., Ruddle N. H. Genomic structure, induction, and production of TNF-beta. Immunol Ser. 1992;56:35–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zee K. J., Kohno T., Fischer E., Rock C. S., Moldawer L. L., Lowry S. F. Tumor necrosis factor soluble receptors circulate during experimental and clinical inflammation and can protect against excessive tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4845–4849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenabeele P., Declercq W., Beyaert R., Fiers W. Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;5(10):392–399. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. Cell death induction by TNF: a matter of self control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Apr;22(4):107–109. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Yue T. L., Young P. R., Barone F. C., Feuerstein G. Z. Expression of interleukin-6, c-fos, and zif268 mRNAs in rat ischemic cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995 Jan;15(1):166–171. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1995.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselingh S. L., Gough N. M., Finlay-Jones J. J., McDonald P. J. Detection of cytokine mRNA in astrocyte cultures using the polymerase chain reaction. Lymphokine Res. 1990 Summer;9(2):177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe M. N., Sarna G. S., Wadhwa M., Hayes G. M., Loughlin A. J., Tinker A., Cuzner M. L. Detection of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in adult rat brain, following mechanical injury, by in vivo microdialysis: evidence of a role for microglia in cytokine production. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Sep;33(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90110-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. L., Chopp M., Li Y., Zaloga C., Jiang N., Jones M. L., Miyasaka M., Ward P. A. Anti-ICAM-1 antibody reduces ischemic cell damage after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Neurology. 1994 Sep;44(9):1747–1751. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.9.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer L. A., Ennis M., Shipley M. T. Soman-induced seizures rapidly activate astrocytes and microglia in discrete brain regions. J Comp Neurol. 1997 Feb 24;378(4):482–492. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19970224)378:4<482::aid-cne4>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., Meistrell M., 3rd, Bloom O., Cockroft K. M., Bianchi M., Risucci D., Broome J., Farmer P., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Neurotoxicity of advanced glycation endproducts during focal stroke and neuroprotective effects of aminoguanidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3744–3748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]