Abstract
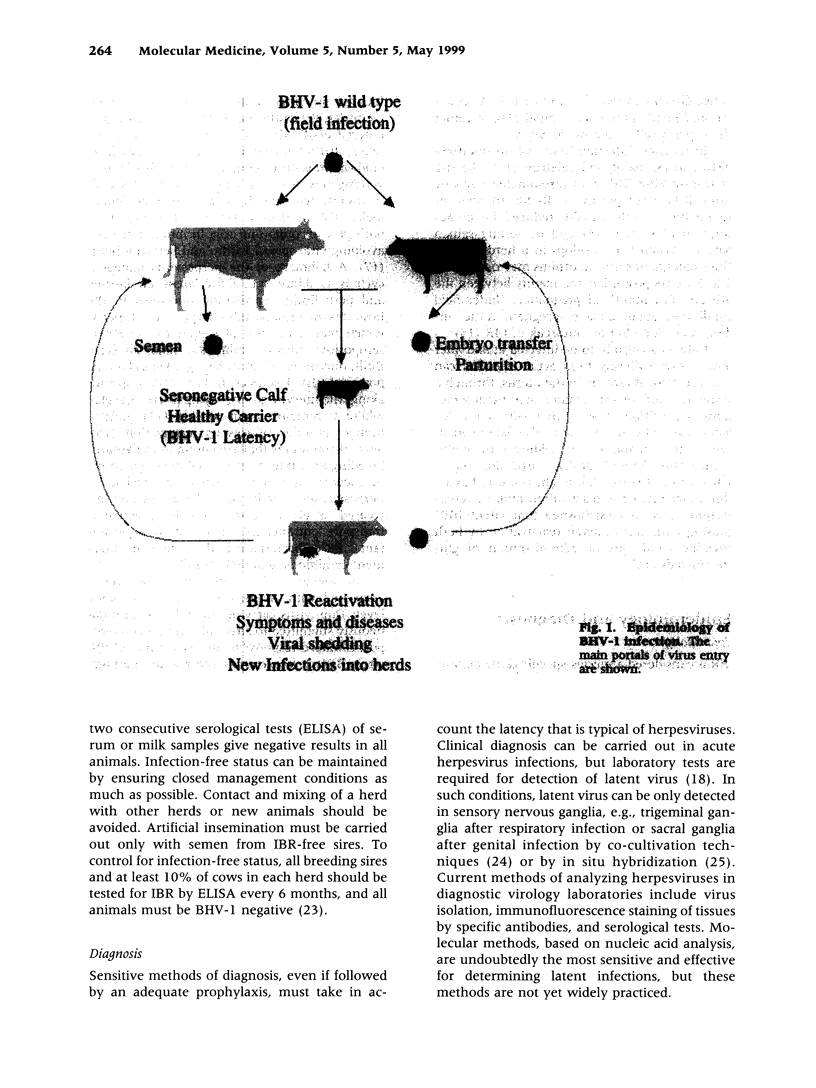
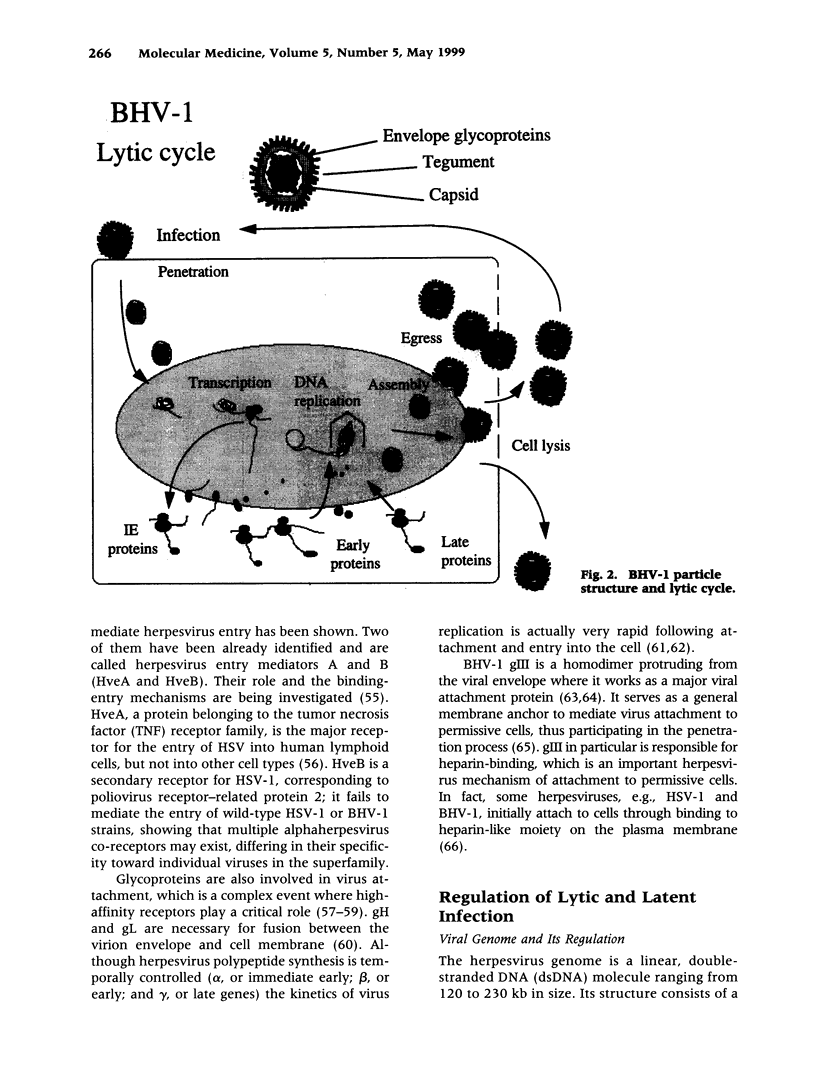
BACKGROUND: Herpesviruses are widespread viruses, causing severe infections in both humans and animals. Eradication of herpesviruses is extremely difficult because of their ability to establish latent and life-long infections. However, latency is only one tool that has evolved in herpesviruses to successfully infect their hosts; such viruses display a wide (and still incompletely known) panoply of genes and proteins that are able to counteract immune responses of their hosts. Envelope glycoproteins and cytokine inhibitors are two examples of such weapons. All of these factors make it difficult to develop diagnostics and vaccines, unless they are based on molecular techniques. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Animal herpesviruses, because of their striking similarity to human ones, are suitable models to study the molecular biology of herpesviruses and develop strategies aimed at designing neurotropic live vectors for gene therapy as well as engineered attenuated vaccines. RESULTS: BHV-1 is a neurotropic herpesvirus causing infectious rhinotracheitis (IBR) in cattle. It is a major plague in zootechnics and commercial trade, because of its ability to spread through asymptomatic carrier animals, frozen semen, and embryos. Such portals of infections are also important for human herpesviruses, which mainly cause systemic, eye, and genital tract infections, leading even to the development of cancer. CONCLUSIONS: This review covers both the genetics and molecular biology of BHV-1 and its related herpesviruses. Epidemiology and diagnostic approaches to herpesvirus infections are presented. The role of herpesviruses in gene therapy and a broad introduction to classic and engineered vaccines against herpesviruses are also provided. http://link.springer-ny. com/link/service/journals/00020/bibs/5n5p261.html
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelmagid O. Y., Mansour M. M., Minocha H. C., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Evaluation of baculovirus-expressed bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) glycoproteins for detection and analysis of BHV-1-specific antibody responses. Vet Microbiol. 1998 Apr 15;61(4):249–259. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(98)00188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann M., Bélak S., Bitsch V., Edwards S., Moussa A., Rockborn G., Thiry E. Round table on infectious bovine rhinotracheitis/infectious pustular vulvovaginitis virus infection diagnosis and control. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Jun;23(1-4):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90167-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann M., Peterhans E., Wyler R. DNA of bovine herpesvirus type 1 in the trigeminal ganglia of latently infected calves. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jan;43(1):36–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R. H., Torres H. N., Polacino P. S., Schudel A., Palma E. L. Detection of bovine herpesvirus-1 nucleic acid sequences, using a dot-blot hybridization procedure. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Jun;48(6):984–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthington J. D., Corah L. R., Blecha F. The effect of molybdenum-induced copper deficiency on acute-phase protein concentrations, superoxide dismutase activity, leukocyte numbers, and lymphocyte proliferation in beef heifers inoculated with bovine herpesvirus-1. J Anim Sci. 1996 Jan;74(1):211–217. doi: 10.2527/1996.741211x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashbaugh S. E., Thompson K. E., Belknap E. B., Schultheiss P. C., Chowdhury S., Collins J. K. Specific detection of shedding and latency of bovine herpesvirus 1 and 5 using a nested polymerase chain reaction. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1997 Oct;9(4):387–394. doi: 10.1177/104063879700900408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., L'Italien J., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Zamb T., Lawman J. P., Hughes G., Gifford G. A. Protection of cattle from bovine herpesvirus type I (BHV-1) infection by immunization with individual viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Tikoo S. K. Immunology of bovine herpesvirus 1 infection. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Tikoo S. K., Lewis P. J., Liang X. Novel viral vaccines for livestock. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Nov;54(1-4):355–363. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(96)05678-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca-Estrada M. E., Godson D. L., Hughes H. P., Van Donkersgoed J., Van Kessel A., Harland R., Shuster D. E., Daley M., Babiuk L. A. Effect of recombinant bovine interleukin-1 beta on viral/bacterial pneumonia in cattle. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995 May;15(5):431–439. doi: 10.1089/jir.1995.15.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. C., Rust S. R., Walker R. D. Transmission of a vaccinal strain of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus from intranasally vaccinated steers commingled with nonvaccinated steers. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jun;50(6):814–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranowski E., Dubuisson J., van Drunen Little-van den Hurk S., Babiuk A. L., Michel A., Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Synthesis and processing of bovine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein H. Virology. 1995 Jan 10;206(1):651–654. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranowski E., Keil G., Lyaku J., Rijsewijk F. A., van Oirschot J. T., Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Structural and functional analysis of bovine herpesvirus 1 minor glycoproteins. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):91–101. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello L. J., Whitbeck J. C., Lawrence W. C. Bovine herpesvirus 1 as a live virus vector for expression of foreign genes. Virology. 1992 Oct;190(2):666–673. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90904-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello L. J., Whitbeck J. C., Lawrence W. C. Map location of the thymidine kinase gene of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4023–4025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4023-4025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielanski A., Loewen K. G., Hare W. C. Inactivation of bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-I) from in vitro infected bovine semen. Theriogenology. 1988 Oct;30(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(88)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeldt Ohmann H., Babiuk L. A., Harland R. Cytokine synergy with viral cytopathic effects and bacterial products during the pathogenesis of respiratory tract infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Aug;60(2):153–170. