Abstract
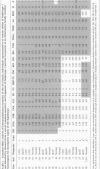
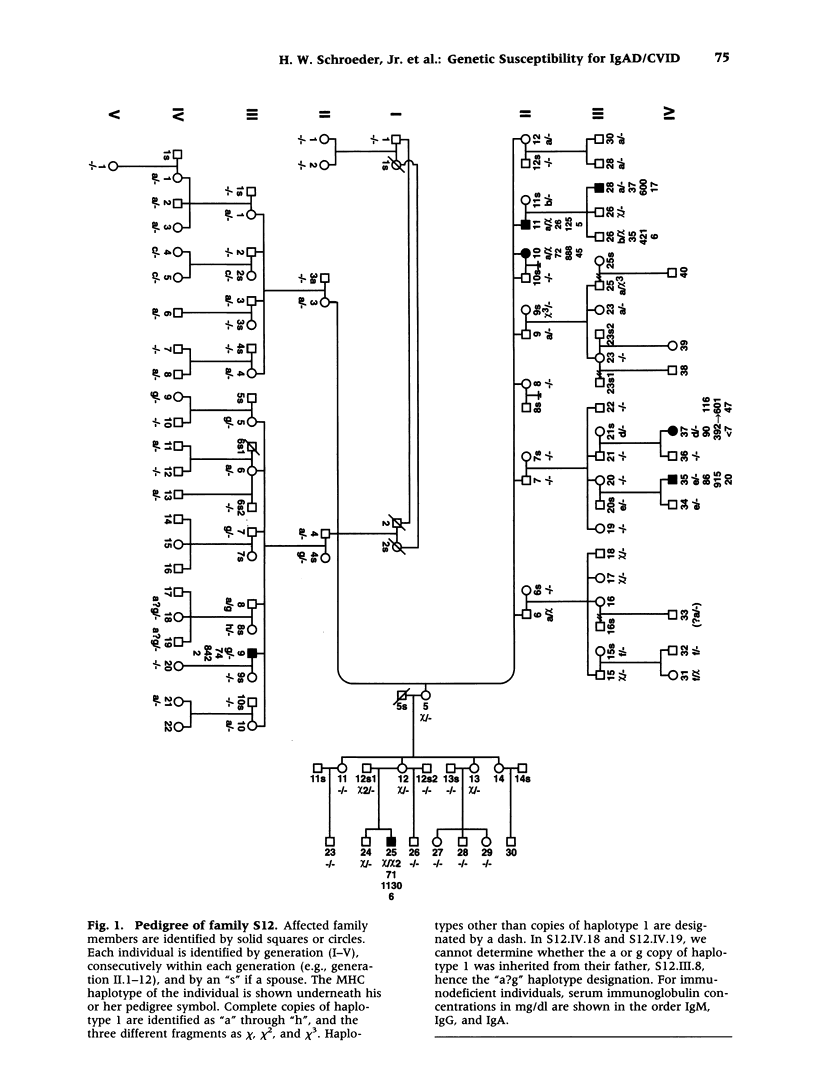
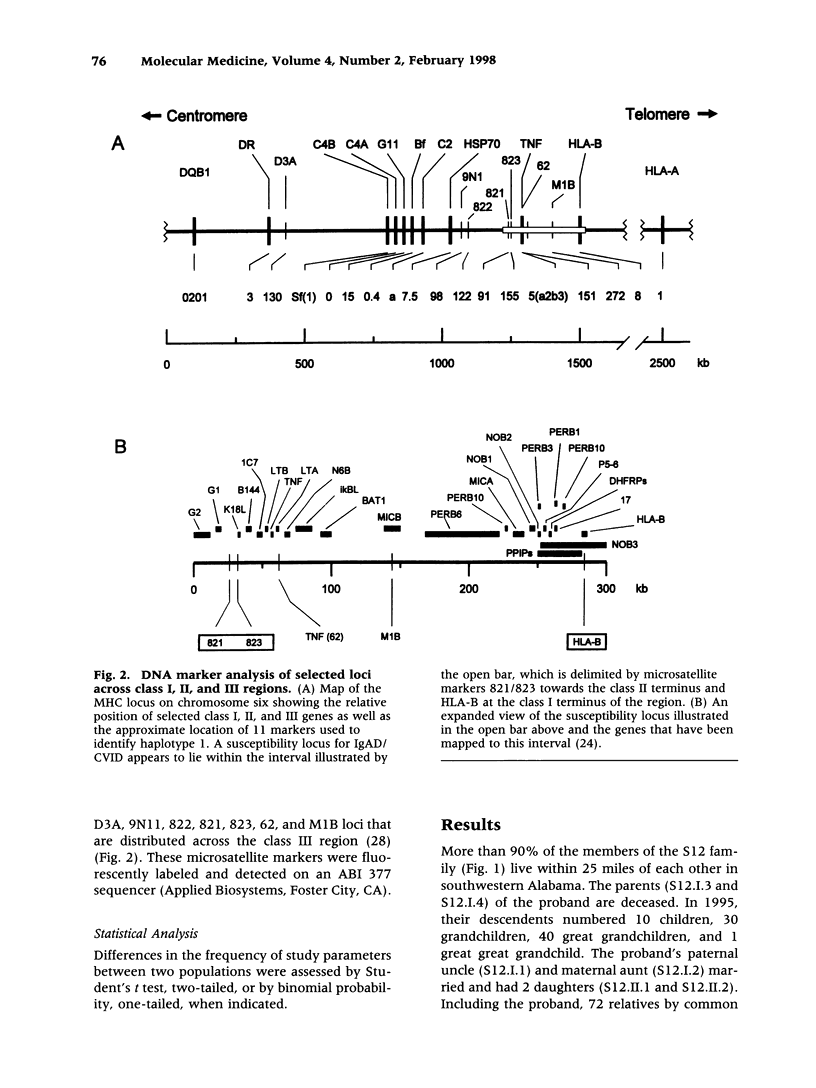
BACKGROUND: A common genetic basis for IgA deficiency (IgAD) and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is suggested by their occurrence in members of the same family and the similarity of the underlying B cell differentiation defects. An association between IgAD/CVID and HLA alleles DR3, B8, and A1 has also been documented. In a search for the gene(s) in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) that predispose to IgAD/CVID, we analyzed the extended MHC haplotypes present in a large family with 8 affected members. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We examined the CVID proband, 72 immediate relatives, and 21 spouses, and determined their serum immunoglobulin concentrations. The MHC haplotype analysis of individual family members employed 21 allelic DNA and protein markers, including seven newly available microsatellite markers. RESULTS: Forty-one (56%) of the 73 relatives by common descent were heterozygous and nine (12%) were homozygous for a fragment or the entire extended MHC haplotype designated haplotype 1 that included HLA- DR3, -C4A-0, -B8, and -A1. The remarkable prevalence of haplotype 1 was due in part to marital introduction into the family of 11 different copies of the haplotype, eight sharing 20 identical genotype markers between HLA-DR3 and HLA-B8, and three that contained fragments of haplotype 1. CONCLUSION: Crossover events within the MHC indicated a susceptibility locus for IgAD/CVID between the class III markers D821/D823 and HLA-B8, a region populated by 21 genes that include tumor necrosis factor alpha and lymphotoxins alpha and beta. Inheritance of at least this fragment of haplotype 1 appears to be necessary for the development of IgAD/CVID in this family.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham L. J., Du D. C., Zahedi K., Dawkins R. L., Whitehead A. S. Haplotypic polymorphisms of the TNFB gene. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(1):50–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00211695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham L. J., Leelayuwat C., Grimsley G., Degli-Esposti M. A., Mann A., Zhang W. J., Christiansen F. T., Dawkins R. L. Sequence differences between HLA-B and TNF distinguish different MHC ancestral haplotypes. Tissue Antigens. 1992 Mar;39(3):117–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1992.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alimzhanov M. B., Kuprash D. V., Kosco-Vilbois M. H., Luz A., Turetskaya R. L., Tarakhovsky A., Rajewsky K., Nedospasov S. A., Pfeffer K. Abnormal development of secondary lymphoid tissues in lymphotoxin beta-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Aug 19;94(17):9302–9307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.17.9302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiot F., Boussadia O., Cases S., Fitting C., Lebastard M., Cavaillon J. M., Milon G., Dautry F. Mice heterozygous for a deletion of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin-alpha genes: biological importance of a nonlinear response of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to gene dosage. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Apr;27(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman R. F., Schaffer F. M., Kemp J. D., Yokoyama W. M., Zhu Z. B., Cooper M. D., Volanakis J. E. Genetic and immunologic analysis of a family containing five patients with common-variable immune deficiency or selective IgA deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1992 Nov;12(6):406–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00918852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks T. A., Rouse B. T., Kerley M. K., Blair P. J., Godfrey V. L., Kuklin N. A., Bouley D. M., Thomas J., Kanangat S., Mucenski M. L. Lymphotoxin-alpha-deficient mice. Effects on secondary lymphoid organ development and humoral immune responsiveness. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 15;155(4):1685–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma G., Crusius J. B., Oudkerk Pool M., Kolkman J. J., von Blomberg B. M., Kostense P. J., Giphart M. J., Schreuder G. M., Meuwissen S. G., Peña A. S. Secretion of tumour necrosis factor alpha and lymphotoxin alpha in relation to polymorphisms in the TNF genes and HLA-DR alleles. Relevance for inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Immunol. 