Abstract
Increasing amounts of data exist in medical databases. When multiple variables are measured for each case in a data set, there exists an underlying relationship between all pairs of variables, some highly correlated and some not. This report describes a technique that creates networks of related variables, or relevance networks, by dropping links with either too weak correlation or too few data points to defend the relationship. The paper describes how applying this methodology to the domain of laboratory results allows the generation of meaningful relations between types of laboratory tests. These relations could be used as the basis of further exploratory research.
Full text
PDF
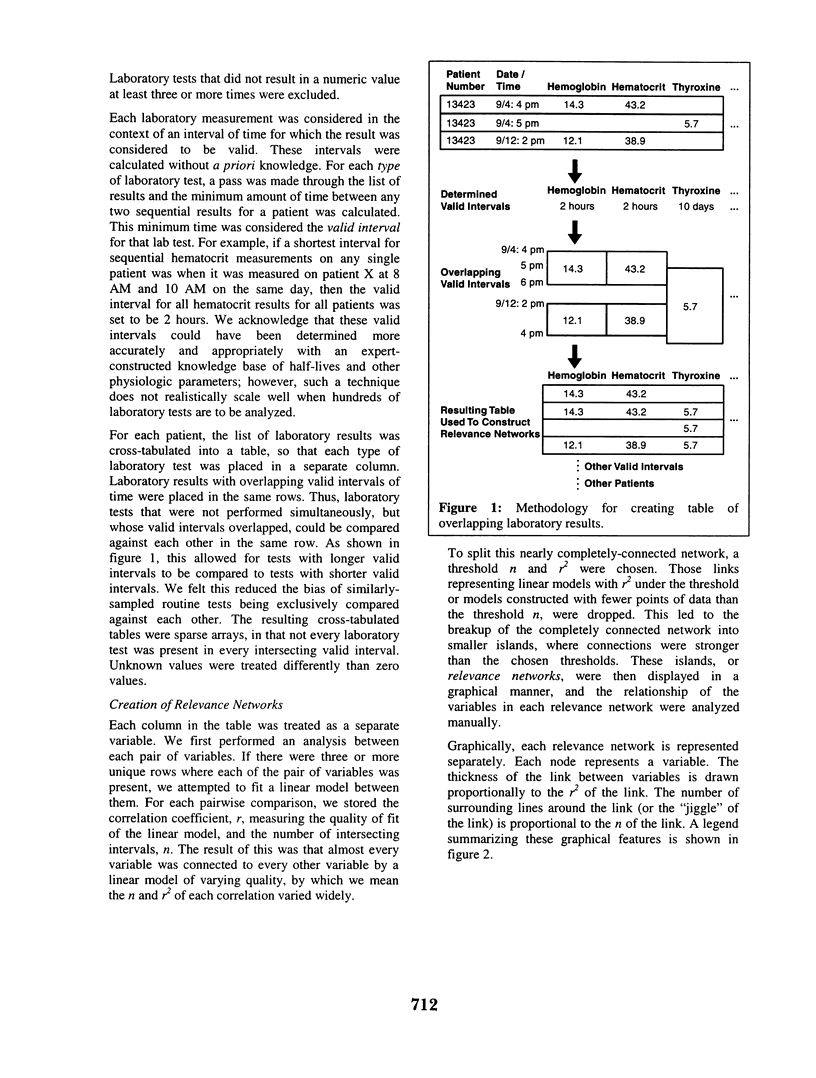
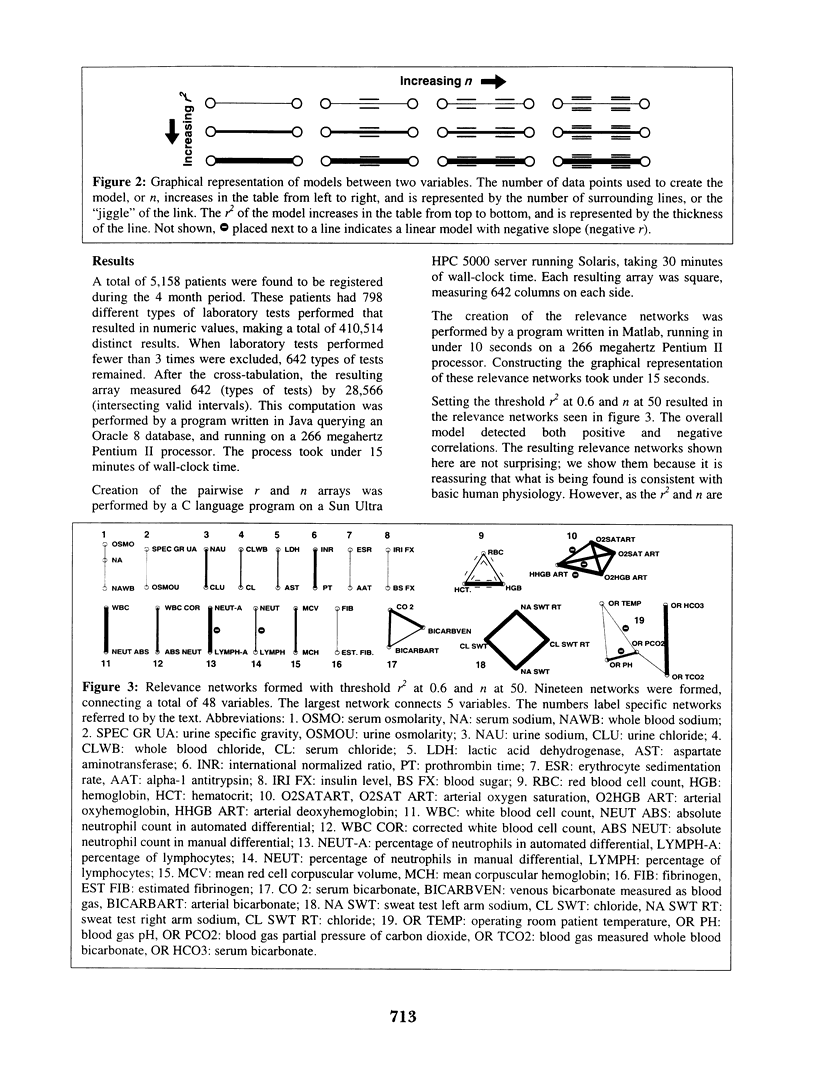
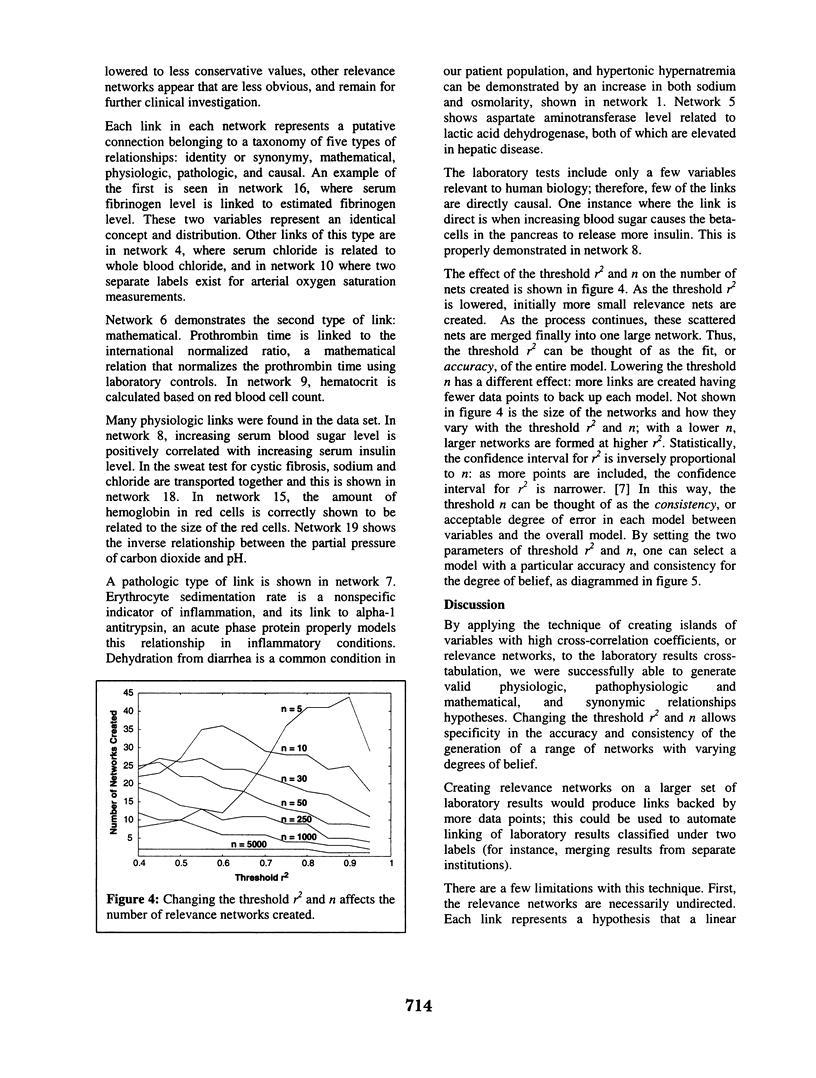

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper G. F., Buchanan B. G., Kayaalp M., Saul M., Vries J. K. Using computer modeling to help identify patient subgroups in clinical data repositories. Proc AMIA Symp. 1998:180–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monti S., Cooper G. F. The impact of modeling the dependencies among patient findings on classification accuracy and calibration. Proc AMIA Symp. 1998:592–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohrn A., Ohno-Machado L., Rowland T. Building manageable rough set classifiers. Proc AMIA Symp. 1998:543–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G. DNA chips: state-of-the art. Nat Biotechnol. 1998 Jan;16(1):40–44. doi: 10.1038/nbt0198-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumoto S. Automated knowledge acquisition from clinical databases based on rough sets and attribute-oriented generalization. Proc AMIA Symp. 1998:548–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