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90060-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J. C., Frankena K., van Oirschot J. T. Effect on milk production of vaccination with a bovine herpesvirus 1 gene-deleted vaccine. Vet Rec. 1997 Feb 22;140(8):196–199. doi: 10.1136/vr.140.8.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratanich A. C., Jones C. J. Localization of cis-acting sequences in the latency-related promoter of bovine herpesvirus 1 which are regulated by neuronal cell type factors and immediate-early genes. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6099–6106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6099-6106.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratanich A. C., Sardi S. I., Smitsaart E. N., Schudel A. A. Comparative studies of BHV-1 variants by in vivo--in vitro tests. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 Feb;38(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruynzeel P. L., Hamelink M. L., Kok P. T., van der Vet A. P., Kreukniet J. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptors on intact human platelets of normal individuals and chronic obstructive lung disease patients. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1984;135:139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. A., Fenton R. A., Misra V., Haines D. M. Fatal, generalized bovine herpesvirus type-1 infection associated with a modified-live infectious bovine rhinotracheitis parainfluenza-3 vaccine administered to neonatal calves. Can Vet J. 1994 Apr;35(4):223–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M., Ohmann H. B., Hutchings D., Rapin N., Babiuk L. A., Lawman M. J. Role of interferon-gamma in inducing cytotoxicity of peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes to bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1)-infected cells. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrucci G., Frigeri F., Ranucci S., Ferrari M., Cilli V., Pedini B., Nettleton P., Caleffi F., Aldrovandi V., Herring A. J. Comparative studies of strains of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus isolated from latently infected calves. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(84)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase C. C., Lohff C., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Resistance and susceptibility of bovine cells expressing herpesviral glycoprotein D homologs to herpesviral infections. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):365–369. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. H., Splitter G. A. Induction of MHC-unrestricted cytolytic CD4+ T cells against virally infected target cells by cross-linking CD4 molecules. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 1;153(9):3874–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury S. I. Construction and characterization of an attenuated bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) recombinant virus. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Sep;52(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(96)00043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury S. I. Fine mapping of bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) glycoprotein C neutralizing epitopes by type-specific monoclonal antibodies and synthetic peptides. Vet Microbiol. 1997 Nov;58(2-4):309–314. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(97)00146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. K., Butcher A. C., Riegel C. A. Immune response to bovine herpes herpesvirus type 1 infections: virus-specific antibodies in sera from infected animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):546–552. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.546-552.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. J., Zamb T. J., Babiuk L. A. Bovine herpesvirus 1: immune responses in mice and cattle injected with plasmid DNA. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5664–5667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5664-5667.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Slaoui M., Keil G., Babiuk L. A., Ernst E., Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Identification of different target glycoproteins for bovine herpes virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes depending on the method of in vitro stimulation. Immunology. 1993 Jan;78(1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deregt D., Cho H. J., Kozub G. C. A comparative evaluation of two sensitive serum neutralization tests for bovine herpesvirus-1 antibodies. Can J Vet Res. 1993 Jan;57(1):56–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devireddy L. R., Jones C. Alternative splicing of the latency-related transcript of bovine herpesvirus 1 yields RNAs containing unique open reading frames. J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7294–7301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.9.7294-7301.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew T. W., Hewitt-Taylor C., Watson L., Edwards S. Effect of storage conditions and culture technique on the isolation of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus from bovine semen. Vet Rec. 1987 Dec 5;121(23):547–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duque H., Marshall R. L., Israel B. A., Letchworth G. J. Effects of formalin inactivation on bovine herpes virus-1 glycoproteins and antibody response elicited by formalin-inactivated vaccines in rabbits. Vaccine. 1989 Dec;7(6):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S., Woods S. B., Westcott D. G., Emmerson M., Jones P. C., Phillips A. J. An evaluation of five serological tests for the detection of antibody to bovine herpesvirus 1 in vaccinated and experimentally infected cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Nov;41(3):378–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels M., Ackermann M. Pathogenesis of ruminant herpesvirus infections. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):3–15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels M., Steck F., Wyler R. Comparison of the genomes of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and infectious pustular vulvovaginitis virus strains by restriction endonuclease analysis. Arch Virol. 1981;67(2):169–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01318601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Nucleotide sequence of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein gIII, a structural model for gIII as a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, and implications for the homologous glycoproteins of other herpesviruses. