Abstract
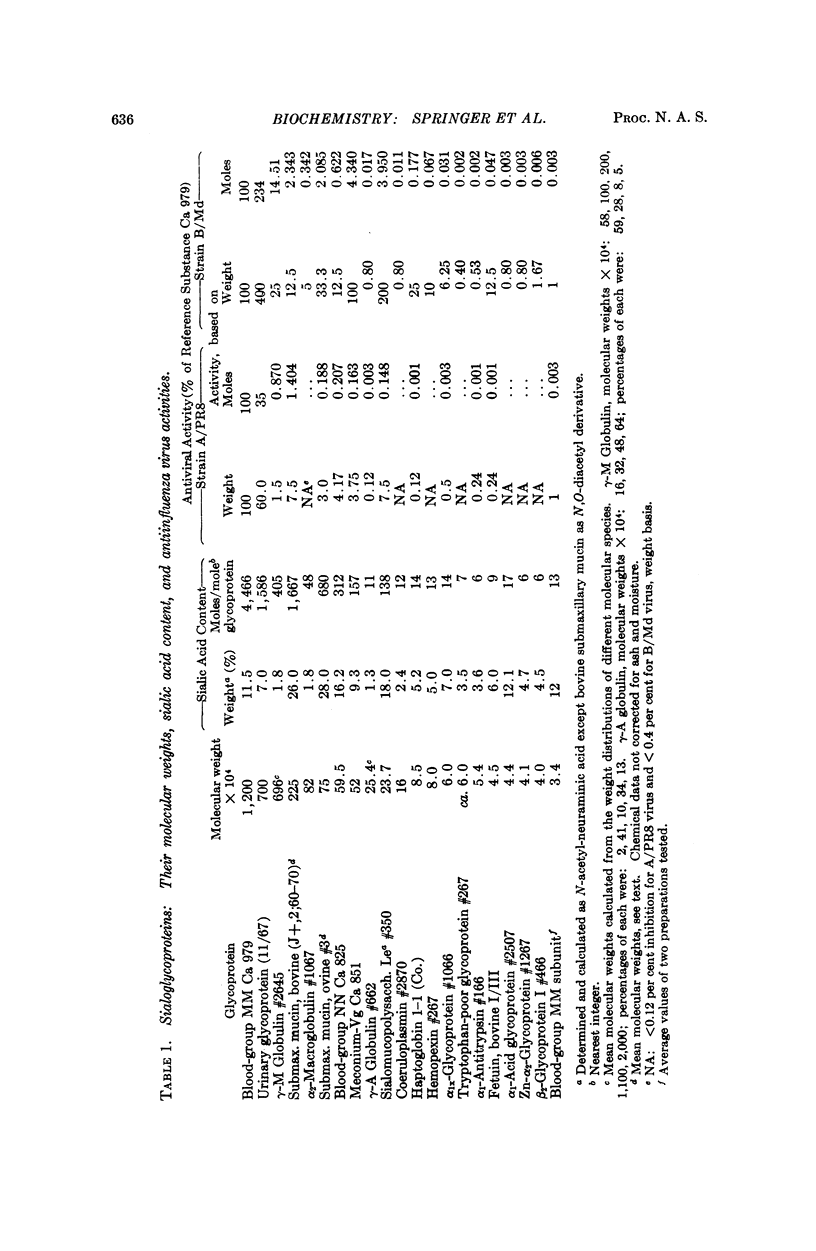
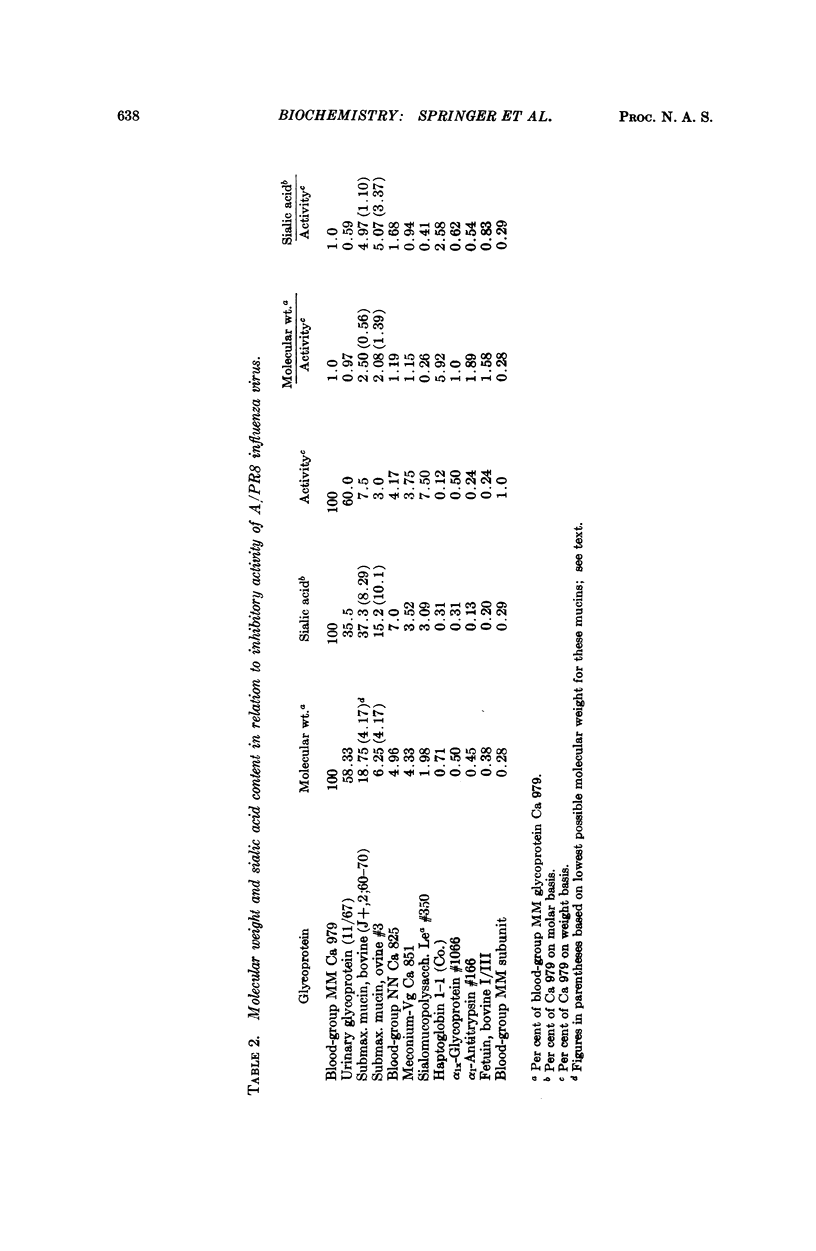
Twenty-four different glycoproteins were investigated for their ability to inhibit hemagglutination by the A/PRS and the B/Md influenza virus strains. A relationship between activity, the molecular size, and sialic acid content was found. This relationship was readily shown for the A/PR8 virus if the properties of the glycoproteins were compared with one another on a per cent basis. A proportion of approximately 1:1:1 for activity (weight basis) to moles sialic acid content to molecular weight existed for each inhibitory glycoprotein with more than 3 per cent sialic acid, on comparison with any other active glycoprotein.
A 1:3 correspondence between viral subunit and sialic acid residues of the inhibitor ovine submaxillary mucin was found experimentally and confirmed by calculation on a molecular model. The most potent inhibitors, were the antigens of the human blood-group MN system and the Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Some observations on the envelope of an influenza virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jan;46(1):107–110. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELL G. E., DIXON G. H., SMITHIES O. Subdivision of the three common haptoglobin types based on 'hidden' diffrences. Nature. 1962 Feb 3;193:505–506. doi: 10.1038/193505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. K. THE AGGLUTINATION OF RED CELLS BY ALLANTOIC FLUID OF CHICK EMBRYOS INFECTED WITH INFLUENZA VIRUS. Science. 1941 Jul 4;94(2427):22–23. doi: 10.1126/science.94.2427.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M. I., Das A. Immunochemistry of ovine and bovine submaxillary mucins. Immunochemistry. 1967 Sep;4(5):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATHAN R. H., WINZLER R. J., JOHNSOM C. A. Preparation of an inhibitor of viral hemagglutination from human erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:37–45. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLENK E., UHLENBRUCK G. [On the isolation of mucoids containing neuraminic acid from human erythrocyte stroma, a contribution to the chemistry of agglutinogens]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1960;319:151–160. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1960.319.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL A. B. Inhibitor capacity of some purified human serum proteins on hemagglutination by influenza virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1960;49:213–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1960.tb01132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODIN L. Carbohydrate residue of a urine mucoprotein inhibiting influenza virus hemagglutination. Nature. 1952 Oct 18;170(4329):663–664. doi: 10.1038/170663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUSZTAI A., MORGAN W. T. Studies in immunochemistry. 18. The isolation and properties of a sialomucopolysaccharide possessing blood-group Le-a specificity and virus-receptor activity. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:135–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0780135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Ansell N. J. INACTIVATION OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE AGGLUTINOGENS M AND N BY INFLUENZA VIRUSES AND RECEPTOR-DESTROYING ENZYME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):182–189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F. Human MN glycoproteins: dependence of blood-group and anti-influenza virus activities on their molecular size. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):510–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKATSY G. The use of spiral loops in serological and virological micro-methods. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


