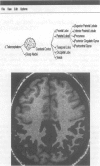
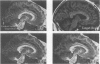
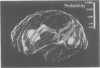
Abstract
Rapid and convenient access to digital image archives, as well as archive-based computational tools, are fundamental to many hypothesis-driven investigations of brain anatomy and function in health and disease. The complexity and density of brain image data requires the design of intelligent tools which allow scientific and clinical data, collected at numerous research centers, to be compared, integrated, and disseminated. We describe our results in the development of image data navigational tools, a World Wide Web repository of image analysis software, and strategies to represent populations of brain image data involving atlas descriptions of its variance.
Full text
PDF
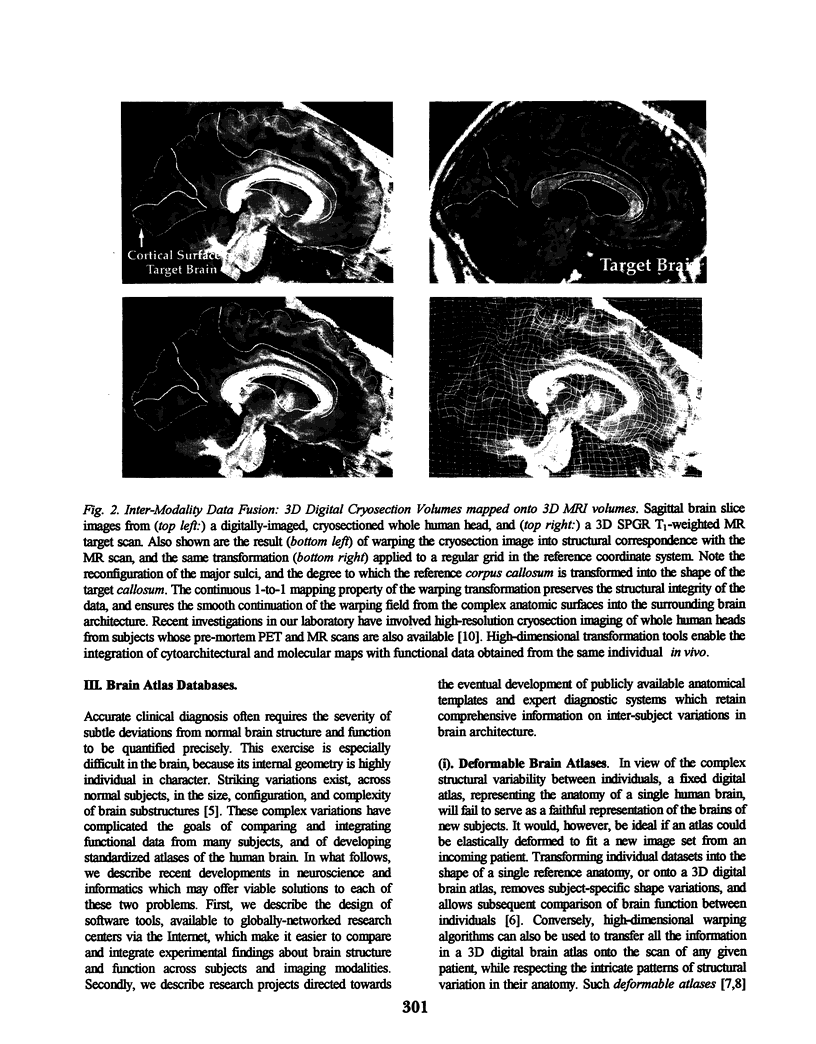


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen N. C., Arndt S., Swayze V., 2nd, Cizadlo T., Flaum M., O'Leary D., Ehrhardt J. C., Yuh W. T. Thalamic abnormalities in schizophrenia visualized through magnetic resonance image averaging. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):294–298. doi: 10.1126/science.7939669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazziotta J. C., Toga A. W., Evans A., Fox P., Lancaster J. A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. The International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM). Neuroimage. 1995 Jun;2(2):89–101. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1995.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. M., Schwartz C., Toga A. W. High-resolution random mesh algorithms for creating a probabilistic 3D surface atlas of the human brain. Neuroimage. 1996 Feb;3(1):19–34. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1996.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]