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Redmond M. J., Attah-Poku S. K., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Mapping of 10 epitopes on bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoproteins gI and gIII. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90239-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Zamb T., Parker M. D., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A., Lawman M. J. Expression of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins gI and gIII in transfected murine cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4239–4248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4239-4248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florent G., de Marneffe C. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay used to monitor serum antibodies to bovine respiratory disease viruses. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Apr;11(4):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores E. F., Osorio F. A., Zanella E. L., Kit S., Kit M. Efficacy of a deletion mutant bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) vaccine that allows serologic differentiation of vaccinated from naturally infected animals. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1993 Oct;5(4):534–540. doi: 10.1177/104063879300500406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraefel C., Ackermann M., Schwyzer M. Identification of the bovine herpesvirus 1 circ protein, a myristylated and virion-associated polypeptide which is not essential for virus replication in cell culture. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):8082–8088. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.8082-8088.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraefel C., Wirth U. V., Vogt B., Schwyzer M. Immediate-early transcription over covalently joined genome ends of bovine herpesvirus 1: the circ gene. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1328–1333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1328-1333.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraefel C., Zeng J., Choffat Y., Engels M., Schwyzer M., Ackermann M. Identification and zinc dependence of the bovine herpesvirus 1 transactivator protein BICP0. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):3154–3162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.5.3154-3162.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerichs G. N., Woods S. B., Lucas M. H., Sands J. J. Safety and efficacy of live and inactivated infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccines. Vet Rec. 1982 Aug 7;111(6):116–122. doi: 10.1136/vr.111.6.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Valcarcel M., Fowler W. J., Harper D. R., Jeffries D. J., Layton G. T. Cloning, expression, and immunogenicity of the assembly protein of varicella-zoster virus and detection of the products of open reading frame 33. J Med Virol. 1997 Dec;53(4):332–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y., Kashanchi F., Wood C. Activation of bovine immunodeficiency-like virus expression by bovine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):832–836. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90489-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George L. W., Ardans A., Mihalyi J., Guerra M. R. Enhancement of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis by modified-live infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Nov;49(11):1800–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty R. J., Krummenacher C., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Spear P. G. Entry of alphaherpesviruses mediated by poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 and poliovirus receptor. Science. 1998 Jun 5;280(5369):1618–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5369.1618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., DeLuca N. A., Fink D. J. Development and application of herpes simplex virus vectors for human gene therapy. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:675–710. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hage J. J., Schukken Y. H., Barkema H. W., Benedictus G., Rijsewijk F. A., Wentink G. H. Population dynamics of bovine herpesvirus 1 infection in a dairy herd. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Ludwig H., Buhk H. J. Specificity of cleavage in replicative-form DNA of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1355–1363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1355-1363.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanon E., Meyer G., Vanderplasschen A., Dessy-Doizé C., Thiry E., Pastoret P. P. Attachment but not penetration of bovine herpesvirus 1 is necessary to induce apoptosis in target cells. J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7638–7641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.9.7638-7641.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harasawa R. Adventitious pestivirus RNA in live virus vaccines against bovine and swine diseases. Vaccine. 1995 Jan;13(1):100–103. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)80018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan M. J., Nataraj C., Srikumaran S. Down regulation of murine MHC class I expression by bovine herpesvirus 1. Viral Immunol. 1993 Winter;6(4):273–284. doi: 10.1089/vim.1993.6.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan E. J., Easterday B. C. Isolation of bovine herpesvirus-1 from trigeminal ganglia of clinically normal cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Aug;41(8):1212–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Herr W. Differential control of transcription by homologous homeodomain coregulators. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;16(6):2967–2976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.6.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huemer H. P., Larcher C., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Species selective interaction of Alphaherpesvirinae with the "unspecific" immune system of the host. Arch Virol. 1993;130(3-4):353–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01309666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Campos M., Godson D. L., Van Drunen Littel-Van den Hurk S., McDougall L., Rapin N., Zamb T., Babiuk L. A. Immunopotentiation of bovine herpes virus subunit vaccination by interleukin-2. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):461–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Campos M., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Zamb T., Sordillo L. M., Godson D., Babiuk L. A. Multiple administration with interleukin-2 potentiates antigen-specific responses to subunit vaccination with bovine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein IV. Vaccine. 1992;10(4):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90157-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings D. L., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Lymphocyte proliferative responses to separated bovine herpesvirus 1 proteins in immune cattle. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5114–5122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5114-5122.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel B. A., Marshall R. L., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Epitope specificity and protective efficacy of the bovine immune response to bovine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein vaccines. Vaccine. 1988 Aug;6(4):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L. Glycoprotein E of pseudorabies virus and homologous proteins in other alphaherpesvirinae. Arch Virol. 1994;137(3-4):209–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01309470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Hossain A., Winkler M. T., Holt T., Doster A., Jones C. A protein encoded by the latency-related gene of bovine herpesvirus 1 is expressed in trigeminal ganglionic neurons of latently infected cattle and interacts with cyclin-dependent kinase 2 during productive infection. J Virol. 1998 Oct;72(10):8133–8142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.10.8133-8142.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Delhon G., Bratanich A., Kutish G., Rock D. Analysis of the transcriptional promoter which regulates the latency-related transcript of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1164-1170.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaashoek M. J., Moerman A., Madić J., Rijsewijk F. A., Quak J., Gielkens A. L., van Oirschot J. T. A conventionally attenuated glycoprotein E-negative strain of bovine herpesvirus type 1 is an efficacious and safe vaccine. Vaccine. 1994 Apr;12(5):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaashoek M. J., Moerman A., Madić J., Weerdmeester K., Maris-Veldhuis M., Rijsewijk F. A., van Oirschot J. T. An inactivated vaccine based on a glycoprotein E-negative strain of bovine herpesvirus 1 induces protective immunity and allows serological differentiation. Vaccine. 1995 Mar;13(4):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)98254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaashoek M. J., van Engelenburg F. A., Moerman A., Gielkens A. L., Rijsewijk F. A., van Oirschot J. T. Virulence and immunogenicity in calves of thymidine kinase- and glycoprotein E-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 mutants. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Jan;48(1-2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil G. M., Engelhardt T., Karger A., Enz M. Bovine herpesvirus 1 U(s) open reading frame 4 encodes a glycoproteoglycan. J Virol. 1996 May;70(5):3032–3038. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.5.3032-3038.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelling C. L., Schipper I. A., Strum G. E., Carlson R. B., Tilton J. E. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR) abortion observations on incidence in vaccinated and non-vaccinated and exposed cattle. Cornell Vet. 1973 Jul;63(3):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khadr A., Tikoo S. K., Babiuk L. A., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Sequence and expression of a bovine herpesvirus-1 gene homologous to the glycoprotein K-encoding gene of herpes simplex virus-1. Gene. 1996 Feb 12;168(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00776-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattar S. K., van Drunen Littel-van den Harke S., Attah-Poku S. K., Babiuk L. A., Tikoo S. K. Identification and characterization of a bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) glycoprotein gL which is required for proper antigenicity, processing, and transport of BHV-1 glycoprotein gH. Virology. 1996 May 1;219(1):66–76. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibenge F. S., Harris L. M., McKenna P. K., Wadowska D., Yason C. V. Amplification of strains of bovine herpesvirus 1 by use of polymerase chain reaction with primers in the thymidine kinase region. Am J Vet Res. 1994 Sep;55(9):1206–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit M., Kit S., Little S. P., Di Marchi R. D., Gale C. Bovine herpesvirus-1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus)-based viral vector which expresses foot-and-mouth disease epitopes. Vaccine. 1991 Aug;9(8):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90243-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Otsuka H., Kit M. Expression of porcine pseudorabies virus genes by a bovine herpesvirus-1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus) vector. Arch Virol. 1992;124(1-2):1–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01314621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Qavi H., Gaines J. D., Billingsley P., McConnell S. Thymidine kinase-negative bovine herpesvirus type 1 mutant is stable and highly attenuated in calves. Arch Virol. 1985;86(1-2):63–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01314114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp A., Mettenleiter T. C. Stable rescue of a glycoprotein gII deletion mutant of pseudorabies virus by glycoprotein gI of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2754–2762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2754-2762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Perrin B., Edwards S., van Oirschot J. T. A European inter-laboratory trial to evaluate the reliability of serological diagnosis of bovine herpesvirus 1 infections. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):153–161. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Quak S., Weerdmeester K., van Oirschot J. T. Comparative study on sixteen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of antibodies to bovine herpesvirus 1 in cattle. Vet Microbiol. 1993 May;35(1-2):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90112-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutish G., Mainprize T., Rock D. Characterization of the latency-related transcriptionally active region of the bovine herpesvirus 1 genome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5730–5737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5730-5737.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnle G., Collins R. A., Scott J. E., Keil G. M. Bovine interleukins 2 and 4 expressed in recombinant bovine herpesvirus 1 are biologically active secreted glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1996 Sep;77(Pt 9):2231–2240. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-9-2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnle G., Heinze A., Schmitt J., Giesow K., Taylor G., Morrison I., Rijsewijk F. A., van Oirschot J. T., Keil G. M. The class II membrane glycoprotein G of bovine respiratory syncytial virus, expressed from a synthetic open reading frame, is incorporated into virions of recombinant bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1998 May;72(5):3804–3811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.5.3804-3811.