1996 Apr;43(4):456–463. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1996.d01-65.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman B. M., Zuijdeest D., Kaijzel E. L., Breedveld F. C., Verweij C. L. Relevance of the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) -308 promoter polymorphism in TNF alpha gene regulation. J Inflamm. 1995;46(1):32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning J. L., Ngam-ek A., Lawton P., DeMarinis J., Tizard R., Chow E. P., Hession C., O'Brine-Greco B., Foley S. F., Ware C. F. Lymphotoxin beta, a novel member of the TNF family that forms a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin on the cell surface. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90574-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H. Clinical and immunologic features of selective IgA deficiency. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows P. D., Cooper M. D. IgA deficiency. Adv Immunol. 1997;65:245–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bućin D., Truedsson L., Hammarström L., Smith C. I., Sjöholm A. G. C4 polymorphism and major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in IgA deficiency: association with C4A null haplotypes. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1991;8(4):233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Hochez J. Effects of misspecifying genetic parameters in lod score analysis. Biometrics. 1986 Jun;42(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Congia M., Frau F., Lampis R., Frau R., Mele R., Cucca F., Muntoni F., Porcu S., Boi F., Contu L. A high frequency of the A30, B18, DR3, DRw52, DQw2 extended haplotype in Sardinian celiac disease patients: further evidence that disease susceptibility is conferred by DQ A1*0501, B1*0201. Tissue Antigens. 1992 Feb;39(2):78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1992.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Cooper M. D. Immature IgA B cells in IgA-deficient patients. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 27;305(9):495–497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108273050905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R. Circulating B-cells in patients with immunodeficiency. Am J Pathol. 1972 Dec;69(3):513–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe P. D., VanArsdale T. L., Walter B. N., Ware C. F., Hession C., Ehrenfels B., Browning J. L., Din W. S., Goodwin R. G., Smith C. A. A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.8171323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cucca F., Zhu Z. B., Khanna A., Cossu F., Congia M., Badiali M., Lampis R., Frau F., De Virgiliis S., Cao A. Evaluation of IgA deficiency in Sardinians indicates a susceptibility gene is encoded within the HLA class III region. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Jan;111(1):76–80. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Wolf E., Gorsuch A. N., Festenstein H. A new look at HLA genetics with particular reference to type-1 diabetes. Lancet. 1979 Aug 25;2(8139):389–391. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C., Fotino M., Rosina O., Peter J. B. Selective IgA deficiency, IgG subclass deficiency, and the major histocompatibility complex. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Nov;61(2 Pt 2):S61–S69. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(05)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham-Rundles C. Genetic aspects of immunoglobulin A deficiency. Adv Hum Genet. 1990;19:235–266. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-9065-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alfonso S., Richiardi P. M. A polymorphic variation in a putative regulation box of the TNFA promoter region. Immunogenetics. 1994;39(2):150–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00188619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Togni P., Goellner J., Ruddle N. H., Streeter P. R., Fick A., Mariathasan S., Smith S. C., Carlson R., Shornick L. P., Strauss-Schoenberger J. Abnormal development of peripheral lymphoid organs in mice deficient in lymphotoxin. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):703–707. doi: 10.1126/science.8171322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. A., Denis K. A., Dawkins R., Peter J. B. Severity of infections in IgA deficiency: correlation with decreased serum antibodies to pneumococcal polysaccharides and decreased serum IgG2 and/or IgG4. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Apr;100(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund Y. R., Sgarlato G., Jacob C. O., Suzuki Y., Remington J. S. Polymorphisms in the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) gene correlate with murine resistance to development of toxoplasmic encephalitis and with levels of TNF-alpha mRNA in infected brain tissue. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):683–688. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. X., Molina H., Matsumoto M., Huang G., Min J., Chaplin D. D. Lymphotoxin-alpha (LTalpha) supports development of splenic follicular structure that is required for IgG responses. J Exp Med. 1997 Jun 16;185(12):2111–2120. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.12.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Merino A., Alper C. A., Usuku K., Marcus-Bagley D., Lincoln R., Awdeh Z., Yunis E. J., Eisenbarth G. S., Brink S. J., Hauser S. L. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) microsatellite haplotypes in relation to extended haplotypes, susceptibility to diseases associated with the major histocompatibility complex and TNF secretion. Hum Immunol. 1996 Sep 15;50(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(96)00064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Doneshka P. Partitioned association-linkage test: distinguishing "necessary" from "susceptibility" loci. Genet Epidemiol. 1996;13(3):243–252. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2272(1996)13:3<243::AID-GEPI2>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe H. S., So A. K., Farrant J., Webster A. D. Common variable immunodeficiency is associated with polymorphic markers in the human major histocompatibility complex. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):387–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Fronek Z., Lewis G. D., Koo M., Hansen J. A., McDevitt H. O. Heritable major histocompatibility complex class II-associated differences in production of tumor necrosis factor alpha: relevance to genetic predisposition to systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1233–1237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Keeton L. G., Zhu Z. B., Volanakis J. E., Cooper M. D., Schroeder H. W., Jr Age-related changes in serum immunoglobulins in patients with familial IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Clin Exp Immunol. 1997 Jun;108(3):477–483. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.3801278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh T., Mizumoto T., Yasuda N., Koya M., Ohno Y., Uchino H., Yoshimura K., Ohkubo Y., Yamaguchi H. Selective IgA deficiency in Japanese blood donors: frequency and statistical analysis. Vox Sang. 1986;50(2):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb04851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitz W., Lo S. K., Neugebauer M., Baur M. P., Albert E. D., Thomson G. A comprehensive search for segregation distortion in HLA. Hum Immunol. 1987 Feb;18(2):163–180. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koni P. A., Sacca R., Lawton P., Browning J. L., Ruddle N. H., Flavell R. A. Distinct roles in lymphoid organogenesis for lymphotoxins alpha and beta revealed in lymphotoxin beta-deficient mice. Immunity. 1997 Apr;6(4):491–500. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Banchereau J. Mutant mice without B lymphocyte follicles. J Exp Med. 1996 Oct 1;184(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Dunn A., Grail D., Inglese M., Noguchi Y., Richards E., Jungbluth A., Wada H., Moore M., Williamson B. Characterization of tumor necrosis factor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 22;94(15):8093–8098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matamoros Florí N., Mila Llambi J., Español Boren T., Raga Borja S., Fontan Casariego G. Primary immunodeficiency syndrome in Spain: first report of the National Registry in Children and Adults. J Clin Immunol. 