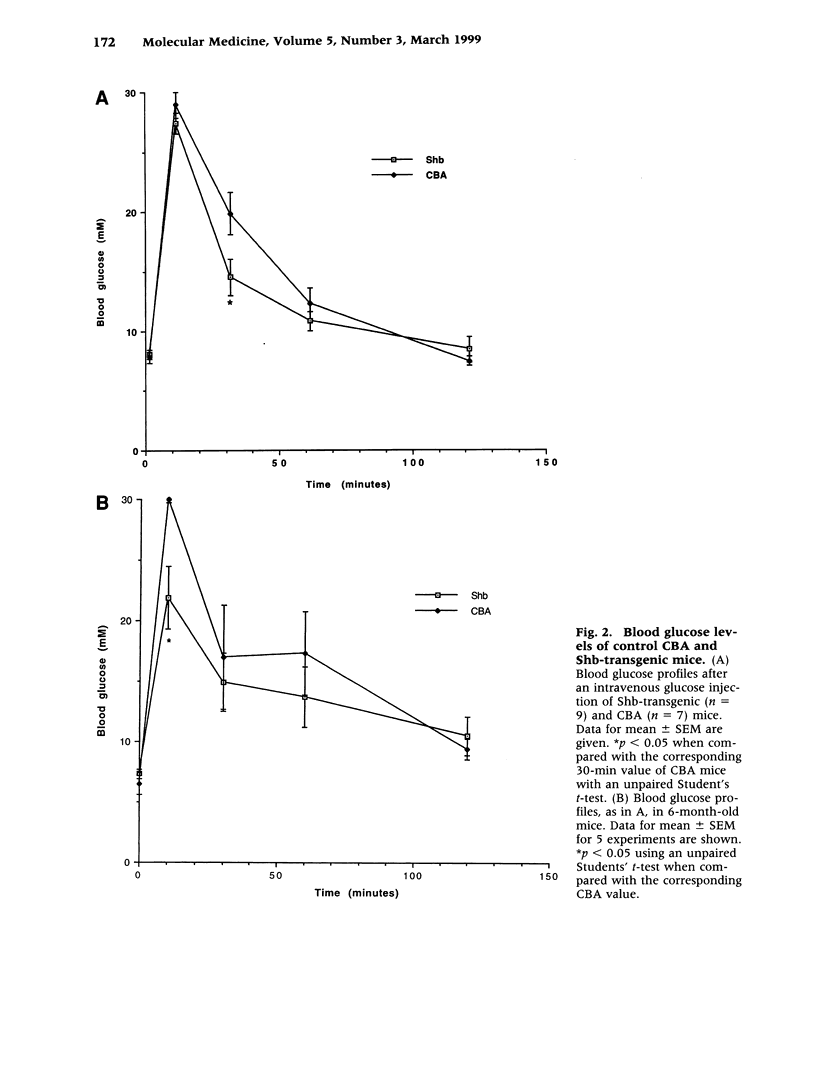
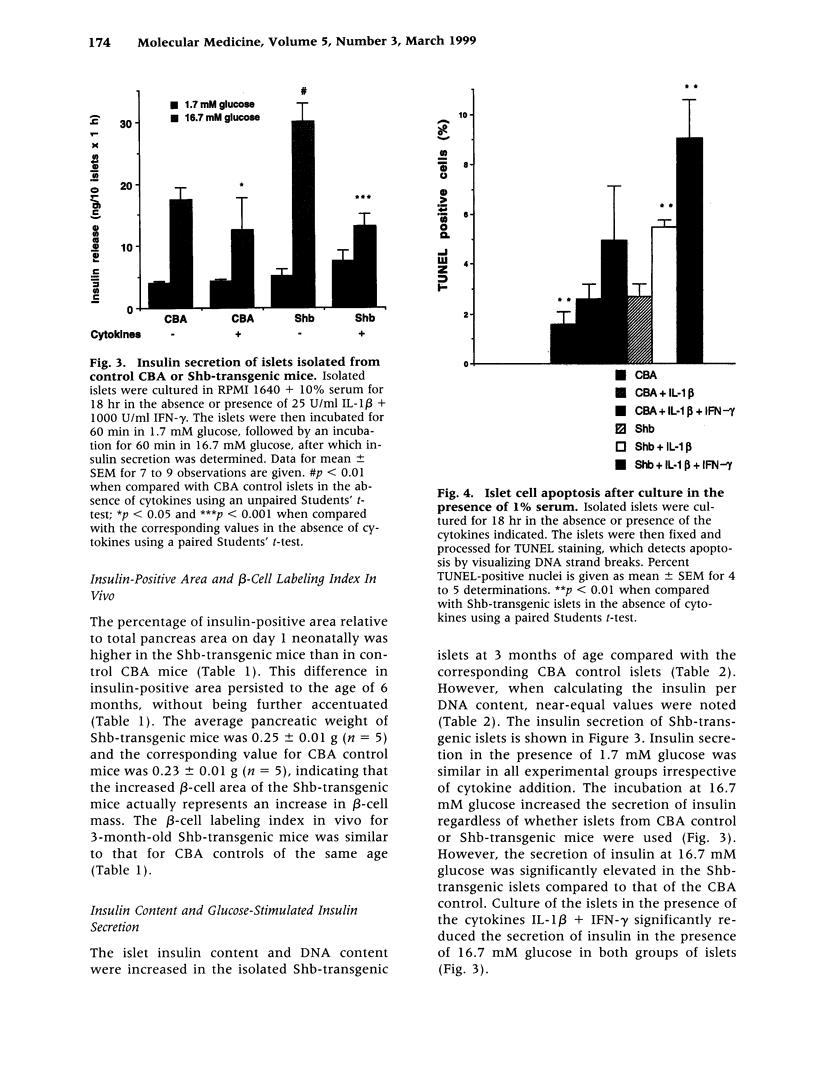
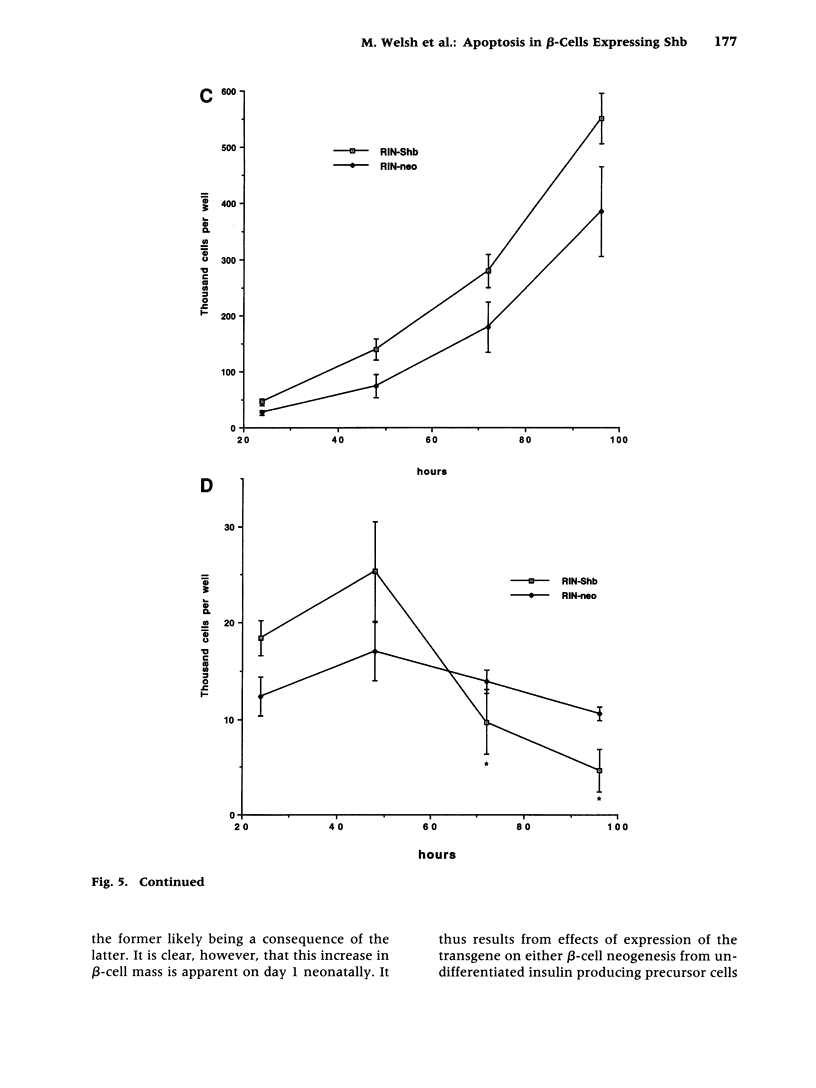
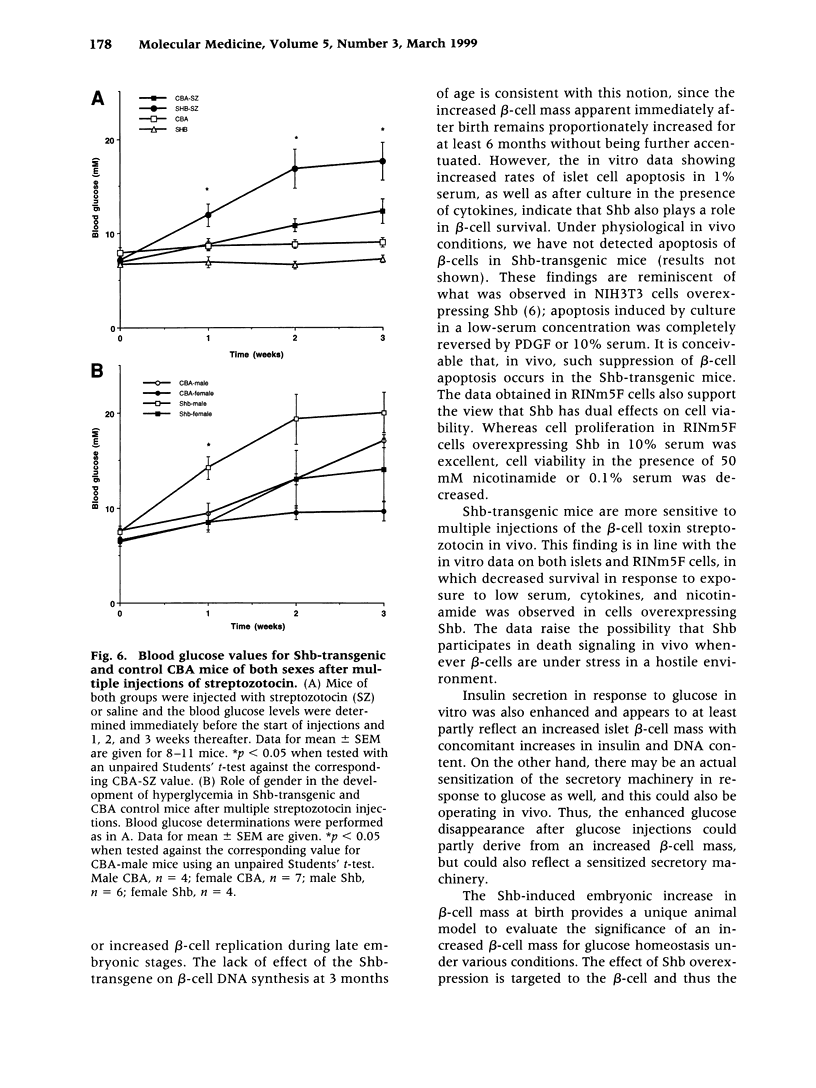
Abstract
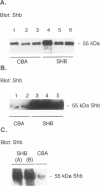
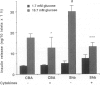
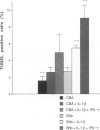
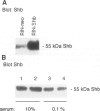
BACKGROUND: The Src-homology 2 domain-containing adaptor protein Shb was recently cloned as a serum-inducible gene in the insulin-producing beta-TC1 cell line. Subsequent studies have revealed an involvement of Shb for apoptosis in NIH3T3 fibroblasts and differentiation in the neuronal PC12 cells. To assess a role of Shb for beta-cell function, transgenic mice utilizing the rat insulin promoter to drive expression of Shb were generated. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A gene construct allowing the Shb cDNA to be expressed from the rat insulin 2 promoter was microinjected into fertilized mouse oocytes and implanted into pseudopregnant mice. Mice containing a low copy number of this transgene were bred and used for further experimentation. Shb expression was determined by Western blot analysis. The insulin-positive area of whole pancreas, insulin secretion of isolated islets and islet cell apoptosis, glucose tolerance tests, and in vivo sensitivity to multiple injections of the beta-cell toxin streptozotocin were determined in control CBA and Shb-transgenic mice. RESULTS: Western blot analysis revealed elevated islet content of the Shb protein. Shb-transgenic mice displayed enhanced glucose-disappearance rates in response to an intravenous glucose injection. The relative pancreatic beta-cell area neonatally and at 6 months of age were increased in