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary T. P., Gao Y., Splitter G. A. Constitutively expressing cell lines that secrete a truncated bovine herpes virus-1 glycoprotein (gpI) stimulate T-lymphocyte responsiveness. Immunology. 1992 Jul;76(3):367–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Olivo P. D. Gene delivery to neurons: is herpes simplex virus the right tool for the job? Bioessays. 1993 Aug;15(8):547–554. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire M., Meyer G., Ernst E., Vanherreweghe V., Limbourg B., Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Latent bovine herpesvirus 1 infection in calves protected by colostral immunity. Vet Rec. 1995 Jul 15;137(3):70–71. doi: 10.1136/vr.137.3.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire M., Schynts F., Meyer G., Thiry E. Antibody response to glycoprotein E after bovine herpesvirus type 1 infection in passively immunised, glycoprotein E-negative calves. Vet Rec. 1999 Feb 13;144(7):172–176. doi: 10.1136/vr.144.7.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A., Liang X. Characterization of cell-binding properties of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins B, C, and D: identification of a dual cell-binding function of gB. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):4758–4768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.4758-4768.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. P., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Pseudorabies virus gIII and bovine herpesvirus 1 gIII share complementary functions. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5553–5557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5553-5557.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. An in vivo study of a glycoprotein gIII-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) mutant expressing beta-galactosidase: evaluation of the role of gIII in virus infectivity and its use as a vector for mucosal immunization. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90586-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Mapping of heparin-binding structures on bovine herpesvirus 1 and pseudorabies virus gIII glycoproteins. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):233–243. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Pyne C., Li Y., Babiuk L. A., Kowalski J. Delineation of the essential function of bovine herpesvirus 1 gD: an indication for the modulatory role of gD in virus entry. Virology. 1995 Mar 10;207(2):429–441. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Tang M., Zamb T. J., Babiuk L. A., Kowalski J., Tykocinski M. L. Expression of glycoprotein gIII-human decay-accelerating factor chimera on the bovine herpesvirus 1 virion via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-based membrane anchor. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4896–4904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4896-4904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K. Y., Manning J. S. Identification of the thymidine kinase gene of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and its function in Escherichia coli hosts. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig G. V., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Temporal control of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3292–3294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3292-3294.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyaku J. R., Vilcek S., Nettleton P. F., Marsden H. S. The distinction of serologically related ruminant alphaherpesviruses by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction endonuclease analysis. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Jan;48(1-2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADIN S. H., MCKERCHER D. G., YORK C. J. Isolation of the infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Science. 1956 Oct 19;124(3225):721–722. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3225.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masri S. A., Olson W., Nguyen P. T., Prins S., Deregt D. Rapid detection of bovine herpesvirus 1 in the semen of infected bulls by a nested polymerase chain reaction assay. Can J Vet Res. 1996 Apr;60(2):100–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield J. E., Good P. J., VanOort H. J., Campbell A. R., Reed D. E. Cloning and cleavage site mapping of DNA from bovine herpesvirus 1 (Cooper strain). J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.259-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merza M., Tibor S., Kucsera L., Bognar G., Morein B. ISCOM of BHV-1 envelope glycoproteins protected calves against both disease and infection. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 Jun;38(4):306–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Conclusions from the symposium. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler A. E., Matile H., Gassmann U., Engels M., Wyler R. European isolates of bovine herpesvirus 1: a comparison of restriction endonuclease sites, polypeptides, and reactivity with monoclonal antibodies. Arch Virol. 1985;85(1-2):57–69. doi: 10.1007/BF01317006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. N., Bernstein D. I. Interferon-gamma enhances resolution of herpes simplex virus type 2 infection of the murine genital tract. Virology. 1997 Mar 3;229(1):259–268. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Babiuk L. A., Darcel C. L. Analysis of bovine herpes virus-type 1 isolates by restriction endonuclease fingerprinting. Arch Virol. 1983;76(4):341–354. doi: 10.1007/BF01311201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Blumenthal R. M., Babiuk L. A. Proteins Specified by bovine herpesvirus 1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus). J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):367–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.367-378.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Bratanich A. C., Carpenter D., O'Hare P. Protein and DNA elements involved in transactivation of the promoter of the bovine herpesvirus (BHV) 1 IE-1 transcription unit by the BHV alpha gene trans-inducing factor. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):4898–4909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.4898-4909.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Nelson R., Smith M. Sequence of a bovine herpesvirus type-1 glycoprotein gene that is homologous to the herpes simplex gene for the glycoprotein gB. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Walker S., Hayes S., O'Hare P. The bovine herpesvirus alpha gene trans-inducing factor activates transcription by mechanisms different from those of its herpes simplex virus type 1 counterpart VP16. J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5209–5216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.9.5209-5216.