1997 Jul;17(4):333–339. doi: 10.1023/a:1027382916924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W., Hill A. V., Allsopp C. E., Greenwood B. M., Kwiatkowski D. Variation in the TNF-alpha promoter region associated with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):508–510. doi: 10.1038/371508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Kark J. D., Zakuth V., Margalit G., Spirer Z. Serum immunoglobulin A levels and ethnicity in an Israeli population sample. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Mar;42(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer G., Spengler U., Jung M. C., Honold G., Blömer K., Pape G. R., Riethmüller G., Weiss E. H. Polymorphic structure of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) locus: an NcoI polymorphism in the first intron of the human TNF-beta gene correlates with a variant amino acid in position 26 and a reduced level of TNF-beta production. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):209–219. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. P., Rich S., Barbosa J. Insulin dependent diabetic families: sex ratio and HLA haplotype segregation. Lancet. 1981 Feb 14;1(8216):388–388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91710-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monos D. S., Kamoun M., Udalova I. A., Csanky E., Cizman B., Turetskaya R. L., Smirnova J. B., Zharkov V. G., Gasser D., Zmijewski C. M. Genetic polymorphism of the human tumor necrosis factor region in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Linkage disequilibrium of TNFab microsatellite alleles with HLA haplotypes. Hum Immunol. 1995 Oct;44(2):70–79. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(95)00060-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. M., Lisby S., Arrighi J. F., Grau G. E., Saurat J. H., Hauser C. H-2D haplotype-linked expression and involvement of TNF-alpha in Th2 cell-mediated tissue inflammation. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 1;153(1):316–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oen K., Petty R. E., Schroeder M. L. Immunoglobulin A deficiency: genetic studies. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Mar;19(3):174–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Smith C. I., Björkander J., Hammarström L. Shared HLA class II-associated genetic susceptibility and resistance, related to the HLA-DQB1 gene, in IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10653–10657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Smith C. I., Hammarström L. Different amino acids at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain associated with susceptibility and resistance to IgA deficiency. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):289–290. doi: 10.1038/347289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A., Laurell A. B., Lindquist B., Golebiowska H., Axelsson U., Björkander J., Hanson L. A. IgG subclasses in selective IgA deficiency: importance of IgG2-IgA deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1476–1477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasparakis M., Alexopoulou L., Episkopou V., Kollias G. Immune and inflammatory responses in TNF alpha-deficient mice: a critical requirement for TNF alpha in the formation of primary B cell follicles, follicular dendritic cell networks and germinal centers, and in the maturation of the humoral immune response. J Exp Med. 1996 Oct 1;184(4):1397–1411. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.4.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert P. D., Browning J. L., Mebius R., Mackay F., Hochman P. S. Surface lymphotoxin alpha/beta complex is required for the development of peripheral lymphoid organs. J Exp Med. 1996 Nov 1;184(5):1999–2006. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. M., Palermos J., Zhu Z. B., Barger B. O., Cooper M. D., Volanakis J. E. Individuals with IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency share polymorphisms of major histocompatibility complex class III genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8015–8019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S. Distorted HLA segregation or biased ascertainment? Lancet. 