the Shb-transgenic mice. Islets isolated from Shb-transgenic mice showed enhanced insulin secretion in response to glucose and increased insulin and DNA content. Apoptosis was increased in islets isolated from Shb-transgenic mice compared with control islets both under basal conditions and after incubation with IL-1 beta + IFN-gamma. Rat insulinoma RINm5F cells overexpressing Shb displayed decreased viability during culture in 0.1% serum and after exposure to a cytotoxic dose of nicotinamide. Shb-transgenic mice injected with multiple doses of streptozotocin showed increased blood glucose values compared with the corresponding controls, suggesting increased in vivo susceptibility to this toxin. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that Shb has dual effects on beta-cell growth: whereas Shb increases beta-cell formation during late embryonal stages, Shb also enhances beta-cell death under certain stressful conditions and may thus contribute to beta-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A. Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Jun;14(6):397–404. doi: 10.1007/BF01228134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwens L., Klöppel G. Islet cell neogenesis in the pancreas. Virchows Arch. 1996 Mar;427(6):553–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00202885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Sandler S., Palmer J. P. Repair of pancreatic beta-cells. A relevant phenomenon in early IDDM? Diabetes. 1993 Oct;42(10):1383–1391. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.10.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Parsons J. A., Burke J. P., Redick J. A., Van Orden D. E., Van Orden L. S. A modification of the unlabeled antibody enzyme method using heterologous antisera for the light microscopic and ultrastructural localization of insulin, glucagon and growth hormone. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Sep;23(9):666–677. doi: 10.1177/23.9.1176760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKKOS D., LUFT R. On the intravenous glucose tolerance test. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1957 Jul;25(3):312–334. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0250312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson T., Kullander K., Welsh M. The Src homology 2 domain protein Shb transmits basic fibroblast growth factor- and nerve growth factor-dependent differentiation signals in PC12 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Sep;9(9):757–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson T., Songyang Z., Landgren E., Lavergne C., Di Fiore P. P., Anafi M., Pawson T., Cantley L. C., Claesson-Welsh L., Welsh M. Molecular interactions of the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb with phosphotyrosine residues, tyrosine kinase receptors and Src homology 3 domain proteins. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1475–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson T., Welsh M. Apoptosis of NIH3T3 cells overexpressing the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb. Oncogene. 1996 Sep 5;13(5):955–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Jansson L., Eizirik D., Andersson A. Functional and morphological differentiation of fetal porcine islet-like cell clusters after transplantation into nude mice. Diabetologia. 