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. I., Warner M. S., Lum B. J., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus-1 entry into cells mediated by a novel member of the TNF/NGF receptor family. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):427–436. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser C. A., Speaker T. J., Offit P. A. Effect of microencapsulation on immunogenicity of a bovine herpes virus glycoprotein and inactivated influenza virus in mice. Vaccine. 1997 Nov;15(16):1767–1772. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(97)00106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka H., Qavi H., Kit S. Inhibition by interferon of biochemical transformation induced by cloned herpesvirus thymidine kinase genes. Antiviral Res. 1982 Oct;2(5):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(82)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka H., Xuan X. Construction of bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) recombinants which express pseudorabies virus (PRV) glycoproteins gB, gC, gD, and gE. Arch Virol. 1996;141(1):57–71. doi: 10.1007/BF01718588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonson I. M., Snowdon W. A. The effect of natural and artificial breeding using bulls infected with, or semen contaminated with, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Aust Vet J. 1975 Aug;51(8):365–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1975.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastoret P. P., Babiuk L. A., Misra V., Griebel P. Reactivation of temperature-sensitive and non-temperature-sensitive infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine virus with dexamethasone. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):483–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.483-488.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Diagnosis and prophylaxis of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis: the role of virus latency. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985;8(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(85)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raggo C., Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Liang X. Expression of bovine interleukin-1 beta in a bovine herpesvirus-1 vector: in vitro analysis. Virology. 1996 Jul 1;221(1):78–86. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Weiland F., Fehler F., Keil G. M., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus mutants lacking the essential glycoprotein gII can be complemented by glycoprotein gI of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):621–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.621-631.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy D. N., Reddy P. G., Minocha H. C., Fenwick B. W., Baker P. E., Davis W. C., Blecha F. Adjuvanticity of recombinant bovine interleukin-1 beta: influence on immunity, infection, and latency in a bovine herpesvirus-1 infection. Lymphokine Res. 1990 Fall;9(3):295–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy D. N., Reddy P. G., Xue W., Minocha H. C., Daley M. J., Blecha F. Immunopotentiation of bovine respiratory disease virus vaccines by interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-2. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jun;37(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90013-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P. G., Blecha F., Minocha H. C., Anderson G. A., Morrill J. L., Fedorka-Cray P. J., Baker P. E. Bovine recombinant interleukin-2 augments immunity and resistance to bovine herpesvirus infection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Nov 30;23(1-2):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D., Lokensgard J., Lewis T., Kutish G. Characterization of dexamethasone-induced reactivation of latent bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2484-2490.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizmann B., Desrosiers R. C., Fleckenstein B., Lopez C., Minson A. C., Studdert M. J. The family Herpesviridae: an update. The Herpesvirus Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch Virol. 1992;123(3-4):425–449. doi: 10.1007/BF01317276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusvai M., Fodor L. Occurrence of some viruses and bacteria involved in respiratory diseases of ruminants in Hungary. Acta Vet Hung. 1998;46(4):405–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan A. M., Womack J. E. A molecular genetic approach to improved animal health. The effect of interferon genotype on the severity of experimental bovine herpesvirus-1 infection. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1997 Nov;13(3):401–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schang L. M., Hossain A., Jones C. The latency-related gene of bovine herpesvirus 1 encodes a product which inhibits cell cycle progression. J Virol. 1996 Jun;70(6):3807–3814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.6.3807-3814.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schang L. M., Jones C. Analysis of bovine herpesvirus 1 transcripts during a primary infection of trigeminal ganglia of cattle. J Virol. 1997 Sep;71(9):6786–6795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.9.6786-6795.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Ackermann M. Molecular virology of ruminant herpesviruses. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):17–29. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Vlcek C., Menekse O., Fraefel C., Paces V. Promoter, spliced leader, and coding sequence for BICP4, the largest of the immediate-early proteins of bovine herpesvirus 1. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):349–357. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal B. S., Whetstone C. A. Immediate-early gene expression and gene mapping comparisons among isolates of bovine herpesvirus 1 and 5. Vet Microbiol. 1994 Feb;38(4):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal B. S., Whetstone C. A., Zamb T. J., Bello L. J., Lawrence W. C. Relationship of bovine herpesvirus 1 immediate-early, early, and late gene expression to host cellular gene transcription. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):152–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90744-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Fraefel C., Bello L. J., Lawrence W. C., Schwyzer M. Identification and characterization of BICP27, an early protein of bovine herpesvirus 1 which may stimulate mRNA 3' processing. J Gen Virol. 1996 Apr;77(Pt 4):615–625. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-4-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. A., Young P. L., Rodwell B. J., Kelly M. A., Storie G. J., Farrah C. A., Mattick J. S. Development and trial of a bovine herpesvirus 1-thymidine kinase deletion virus as a vaccine. Aust Vet J. 1994 Mar;71(3):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1994.