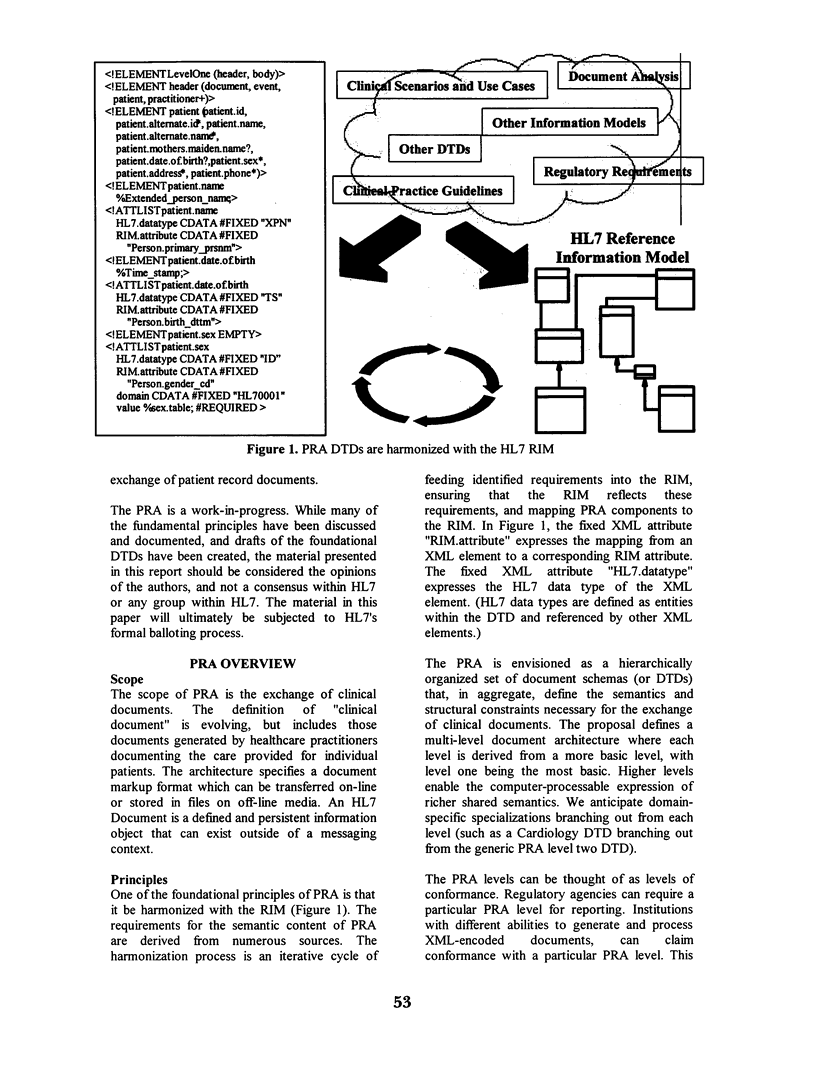
Abstract
The HL7 SGML/XML Special Interest Group is developing the HL7 Document Patient Record Architecture. This draft proposal strives to create a common data architecture for the interoperability of healthcare documents. Key components are that it is under the umbrella of HL7 standards, it is specified in Extensible Markup Language, the semantics are drawn from the HL7 Reference Information Model, and the document specifications form an architecture that, in aggregate, define the semantics and structural constraints necessary for the exchange of clinical documents. The proposal is a work in progress and has not yet been submitted to HL7's formal balloting process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell K. E., Oliver D. E., Spackman K. A., Shortliffe E. H. Representing thoughts, words, and things in the UMLS. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1998 Sep-Oct;5(5):421–431. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1998.0050421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R. H., Rishel W., Biron P. V., Spinosa J., Mattison J. E. SGML and XML as interchange formats for HL7 messages. Proc AMIA Symp. 1998:720–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman C., Hripcsak G., Shagina L., Liu H. Representing information in patient reports using natural language processing and the extensible markup language. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1999 Jan-Feb;6(1):76–87. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1999.0060076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