1991 Jun;34(6):379–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00403174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A. Streptozotocin-induced pancreatic insulitis: new model of diabetes mellitus. Science. 1976 Jul 30;193(4251):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.180605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldeen J., Welsh N. Nicotinamide-induced apoptosis in insulin producing cells is associated with cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998 Apr 30;139(1-2):99–107. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I. Effects of aging on the regenerative capacity of the pancreatic B-cell of the rat. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):14–19. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Mares J., Karlsson T., Lavergne C., Bréant B., Claesson-Welsh L. Shb is a ubiquitously expressed Src homology 2 protein. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Songyang Z., Frantz J. D., Trüb T., Reedquist K. A., Karlsson T., Miyazaki M., Cantley L. C., Band H., Shoelson S. E. Stimulation through the T cell receptor leads to interactions between SHB and several signaling proteins. Oncogene. 1998 Feb 19;16(7):891–901. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N., Eizirik D. L., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3167–3173. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N., Margulis B., Borg L. A., Wiklund H. J., Saldeen J., Flodström M., Mello M. A., Andersson A., Pipeleers D. G., Hellerström C. Differences in the expression of heat-shock proteins and antioxidant enzymes between human and rodent pancreatic islets: implications for the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Mol Med. 1995 Nov;1(7):806–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]