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. C., Nusbaum K. E., Kwapien R. P., Stringfellow D. A., Driggers K. Necrotic oophoritis in heifers vaccinated intravenously with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus vaccine during estrus. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Jul;51(7):969–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub O. C., Mawhinney I. C. Vaccination to protect calves against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Vet Rec. 1988 Apr 23;122(17):407–411. doi: 10.1136/vr.122.17.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strube W., Abar B., Bergle R. D., Block W., Heinen E., Kretzdorn D., Rodenbach C., Schmeer N. Safety aspects in the development of an infectious bovine rhinotracheitis marker vaccine. Dev Biol Stand. 1995;84:75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strube W., Auer S., Block W., Heinen E., Kretzdorn D., Rodenbach C., Schmeer N. A gE deleted infectious bovine rhinotracheitis marker vaccine for use in improved bovine herpesvirus 1 control programs. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanyi J., Varga J. Guidelines for the eradication of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis in Hungary. Acta Vet Hung. 1992;40(3):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra C., Kroese A. H. Potency control of modified live viral vaccines for veterinary use. Vaccine. 1996 Jan;14(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)00177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiry E., Saliki J., Pastoret P. P., Lambert A. F., Ligot J. Failure to demonstrate infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus reactivation in parturient cows. Vet Rec. 1984 Sep 8;115(10):248–249. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.10.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikoo S. K., Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of functional bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein gIV in transfected bovine cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5132–5142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5132-5142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikoo S. K., Zamb T. J., Babiuk L. A. Analysis of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein gIV truncations and deletions expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2103–2109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2103-2109.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Nadon F., Seguin C., Boulay G., Lussier G. Vaccination of rabbits with a bovine herpesvirus type 1 subunit vaccine: adjuvant effect of ISCOMs. Vaccine. 1987 Sep;5(3):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Engelenburg F. A., Van Schie F. W., Rijsewijk F. A., Van Oirschot J. T. Excretion of bovine herpesvirus 1 in semen is detected much longer by PCR than by virus isolation. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Feb;33(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.2.308-312.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wuijckhuise L., Bosch J., Franken P., Frankena K., Elbers A. R. Epidemiological characteristics of bovine herpesvirus 1 infections determined by bulk milk testing of all Dutch dairy herds. Vet Rec. 1998 Feb 21;142(8):181–184. doi: 10.1136/vr.142.8.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten M. J., Miller J. M., Whetstone C. A. Ovarian lesions induced in heifers by intravenous inoculation with modified-live infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus on the day after breeding. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Sep;46(9):1996–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varthakavi V., Minocha H. C. Identification of a 56 kDa putative bovine herpesvirus 1 cellular receptor by anti-idiotype antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1996 Aug;77(Pt 8):1875–1882. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-8-1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek S., Deliová I., Forgác O., Strojný L., Takácsová I., Harvan M., Benko G. Detection of bovine herpesvirus 1 with various types of DNA probes. Acta Vet Hung. 1993;41(1-2):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek S., Nettleton P. F., Herring J. A., Herring A. J. Rapid detection of bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV 1) using the polymerase chain reaction. Vet Microbiol. 1994 Sep;42(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlcek C., Benes V., Lu Z., Kutish G. F., Paces V., Rock D., Letchworth G. J., Schwyzer M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a 30-kb region of the bovine herpesvirus 1 genome which exhibits a colinear gene arrangement with the UL21 to UL4 genes of herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1995 Jun 20;210(1):100–108. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Splitter G. A. CD4(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity against macrophages pulsed with bovine herpesvirus 1 polypeptides. J Virol. 1998 Sep;72(9):7040–7047. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.9.7040-7047.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentink G. H., Rutten V. P., van Exsel A. C., de Jong W. A., Vleugel H., Hensen E. J. Failure of an in vitro lymphoproliferative assay specific for bovine herpes virus type 1 to detect immunised or latently infected animals. Vet Q. 1990 Jul;12(3):175–182. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1990.9694263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., Miller J. M., Seal B. S., Bello L. J., Lawrence W. C. Latency and reactivation of a thymidine kinase-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 deletion mutant. Arch Virol. 1992;122(1-2):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01321129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., Seal B. S., Miller J. M. Variability occurs in the inverted repeat region of genomic DNA from bovine herpesvirus 1 respiratory, genital and bovine herpesvirus 5 encephalitic isolates. Vet Microbiol. 1993 Dec;38(1-2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90085-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., Wheeler J. G., Reed D. E. Investigation of possible vaccine-induced epizootics of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, using restriction endonuclease analysis of viral DNA. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Aug;47(8):1789–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C., Miller J., Bortner D., Van der Maaten M. Changes in the restriction endonuclease patterns of four modified-live infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (IBRV) vaccines after one passage in host animal. Vaccine. 