1980 Jan 5;1(8158):40–41. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90574-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Cross S. J. Phenotyping of human complement component C4, a class-III HLA antigen. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):763–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2390763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuber F., Udalova I. A., Book M., Drutskaya L. N., Kuprash D. V., Turetskaya R. L., Schade F. U., Nedospasov S. A. -308 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) polymorphism is not associated with survival in severe sepsis and is unrelated to lipopolysaccharide inducibility of the human TNF promoter. J Inflamm. 1995;46(1):42–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udalova I. A., Nedospasov S. A., Webb G. C., Chaplin D. D., Turetskaya R. L. Highly informative typing of the human TNF locus using six adjacent polymorphic markers. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):180–186. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadheim C. M., Rotter J. I., Maclaren N. K., Riley W. J., Anderson C. E. Preferential transmission of diabetic alleles within the HLA gene complex. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 20;315(21):1314–1318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611203152103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Zhu Z. B., Schaffer F. M., Macon K. J., Palermos J., Barger B. O., Go R., Campbell R. D., Schroeder H. W., Jr, Cooper M. D. Major histocompatibility complex class III genes and susceptibility to immunoglobulin A deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1914–1922. doi: 10.1172/JCI115797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorechovský I., Zetterquist H., Paganelli R., Koskinen S., Webster A. D., Björkander J., Smith C. I., Hammarström L. Family and linkage study of selective IgA deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Nov;77(2):185–192. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukmanović S., Vucković S., Stosić-Grujicić S., Ramić Z., Abinun M. An unusual T-cell surface phenotype in vivo correlates with the failure to proliferate and produce IL-2 in vitro in a patient with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Dec;65(3):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90156-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., VanArsdale T. L., Crowe P. D., Browning J. L. The ligands and receptors of the lymphotoxin system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;198:175–218. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79414-8_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Jacob C. O. Regulation of MHC class II antigen expression. Opposing effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR and Ia expression depends on the maturation and differentiation stage of the cell. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):899–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R. HLA segregation ratios. Lancet. 1979 Oct 6;2(8145):745–745. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90674-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. G., Symons J. A., McDowell T. L., McDevitt H. O., Duff G. W. Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 1;94(7):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.7.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. G., de Vries N., Pociot F., di Giovine F. S., van der Putte L. B., Duff G. W. An allelic polymorphism within the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter region is strongly associated with HLA A1, B8, and DR3 alleles. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):557–560. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton A. N., Cobain T. J., Dawkins R. L. Family studies of IgA deficiency. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):333–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00430799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A., Williams R. C., Jr Immunoglobulin studies in six kindreds of patients with adult hypogammaglobulinemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Sep;66(3):433–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]