1989 Dec;7(6):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitbeck J. C., Bello L. J., Lawrence W. C. Comparison of the bovine herpesvirus 1 gI gene and the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3319–3327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3319-3327.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Brandon R., Wagner P., Dubovi E. J., Batt C. A. Detection of bovine herpesvirus-1 in bovine semen by a nested PCR assay. J Virol Methods. 1993 Sep;44(1):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(93)90015-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth U. V., Fraefel C., Vogt B., Vlcek C., Paces V., Schwyzer M. Immediate-early RNA 2.9 and early RNA 2.6 of bovine herpesvirus 1 are 3' coterminal and encode a putative zinc finger transactivator protein. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2763–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2763-2772.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth U. V., Gunkel K., Engels M., Schwyzer M. Spatial and temporal distribution of bovine herpesvirus 1 transcripts. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4882–4889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4882-4889.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth U. V., Vogt B., Schwyzer M. The three major immediate-early transcripts of bovine herpesvirus 1 arise from two divergent and spliced transcription units. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):195–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.195-205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. X., Zhu X. P., Letchworth G. J. Bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein M forms a disulfide-linked heterodimer with the U(L)49.5 protein. J Virol. 1998 Apr;72(4):3029–3036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.4.3029-3036.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yason C. V., Harris L. M., McKenna P. K., Wadowska D., Kibenge F. S. Establishment of conditions for the detection of bovine herpesvirus-1 by polymerase chain reaction using primers in the thymidine kinase region. Can J Vet Res. 1995 Apr;59(2):94–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. L., Smith G. A. Genetically altered herpesviruses as vaccines. Vet Microbiol. 1995 Sep;46(1-3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00081-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Z., Manickan E., Rouse B. T. Role of interferon-gamma in immunity to herpes simplex virus. J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Oct;60(4):528–532. doi: 10.1002/jlb.60.4.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Mucosal and systemic immunity to bovine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein D confer resistance to viral replication and latency in cattle. Vaccine. 1996 Jan;14(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)00123-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygraich N., Lobmann M., Vascoboinic E., Berge E., Huygelen C. In vivo and in vitro properties of a temperature sensitive mutant of infectious bovine Rhinotracheitis virus. Res Vet Sci. 1974 May;16(3):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Garzon S., van den Hurk J. V., Babiuk L. A., Tijssen P. The role of the major tegument protein VP8 of bovine herpesvirus-1 in infection and immunity. Virology. 1995 Jan 10;206(1):413–425. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Khattar S., Tikoo S. K., Babiuk L. A., Baranowski E., Plainchamp D., Thiry E. Glycoprotein H (gII/gp108) and glycoprotein L form a functional complex which plays a role in penetration, but not in attachment, of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Gen Virol. 1996 Jul;77(Pt 7):1515–1520. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-77-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Parker M. D., Fitzpatrick D. R., Zamb T. J., van den Hurk J. V., Campos M., Harland R., Babiuk L. A. Expression of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoprotein gIV by recombinant baculovirus and analysis of its immunogenic properties. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.263-271.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Parker M. D., Massie B., van den Hurk J. V., Harland R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Protection of cattle from BHV-1 infection by immunization with recombinant glycoprotein gIV. Vaccine. 1993;11(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90336-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Van Donkersgoed J., Kowalski J., van den Hurk J. V., Harland R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. A subunit gIV vaccine, produced by transfected mammalian cells in culture, induces mucosal immunity against bovine herpesvirus-1 in cattle. Vaccine. 1994 Nov;12(14):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(94)80055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Zamb T., Babiuk L. A. Synthesis, cellular location, and immunogenicity of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins gI and gIII expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2159–2168. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2159-2168.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., van den Hurk J. V., Gilchrist J. E., Misra V., Babiuk L. A. Interactions of monoclonal antibodies and bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) glycoproteins: characterization of their biochemical and immunological properties. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):466–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Engelenburg F. A., Kaashoek M. J., van Oirschot J. T., Rijsewijk F. A. A glycoprotein E deletion mutant of bovine herpesvirus 1 infects the same limited number of tissues in calves as wild-type virus, but for a shorter period. J Gen Virol. 1995 Sep;76(Pt 9):2387–2392. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-9-2387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Engelenburg F. A., Maes R. K., van Oirschot J. T., Rijsewijk F. A. Development of a rapid and sensitive polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of bovine herpesvirus type 1 in bovine semen. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Dec;31(12):3129–3135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.12.3129-3135.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oirschot J. T. Bovine herpesvirus 1 in semen of bulls and the risk of transmission: a brief review. Vet Q. 1995 Mar;17(1):29–33. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1995.9694526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oirschot J. T., Kaashoek M. J., Rijsewijk F. A. Advances in the development and evaluation of bovine herpesvirus 1 vaccines. Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oirschot J. T. Vaccination in food animal populations. Vaccine. 1994 Apr;12(5):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]